|
Eye Liner
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual perception, visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system. In higher organisms, the eye is a complex optics, optical system that collects light from the surrounding environment, regulates its intensity through a Iris (anatomy), diaphragm, Focus (optics), focuses it through an adjustable assembly of Lens (anatomy), lenses to form an image, converts this image into a set of electrical signals, and transmits these signals to the brain through neural pathways that connect the eye via the optic nerve to the visual cortex and other areas of the brain. Eyes with resolving power have come in ten fundamentally different forms, classified into compound eyes and non-compound eyes. Compound eyes are made up of multiple small visual units, and are common on insects and crustaceans. Non-compound eyes have a single lens a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nervous System
In biology, the nervous system is the complex system, highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its behavior, actions and sense, sensory information by transmitting action potential, signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Nervous tissue first arose in Ediacara biota, wormlike organisms about 550 to 600 million years ago. In Vertebrate, vertebrates, it consists of two main parts, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists mainly of nerves, which are enclosed bundles of the long fibers, or axons, that connect the CNS to every other part of the body. Nerves that transmit signals from the brain are called motor nerves (efferent), while those nerves that transmit information from the body to the CNS are called sensory nerves (aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus and then reaches the visual cortex. The area of the visual cortex that receives the sensory input from the lateral geniculate nucleus is the primary visual cortex, also known as visual area 1 ( V1), Brodmann area 17, or the striate cortex. The extrastriate areas consist of visual areas 2, 3, 4, and 5 (also known as V2, V3, V4, and V5, or Brodmann area 18 and all Brodmann area 19). Both hemispheres of the brain include a visual cortex; the visual cortex in the left hemisphere receives signals from the right visual field, and the visual cortex in the right hemisphere receives signals from the left visual field. Introduction The primary visual cortex (V1) is located in and around the calcarine fissure in the occipital lobe. Each h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Perception
Visual perception is the ability to detect light and use it to form an image of the surrounding Biophysical environment, environment. Photodetection without image formation is classified as ''light sensing''. In most vertebrates, visual perception can be enabled by photopic vision (daytime vision) or scotopic vision (night vision), with most vertebrates having both. Visual perception detects light (photons) in the visible spectrum reflected by objects in the environment or emitted by light sources. The light, visible range of light is defined by what is readily perceptible to humans, though the visual perception of non-humans often extends beyond the visual spectrum. The resulting perception is also known as vision, sight, or eyesight (adjectives ''visual'', ''optical'', and ''ocular'', respectively). The various physiological components involved in vision are referred to collectively as the visual system, and are the focus of much research in linguistics, psychology, cognitive s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colour
Color (or colour in Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is the visual perception based on the electromagnetic spectrum. Though color is not an inherent property of matter, color perception is related to an object's light absorption, emission, reflection and transmission. For most humans, colors are perceived in the visible light spectrum with three types of cone cells ( trichromacy). Other animals may have a different number of cone cell types or have eyes sensitive to different wavelengths, such as bees that can distinguish ultraviolet, and thus have a different color sensitivity range. Animal perception of color originates from different light wavelength or spectral sensitivity in cone cell types, which is then processed by the brain. Colors have perceived properties such as hue, colorfulness (saturation), and luminance. Colors can also be additively mixed (commonly used for actual light) or subtractively mixed (commonly used for materials). If the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bison Bonasus Right Eye Close-up
A bison (: bison) is a large bovine in the genus ''Bison'' (from Greek, meaning 'wild ox') within the tribe Bovini. Two extant taxon, extant and numerous extinction, extinct species are recognised. Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North America, is the more numerous. Although colloquially referred to as a buffalo in the United States and Canada, it is only distantly related to the true buffalo. The North American species is composed of two subspecies, the Plains bison, ''B. b. bison'', and the generally more northern wood bison, ''B. b. athabascae''. A third subspecies, the eastern bison (''B. b. pennsylvanicus'') is no longer considered a valid taxon, being a junior synonym of ''B. b. bison''. Historical references to "woods bison" or "wood bison" from the Eastern United States refer to this synonym animal (and to their eastern woodland habitat), not to ''B. b. athabascae'', wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
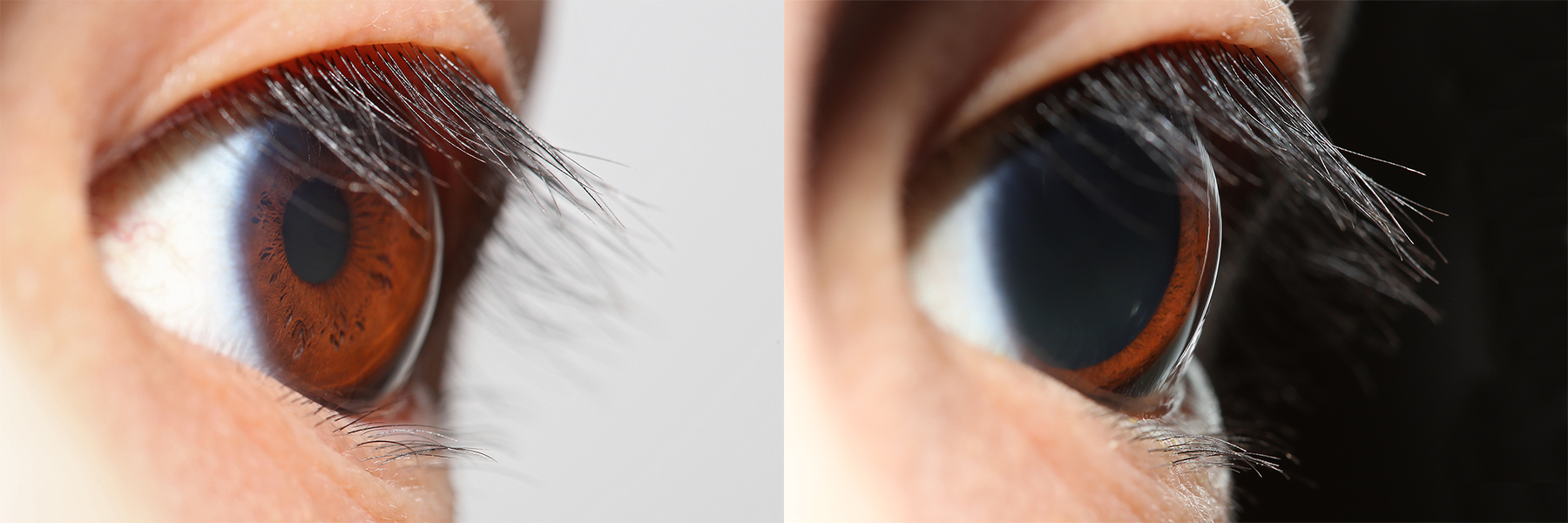
Pupillary Light Reflex
The pupillary light reflex (PLR) or photopupillary reflex is a reflex that controls the diameter of the pupil, in response to the intensity ( luminance) of light that falls on the retinal ganglion cells of the retina in the back of the eye, thereby assisting in adaptation of vision to various levels of lightness/darkness. A greater intensity of light causes the pupil to constrict ( miosis/myosis; thereby allowing less light in), whereas a lower intensity of light causes the pupil to dilate ( mydriasis, expansion; thereby allowing more light in). Thus, the pupillary light reflex regulates the intensity of light entering the eye. Light shone into one eye will cause both pupils to constrict. Terminology The pupil is the dark circular opening in the center of the iris and is where light enters the eye. By analogy with a camera, the pupil is equivalent to aperture, whereas the iris is equivalent to the diaphragm. It may be helpful to consider the ''Pupillary reflex'' as an Iris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pretectal Area
In neuroanatomy, the pretectal area, or pretectum, is a midbrain structure composed of seven nuclei and comprises part of the subcortical visual system. Through reciprocal bilateral projections from the retina, it is involved primarily in mediating behavioral responses to acute changes in ambient light such as the pupillary light reflex, the optokinetic reflex, and temporary changes to the circadian rhythm. In addition to the pretectum's role in the visual system, the anterior pretectal nucleus has been found to mediate somatosensory and nociceptive information. Location and structure The pretectum is a bilateral group of highly interconnected nuclei located near the junction of the midbrain and forebrain. The pretectum is generally classified as a midbrain structure, although because of its proximity to the forebrain it is sometimes classified as part of the caudal diencephalon (forebrain). Within vertebrates, the pretectum is located directly anterior to the superior col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
The suprachiasmatic nucleus or nuclei (SCN) is a small region of the brain in the hypothalamus, situated directly above the optic chiasm. It is responsible for regulating sleep cycles in animals. Reception of light inputs from photosensitive retinal ganglion cells allow it to coordinate the subordinate cellular clocks of the body and entrain to the environment. The neuronal and hormonal activities it generates regulate many different body functions in an approximately 24-hour cycle. The SCN also interacts with many other regions of the brain. It contains several cell types, neurotransmitters and peptides, including vasopressin and vasoactive intestinal peptide. Disruptions or damage to the SCN has been associated with different mood disorders and sleep disorders, suggesting the significance of the SCN in regulating circadian timing. Neuroanatomy The SCN is situated in the anterior part of the hypothalamus immediately dorsal, or ''superior'' (hence supra) to the optic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinohypothalamic Tract
In neuroanatomy, the retinohypothalamic tract (RHT) is a photic neural input pathway involved in the circadian rhythms of mammals. The origin of the retinohypothalamic tract is the intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGC), which contain the photopigment melanopsin. The axons of the ipRGCs belonging to the retinohypothalamic tract project directly, monosynaptically, to the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) via the optic nerve and the optic chiasm. The suprachiasmatic nuclei receive and interpret information on environmental light, dark and day length, important in the entrainment of the "body clock". They can coordinate peripheral "clocks" and direct the pineal gland to secrete the hormone melatonin. Structure The retinohypothalamic tract consists of retinal ganglion cells. A distinct population of ganglion cells, known as intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs), is critically responsible for providing non-image-forming visual signals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
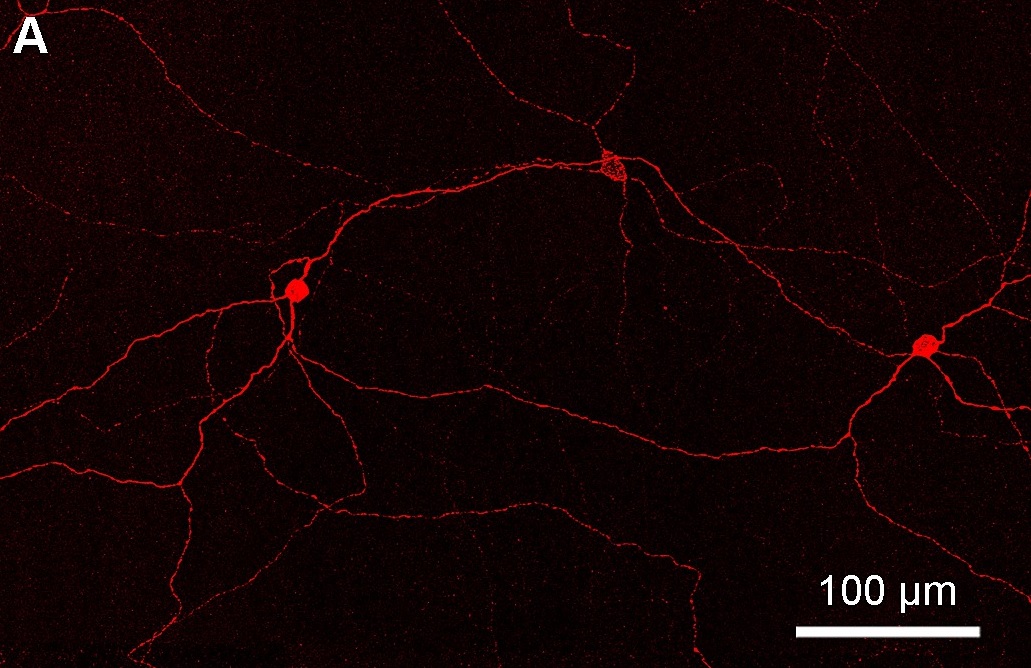
Photosensitive Ganglion Cell
Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs), also called photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (pRGC), or melanopsin-containing retinal ganglion cells (mRGCs), are a type of neuron in the retina of the mammalian eye. The presence of an additional photoreceptor was first suspected in 1927 when mice lacking rod and cone cells still responded to changing light levels through pupil constriction; this suggested that rods and cones are not the only light-sensitive tissue. However, it was unclear whether this light sensitivity arose from an additional retinal photoreceptor or elsewhere in the body. Recent research has shown that these retinal ganglion cells, unlike other retinal ganglion cells, are intrinsically photosensitive due to the presence of melanopsin, a light-sensitive protein. Therefore, they constitute a third class of photoreceptors, in addition to rod and cone cells. Overview Compared to the rods and cones, the ipRGCs respond more sluggishly and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Review Of Neuroscience
The ''Annual Review of Neuroscience'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes review articles relevant to neuroscience. In publication since 1978 by Annual Reviews, founding editor W. Maxwell Cowan led the editorial committee until his death in 2002. Mary E. Hatten and Botond Roska are the current co-editors. As of 2023, it is being published as open access, under the Subscribe to Open model. History In 1975, the nonprofit publisher Annual Reviews had two meetings in New York to coincide with the annual meeting of the Society for Neuroscience. In the meetings, neuroscientists from the US and Canada concurred that it would be useful to establish a journal that published an annual volume of review articles relevant to neuroscience. The board of directors of Annual Reviews gave the final approval for the journal in early 1976, appointing the first editorial committee with W. Maxwell Cowan appointed editor. In April 1976 the editorial committee planned the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |