|
F. B. Culley Generating Station
F. B. Culley Generating Station is a 369 megawatt ( MW) coal power plant located southeast of Newburgh in Warrick County, Indiana. It sits on the north bank of Ohio River, immediately adjacent and upstream of the Warrick Power Plant, and is owned and operated by Vectren (formerly Southern Indiana Gas and Electric Company). History F. B. Culley has two units still in service: a 104 MW Unit 2 (built in 1966) and a larger 265 MW Unit 3 (built in 1973). Unit 1 with 46 MW, began electricity generation in 1955. The unit closed in 2006 in order to comply with the Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) Clean Air Interstate Rule. It was announced in February 2018 that F. B. Culley's Unit 2 will be shut down in 2023. It was announced in April 2023 that F. B. Culley's Unit 3 will be converted to natural gas by 2027. Environmental impact In 1992, Vectren installed a flue-gas desulfurization (FGD) system on Units 2 and 3 to reduce sulfur dioxide () emissions and satisfy the requirement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anderson Township, Warrick County, Indiana
Anderson Township is one of ten townships in Warrick County, Indiana, United States. As of the 2010 census, its population was 1,274 and it contained 500 housing units. History Southern Anderson Township is the location of the Yankeetown site, an important archaeological site from the Woodland and Mississippian periods. Anderson Township was established in 1813. The township was named for Bailey Anderson, a pioneer settler. Geography According to the 2010 census, the township has a total area of , of which (or 93.63%) is land and (or 6.37%) is water. Cities, towns, villages * Newburgh (east edge) Unincorporated towns * Dayville at * Red Brush at * Vanada at * Yankeetown at (This list is based on USGS data and may include former settlements.) Adjacent townships * Boon Township (north) * Luce Township, Spencer County (east) * Ohio Township (northwest) Cemeteries The township contains Bates Hill Cemetery. Rivers * Ohio River Lakes * Collins Lake School distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flue-gas Desulfurization
Flue-gas desulfurization (FGD) is a set of technologies used to remove sulfur dioxide () from exhaust flue gases of fossil-fuel power plants, and from the emissions of other sulfur oxide emitting processes such as waste incineration, petroleum refineries, cement and lime kilns. Methods Since stringent environmental regulations limiting emissions have been enacted in many countries, is being removed from flue gases by a variety of methods. Common methods used: * Wet scrubbing using a slurry of alkaline sorbent, usually limestone or lime, or seawater to scrub gases; * Spray-dry scrubbing using similar sorbent slurries; * Wet sulfuric acid process recovering sulfur in the form of commercial quality sulfuric acid; * SNOX Flue gas desulfurization removes sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides and particulates from flue gases; *Dry sorbent injection systems that introduce powdered hydrated lime (or other sorbent material) into exhaust ducts to eliminate and from process emissions. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal-fired Power Stations In Indiana
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. Coal is a type of fossil fuel, formed when dead plant matter decays into peat which is converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years. Vast deposits of coal originate in former wetlands called coal forests that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous ( Pennsylvanian) and Permian times. Coal is used primarily as a fuel. While coal has been known and used for thousands of years, its usage was limited until the Industrial Revolution. With the invention of the steam engine, coal consumption increased. In 2020, coal supplied about a quarter of the world's primary energy and over a third of its electricity. Some iron and steel-making and other industrial processes burn coal. The extraction and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Infrastructure Completed In 1973
Energy () is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system, and rest energy associated with an object's rest mass. These are not mutually exclusive. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven primarily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Power Stations In Indiana
This is a list of electricity-generating power stations in the U.S. state of Indiana, sorted by type and name. In 2023, Indiana had a total summer capacity of 26,578 MW through all of its power plants, and a net generation of 90,046 GWh. In 2024, the electrical energy generation mix was 42.8% coal, 40.5% natural gas, 10.3% wind, 3.3% solar, 1.8% other gases, 0.5% hydroelectric, 0.2% biomass, 0.1% petroleum, and 0.5% other. GridInfo maintains a directory of power plants in Indiana using data from the U.S. Energy Information Administration. Coal-fired *1 Also includes cooling towers. *0 active units indicates decommissioned stations. Coal gasification 1 The existing plant will be decommissioned and demolished upon completion of new IGCC facility. Oil-fired peaking stations * Connersville Peaking Station * Miami-Wabash County Peaking Station * Wheatland Peaking Station Natural gas fired Hydroelectric dams Wind farms Solar Biomass to energy plant * Milltow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Particulate Matter
Particulate matter (PM) or particulates are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspension (chemistry), suspended in the atmosphere of Earth, air. An ''aerosol'' is a mixture of particulates and air, as opposed to the particulate matter alone, though it is sometimes defined as a subset of aerosol terminology. Sources of particulate matter can be natural or anthropogenic hazard, anthropogenic. Particulates have impacts on climate and precipitation that adversely affect human health. Types of atmosphere, atmospheric particles include suspended particulate matter; thoracic and respirable particles; inhalable coarse particles, designated PM, which are granularity, coarse particles with a particle size, diameter of 10 micrometre, micrometers (μm) or less; fine particles, designated PM, with a diameter of 2.5 μm or less; ultrafine particles, with a diameter of 100 nm or less; and soot. Airborne particulate matter is a List of IARC Group 1 carcinogens, Group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Oxide
Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds: Charge-neutral *Nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen(II) oxide, or nitrogen monoxide * Nitrogen dioxide (), nitrogen(IV) oxide * Nitrogen trioxide (), or nitrate radical *Nitrous oxide (), nitrogen(0,II) oxide * Dinitrogen dioxide (), nitrogen(II) oxide dimer * Dinitrogen trioxide (), nitrogen(II,IV) oxide * Dinitrogen tetroxide (), nitrogen(IV) oxide dimer *Dinitrogen pentoxide (), nitrogen(V) oxide, or nitronium nitrate * Nitrosyl azide (), nitrogen(−I,0,I,II) oxide * Nitryl azide () * Oxatetrazole () * Trinitramide ( or ), nitrogen(0,IV) oxide Anions Cations * Nitrosonium ( or ) * Nitronium ( or ) Atmospheric sciences In atmospheric chemistry: * (or NO''x'') refers to the sum of NO and . * (or NO''y'') refers to the sum of and all oxidized atmospheric odd-nitrogen species (''e.g.'' the sum of , , , etc.) * (or NO''z'') = − * Mixed Oxides of Nitrogen ("MON"): solu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
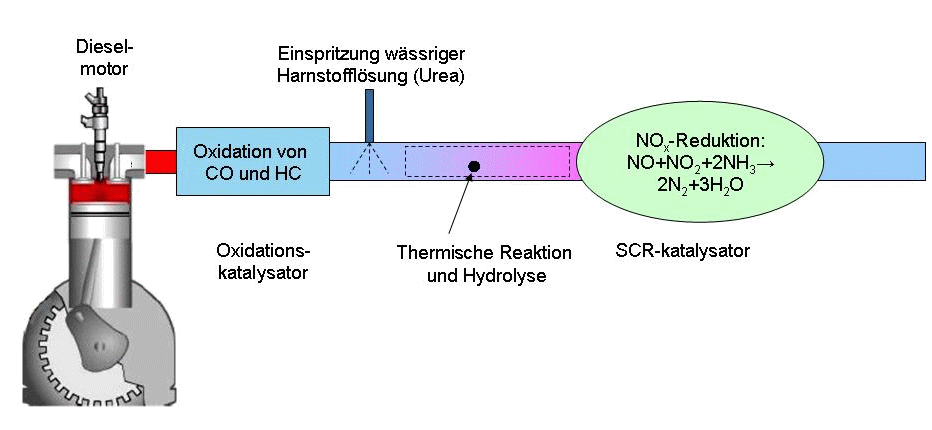
Selective Catalytic Reduction
Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) means converting nitrogen oxides, also referred to as with the aid of a catalyst into diatomic nitrogen (), and water (). A reductant, typically anhydrous ammonia (), aqueous ammonia (), or a urea () solution, is added to a stream of flue or exhaust gas and is reacted onto a catalyst. As the reaction drives toward completion, nitrogen (), and carbon dioxide (), in the case of urea use, are produced. Selective catalytic reduction of using ammonia as the reducing agent was patented in the United States by the Engelhard Corporation in 1957. Development of SCR technology continued in Japan and the US in the early 1960s with research focusing on less expensive and more durable catalyst agents. The first large-scale SCR was installed by the IHI Corporation in 1978.Steam: Its Generation and Uses. Babcock & Wilcox. Commercial selective catalytic reduction systems are typically found on large utility boilers, industrial boilers, and municipal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Rain Program
The Acid Rain Program is a market-based initiative taken by the United States Environmental Protection Agency in an effort to reduce overall atmospheric levels of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which cause acid rain. The program is an implementation of emissions trading that primarily targets coal-burning power plants, allowing them to buy and sell emission permits (called "allowances") according to individual needs and costs. In 2011, the trading program that existed since 1995 was supplemented by four separate trading programs under the Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR). On August 21, 2012, the United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia issued its Opinion and Order in the appeal of the Cross State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR) for two independent legal reasons. The stay on CSAPR was lifted in October 2014, allowing implementation of the law and its trading programs to begin. A 2021 study found that the "Acid Rain Program caused lasting improvements in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activity and is produced as a by-product of metals refining and the burning of Sour gas, sulfur-Sour crude oil, bearing fossil fuels. Sulfur dioxide is somewhat toxic to humans, although only when inhaled in relatively large quantities for a period of several minutes or more. It was known to medieval alchemy, alchemists as "volatile spirit of sulfur". Structure and bonding SO2 is a bent molecule with ''C''2v Point groups in three dimensions, symmetry point group. A valence bond theory approach considering just ''s'' and ''p'' orbitals would describe the bonding in terms of resonance (chemistry), resonance between two resonance structures. The sulfur–oxygen bond has a bond order of 1.5. There is support f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |