|
FS Marjata (1992)
''Eger'' ( ''Marjata'' for most of its career) is a purpose-built electronic intelligence collection vessel (ELINT). She is the third ship that bears the name ''Marjata''; the first was operational in the period of 1966-1975 and the second during the years 1976-1995. All of these ships have been used for military intelligence purposes by the Norwegian Armed Forces, the first two entering service during the Cold War. She is owned by the Norwegian Defence Research Establishment, but operated by the Norwegian Intelligence Service, and is considered to be one of the most advanced ships of her kind in the world. Her main role is surveillance of the Russian Northern fleet's activity in the Barents Sea, but is constructed for operations all over the world. She operates in international waters close to the Russian border. ''Marjata'' officially serves as a research ship for the Norwegian Intelligence Service. Construction The ship was contracted in March 1991 from Aker Yards and wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkenes
(Norwegian language, Norwegian; ), (Northern Sami language, Northern Sami; , or is a List of towns and cities in Norway, town in Sør-Varanger Municipality in Finnmark county, in the far northeastern part of Norway. The town lies on a peninsula along the Bøkfjorden, an arm of the large Varangerfjorden, and is located just a few kilometres from the Norway–Russia border. The town has a population (2023) of 3,404 and a population density of . When the neighbouring suburban villages of Hesseng, Skytterhusfjellet, Sandnes, Finnmark, Sandnes and Bjørnevatn are all included with Kirkenes, the urban area reaches a population of almost 8,000. Although Kirkenes is the Norwegian town closest to the Russian border, the town of Vardø (town), Vardø to its north is located further east in Norway. Names Due to its close proximity to Russians, Finns and Skolt Sami, the town is also known as , , and . History The area around Kirkenes was a common Norwegian–Russian district until 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Waters
The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water (or their drainage basins) transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed regional seas and estuaries, rivers, lakes, groundwater systems (aquifers), and wetlands. "International waters" is not a defined term in international law. It is an informal term, which sometimes refers to waters beyond the "territorial sea" of any country. In other words, "international waters" is sometimes used as an informal synonym for the more formal term "high seas", which under the doctrine of ''mare liberum'' (Latin for "freedom of the seas"), do not belong to any state's jurisdiction. As such, states have the right to fishing, navigation, overflight, laying cables and pipelines, as well as scientific research. The Convention on the High Seas, signed in 1958, which has 63 signatories, defined "high seas" to mean "all parts of the sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway (Nordland, Troms, Finnmark, Svalbard and Jan Mayen), northernmost Sweden (Västerbotten, Norrbotten and Lapland (Sweden), Lappland), northern Finland (North Ostrobothnia, Kainuu and Lapland (Finland), Lappi), Russia (Murmansk Oblast, Murmansk, Siberia, Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Nenets Okrug, Novaya Zemlya), the United States (Alaska), Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), and northern Iceland (Grímsey and Kolbeinsey), along with the Arctic Ocean and adjacent seas. Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying cryosphere, snow and ice cover, with predominantly treeless permafrost under the tundra. Arctic seas contain seasonal sea ice in many places. The Arctic region is a unique area among Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflection Seismology
Reflection seismology (or seismic reflection) is a method of exploration geophysics that uses the principles of seismology to estimate the properties of the Earth's subsurface from reflection (physics), reflected seismic waves. The method requires a controlled seismic source of energy, such as dynamite or Tovex blast, a specialized Seismic source#Air gun, air gun or a seismic vibrator. Reflection seismology is similar to sonar and acoustic location, echolocation. History Reflections and refractions of seismic waves at geologic Interface (matter), interfaces within the Earth were first observed on recordings of earthquake-generated seismic waves. The basic model of the Earth's deep interior is based on observations of earthquake-generated seismic waves transmitted through the Earth's interior (e.g., Mohorovičić, 1910). The use of human-generated seismic waves to map in detail the geology of the upper few kilometers of the Earth's crust followed shortly thereafter and has deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconnaissance
In military operations, military reconnaissance () or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, the terrain, and civil activities in the area of operations. In military jargon, reconnaissance is abbreviated to ''recce'' (in British, Canadian, Australian English) and to ''recon'' (in American English), both derived from the root word ''reconnoitre'' / ''reconnoitering''. The types of reconnaissance include patrolling the local area of operations and long-range reconnaissance patrols, which are tasks usually realized in the United States of America by U.S. Army Rangers, cavalry scouts, and military intelligence specialists, using navy ships and submarines, Aerial reconnaissance, reconnaissance aircraft, satellites to collect raw intelligence; and establishing observation posts. Moreover, espionage is different from reconnaissance, because spies work as civilians in enemy territory. Etymology The word is derived from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
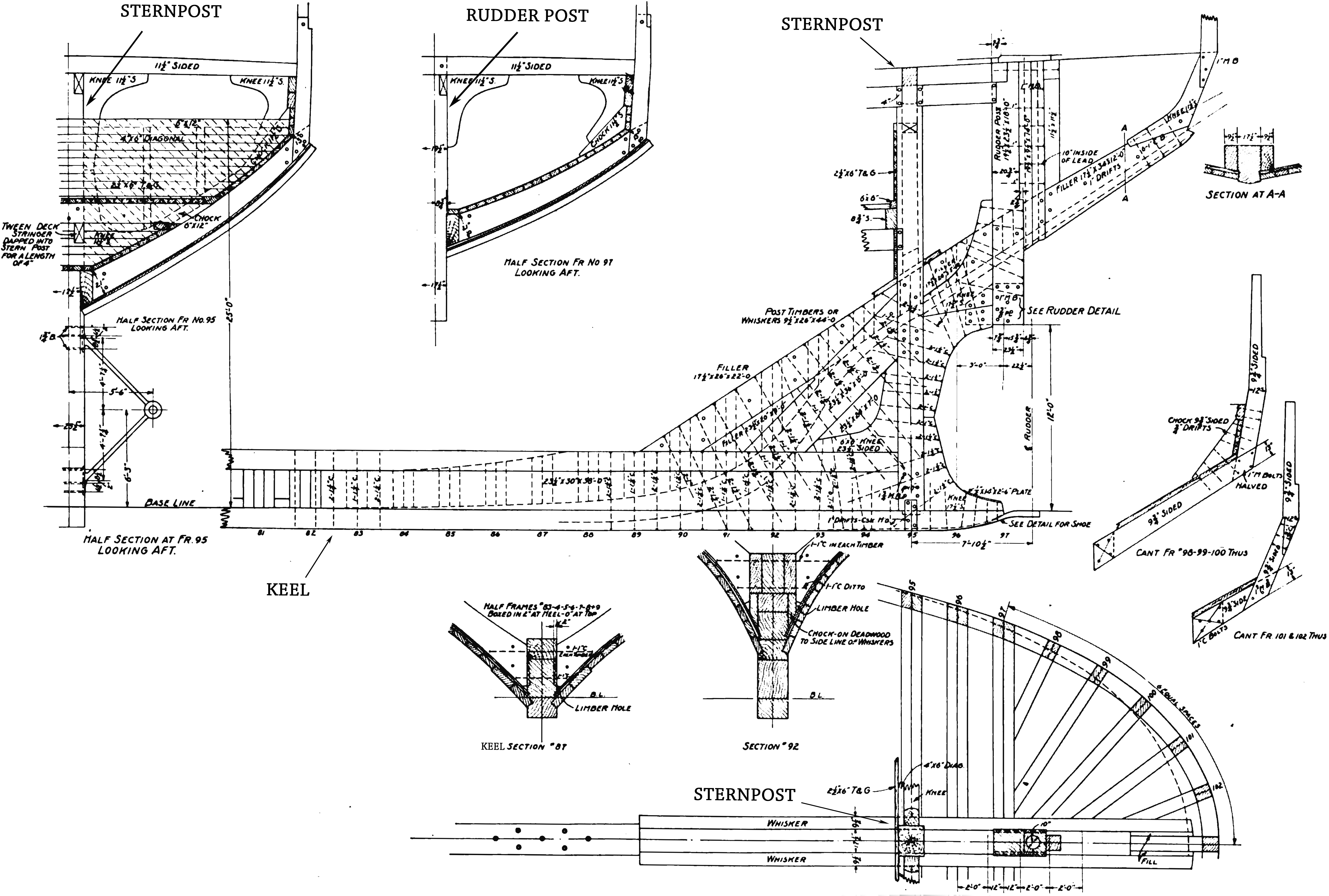
Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterline
The waterline is the line where the hull of a ship meets the surface of the water. A waterline can also refer to any line on a ship's hull that is parallel to the water's surface when the ship is afloat in a level trimmed position. Hence, waterlines are a class of "ships lines" used to denote the shape of a hull in naval architecture lines plans. The load line (also known as Plimsoll line) is the waterline which indicates the legal limit to which a ship may be loaded for specific water types and temperatures in order to safely maintain buoyancy. For vessels with displacement hulls, the hull speed is defined by, among other things, the waterline length. In a sailing boat, the waterline length can change significantly as the boat heels, and can dynamically affect the speed of the boat. Aircraft In the aircraft design the term ''waterline'' designates a horizontal reference line used in alignment checks. The base line of the aircraft is designated as waterline 0 (zero). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinusoidal
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or sinusoid (symbol: ∿) is a periodic wave whose waveform (shape) is the trigonometric sine function. In mechanics, as a linear motion over time, this is '' simple harmonic motion''; as rotation, it corresponds to '' uniform circular motion''. Sine waves occur often in physics, including wind waves, sound waves, and light waves, such as monochromatic radiation. In engineering, signal processing, and mathematics, Fourier analysis decomposes general functions into a sum of sine waves of various frequencies, relative phases, and magnitudes. When any two sine waves of the same frequency (but arbitrary phase) are linearly combined, the result is another sine wave of the same frequency; this property is unique among periodic waves. Conversely, if some phase is chosen as a zero reference, a sine wave of arbitrary phase can be written as the linear combination of two sine waves with phases of zero and a quarter cycle, the ''sine'' and ''cosine'' co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bow (ship)
The bow () is the forward part of the hull of a ship or boat, the point that is usually most forward when the vessel is underway. The aft end of the boat is the stern. Prow may be used as a synonym for bow or it may mean the forward-most part of the bow above the waterline. Function A ship's bow should be designed to enable the hull to pass efficiently through the water. Bow shapes vary according to the speed of the boat, the seas or waterways being navigated, and the vessel's function. Where sea conditions are likely to promote pitching, it is useful if the bow provides reserve buoyancy; a flared bow (a raked stem with flared topsides) is ideal to reduce the amount of water shipped over the bow. Ideally, the bow should reduce the resistance and should be tall enough to prevent water from regularly washing over the top of it. Large commercial barges on inland waterways rarely meet big waves and may have remarkably little freeboard at the bow, whereas fast military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hull (watercraft)
A hull is the watertight body of a ship, boat, submarine, or flying boat. The hull may open at the top (such as a dinghy), or it may be fully or partially covered with a deck. Atop the deck may be a deckhouse and other superstructures, such as a funnel, derrick, or Mast (sailing), mast. The line where the hull meets the water surface is called the waterline. General features There is a wide variety of hull types that are chosen for suitability for different usages, the hull shape being dependent upon the needs of the design. Shapes range from a nearly perfect box, in the case of scow barges, to a needle-sharp surface of revolution in the case of a racing multihull sailboat. The shape is chosen to strike a balance between cost, hydrostatic considerations (accommodation, load carrying, and stability), hydrodynamics (speed, power requirements, and motion and behavior in a seaway) and special considerations for the ship's role, such as the rounded bow of an icebreaker or the flat bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |