|
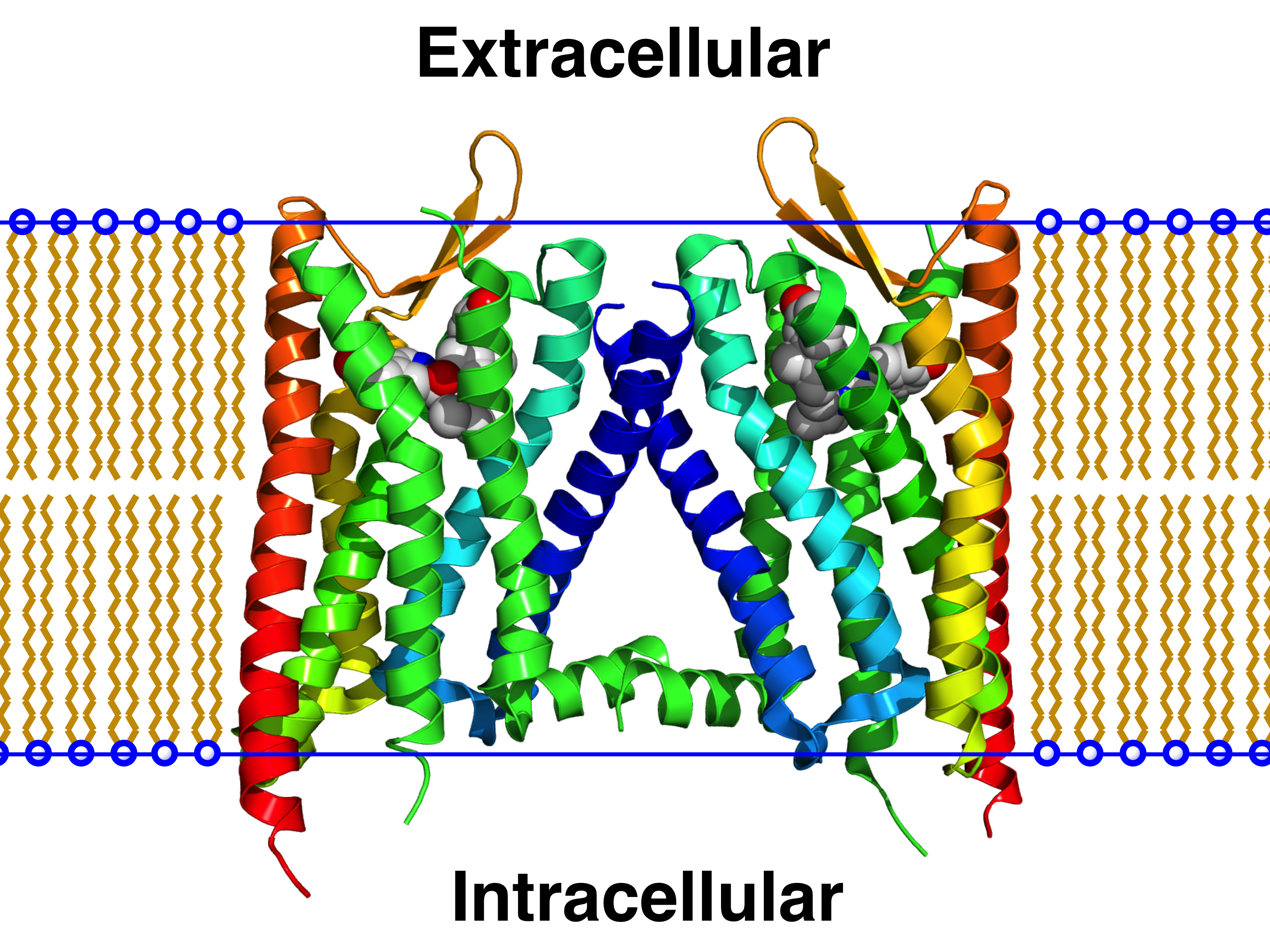
FFAR2-FFAR3 Receptor Heteromer
The FFAR2–FFAR3 receptor heteromer is a receptor heteromer consisting of free fatty acid receptors, FFAR2 and FFAR3 protomers. Signal transduction The signalling of the FFAR2-FFAR3 receptor heteromer is distinct from that of the parent receptor homomers. The FFAR2-FFAR3 heteromer displays enhanced intracellular calcium release and Arrestin beta 2 recruitment. The heteromer also lacks the ability to inhibit the cAMP-dependent pathway but gained the ability to induce P38 mitogen-activated protein kinases p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases are a class of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) that are responsive to stress stimuli, such as cytokines, ultraviolet irradiation, heat shock, and osmotic shock, and are involved in cell differe .... References {{Reflist, 32em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Fatty Acid Receptor 2
Free fatty acid receptor 2 (FFA2) is a G-protein coupled receptor encoded by the ''FFAR2'' gene. Expression ''FFAR2'' mRNA is expressed in adipose tissue, pancreas, spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. ''FFAR2'' transcription is regulated by the XBP1 transcription factor which binds to the core promoter. Function Mouse studies utilizing Ffar2 gene deletions have implicated the receptor in the regulation of energy metabolism and immune responses. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFA's) generated in the processing of fiber by intestinal microbiota act as ligands for the receptor and can affect neutrophil chemotaxis. However, discrepancies between the pathways activated by FFAR2 agonists in human cells and the equivalent murine counterparts have been observed. Heteromerization FFA2 may interact with FFAR3 to form a FFAR2-FFAR3 receptor heteromer with signalling that is distinct from the parent homomers. See also * Free fatty acid receptor *Short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Fatty Acid Receptor 3
Free fatty acid receptor 3 (FFA3) is a G-protein coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''FFAR3'' gene. Animal studies Knockout mouse studies have implicated FFAR3 in diabetes, colitis, hypertension and asthma. However, discrepancies between the pathways activated by FFAR3 agonists in human cells and the equivalent murine counterparts have been observed. Heteromerization FFAR3 may interact with FFAR2 to form a FFAR2-FFAR3 receptor heteromer with signalling that is distinct from the parent homomers. See also * Free fatty acid receptor The free fatty acid receptor is a G-protein coupled receptor which binds free fatty acids. There are four variants of the receptor, each encoded by a separate gene ( FFAR1, FFAR2, FFAR3, FFAR4). Preliminary findings suggest that FFAR2 and ... References Further reading * * * * * G protein-coupled receptors {{transmembranereceptor-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPCR Oligomer
A GPCR oligomer is a protein complex that consists of a small number ( ''oligoi'' "a few", ''méros'' "part, piece, component") of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). It is held together by covalent bonds or by intermolecular forces. The subunits within this complex are called protomers, while unconnected receptors are called monomers. Receptor homomers consist of identical protomers, while heteromers consist of different protomers. Receptor homodimers – which consist of two identical GPCRs – are the simplest homomeric GPCR oligomers. Receptor heterodimers – which consist of two different GPCRs – are the simplest heteromeric GPCR oligomers. The existence of receptor oligomers is a general phenomenon, whose discovery has superseded the prevailing paradigmatic concept of the function of receptors as plain monomers, and has far-reaching implications for the understanding of neurobiological diseases as well as for the development of drugs. Discovery For a long time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FFAR2
Free fatty acid receptor 2 (FFA2) is a G-protein coupled receptor encoded by the ''FFAR2'' gene. Expression ''FFAR2'' mRNA is expressed in adipose tissue, pancreas, spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. ''FFAR2'' transcription is regulated by the XBP1 transcription factor which binds to the core promoter. Function Mouse studies utilizing Ffar2 gene deletions have implicated the receptor in the regulation of energy metabolism and immune responses. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFA's) generated in the processing of fiber by intestinal microbiota act as ligands for the receptor and can affect neutrophil chemotaxis. However, discrepancies between the pathways activated by FFAR2 agonists in human cells and the equivalent murine counterparts have been observed. Heteromerization FFA2 may interact with FFAR3 to form a FFAR2-FFAR3 receptor heteromer with signalling that is distinct from the parent homomers. See also * Free fatty acid receptor *Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FFAR3
Free fatty acid receptor 3 (FFA3) is a G-protein coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''FFAR3'' gene. Animal studies Knockout mouse studies have implicated FFAR3 in diabetes, colitis, hypertension and asthma. However, discrepancies between the pathways activated by FFAR3 agonists in human cells and the equivalent murine counterparts have been observed. Heteromerization FFAR3 may interact with FFAR2 to form a FFAR2-FFAR3 receptor heteromer with signalling that is distinct from the parent homomers. See also * Free fatty acid receptor The free fatty acid receptor is a G-protein coupled receptor which binds free fatty acids. There are four variants of the receptor, each encoded by a separate gene ( FFAR1, FFAR2, FFAR3, FFAR4). Preliminary findings suggest that FFAR2 and ... References Further reading * * * * * G protein-coupled receptors {{transmembranereceptor-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellular response. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptors, although in some cases the term sensor is used. The changes elicited by ligand binding (or signal sensing) in a receptor give rise to a biochemical cascade, which is a chain of biochemical events known as a signaling pathway. When signaling pathways interact with one another they form networks, which allow cellular responses to be coordinated, often by combinatorial signaling events. At the molecular level, such responses include changes in the transcription or translation of genes, and post-translational and conformational changes in proteins, as well as changes in their location. These molecular events are the basic mechanisms controlling cell gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrestin Beta 2
Beta-arrestin-2, also known as arrestin beta-2, is an intracellular protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ARRB2'' gene. Members of arrestin/beta-arrestin protein family are thought to participate in agonist-mediated desensitization of G protein-coupled receptors and cause specific dampening of cellular responses to stimuli such as hormones, neurotransmitters, or sensory signals, as well as having signalling roles in their own right. Arrestin beta 2, like arrestin beta 1, was shown to inhibit beta-adrenergic receptor function in vitro. It is expressed at high levels in the central nervous system and may play a role in the regulation of synaptic receptors. Besides the brain, a cDNA for arrestin beta 2 was isolated from thyroid gland, and thus it may also be involved in hormone-specific desensitization of TSH receptors. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene, but the full-length nature of some variants has not been defined. The protein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAMP-dependent Pathway
In the field of molecular biology, the cAMP-dependent pathway, also known as the adenylyl cyclase pathway, is a G protein-coupled receptor-triggered signaling cascade used in cell communication. Discovery cAMP was discovered by Earl Sutherland and Ted Rall. cAMP is considered a secondary messenger along with Ca2+. Sutherland won the Nobel Prize in 1971 for his discovery of the mechanism of action of epinephrine in glycogenolysis, that requires cAMP as secondary messenger. Mechanism G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are a large family of integral membrane proteins that respond to a variety of extracellular stimuli. Each GPCR binds to and is activated by a specific ligand stimulus that ranges in size from small molecule catecholamines, lipids, or neurotransmitters to large protein hormones. When a GPCR is activated by its extracellular ligand, a conformational change is induced in the receptor that is transmitted to an attached intracellular heterotrimeric G protein complex. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |