|
Eye Chart
__NOTOC__ An eye chart is a chart used to measure visual acuity comprising lines of optotypes in ranges of sizes. Optotypes are the letters or symbols shown on an eye chart. Eye charts are often used by health care professionals, such as optometrists, physicians and nurses, to screen persons for vision impairment. Ophthalmology, Ophthalmologists, physicians who specialize in the eye, also use eye charts to monitor the visual acuity of their patients in response to various therapies such as Eye drop, medications or Eye surgery, surgery. The chart is placed at a standardized distance away from the person whose vision is being tested. The person then attempts to identify the optotypes on the chart, starting with the larger ones and continuing with progressively smaller ones until the person cannot identify the optotypes. The size of the smallest optotypes that can be reliably identified is considered the person's visual acuity. The Snellen chart is the most widely used. Alternative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snellen Chart
A Snellen chart is an eye chart that can be used to measure visual acuity. Snellen charts are named after the Dutch ophthalmologist Herman Snellen who developed the chart in 1862 as a measurement tool for the acuity formula developed by his professor Franciscus_Donders, Franciscus Cornelius Donders. Many ophthalmologists and vision scientists now use an improved chart known as the LogMAR chart. History Snellen developed charts using symbols based in a 5×5 unit grid. The experimental charts developed in 1861 used abstract symbols. Snellen's charts published in 1862 used alphanumeric capitals in the 5×5 grid. The original chart shows A, C, E, G, L, N, P, R, T, 5, V, Z, B, D, 4, F, H, K, O, S, 3, U, Y, A, C, E, G, L, 2. Description The normal Snellen chart is printed with eleven lines of block letters. The first line consists of one very large letter, which may be one of several letters, for example E, H, or N. Subsequent rows have increasing numbers of letters that decrease in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then processes that image within the retina and sends nerve impulses along the optic nerve to the visual cortex to create visual perception. The retina serves a function which is in many ways analogous to that of the photographic film, film or image sensor in a camera. The neural retina consists of several layers of neurons interconnected by Chemical synapse, synapses and is supported by an outer layer of pigmented epithelial cells. The primary light-sensing cells in the retina are the photoreceptor cells, which are of two types: rod cell, rods and cone cell, cones. Rods function mainly in dim light and provide monochromatic vision. Cones function in well-lit conditions and are responsible fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerator
A fraction (from , "broken") represents a part of a whole or, more generally, any number of equal parts. When spoken in everyday English, a fraction describes how many parts of a certain size there are, for example, one-half, eight-fifths, three-quarters. A ''common'', ''vulgar'', or ''simple'' fraction (examples: and ) consists of an integer numerator, displayed above a line (or before a slash like ), and a non-zero integer denominator, displayed below (or after) that line. If these integers are positive, then the numerator represents a number of equal parts, and the denominator indicates how many of those parts make up a unit or a whole. For example, in the fraction , the numerator 3 indicates that the fraction represents 3 equal parts, and the denominator 4 indicates that 4 parts make up a whole. The picture to the right illustrates of a cake. Fractions can be used to represent ratios and division. Thus the fraction can be used to represent the ratio 3:4 (the ratio of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squint
Squinting is the action of looking at something with partially closed eyes. Squinting is most often practiced by people who suffer from Refractive error, refractive errors of the eye who either do not have or are not using their glasses. Squinting helps momentarily improve their Visual perception, eyesight by slightly changing the shape of the eye to make it rounder, which helps light properly reach the Fovea centralis, fovea. Squinting also decreases the amount of light entering the eye, making it easier to focus on what the observer is looking at by removing rays of light which enter the eye at an angle and would need to otherwise be focused by the observer's faulty Lens (anatomy), lens and cornea. Pinhole glasses, which severely restrict the amount of light entering the cornea, have the same effect as squinting. It is a common belief that squinting worsens eyesight. However, according to Robert MacLaren, a professor of ophthalmology at the University of Oxford, this is nothi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinhole Occluder
A pinhole occluder is an opaque disk with one or more small holes through it, used by ophthalmologists, orthoptists and optometrists to test visual acuity. The occluder is a simple way to focus light, as in a pinhole camera, temporarily removing the effects of refractive errors such as myopia. Because light passes only through the center of the eye's lens, defects in the shape of the lens (errors of refraction) have no effect while the occluder is used. In this way, the ophthalmologist, orthoptist or optometrist can estimate the maximum improvement in a patient's vision that can be attained by lenses to correct errors of refraction. This can be used to distinguish visual defects caused by refractive error, which improve when the occluder is used, from other problems, which do not. The pinhole occluder can also be used in testing visual acuity in mydriatic patients. In this case, the pinhole occluder compensates for the inability to contract the iris assisting the eye in obtain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
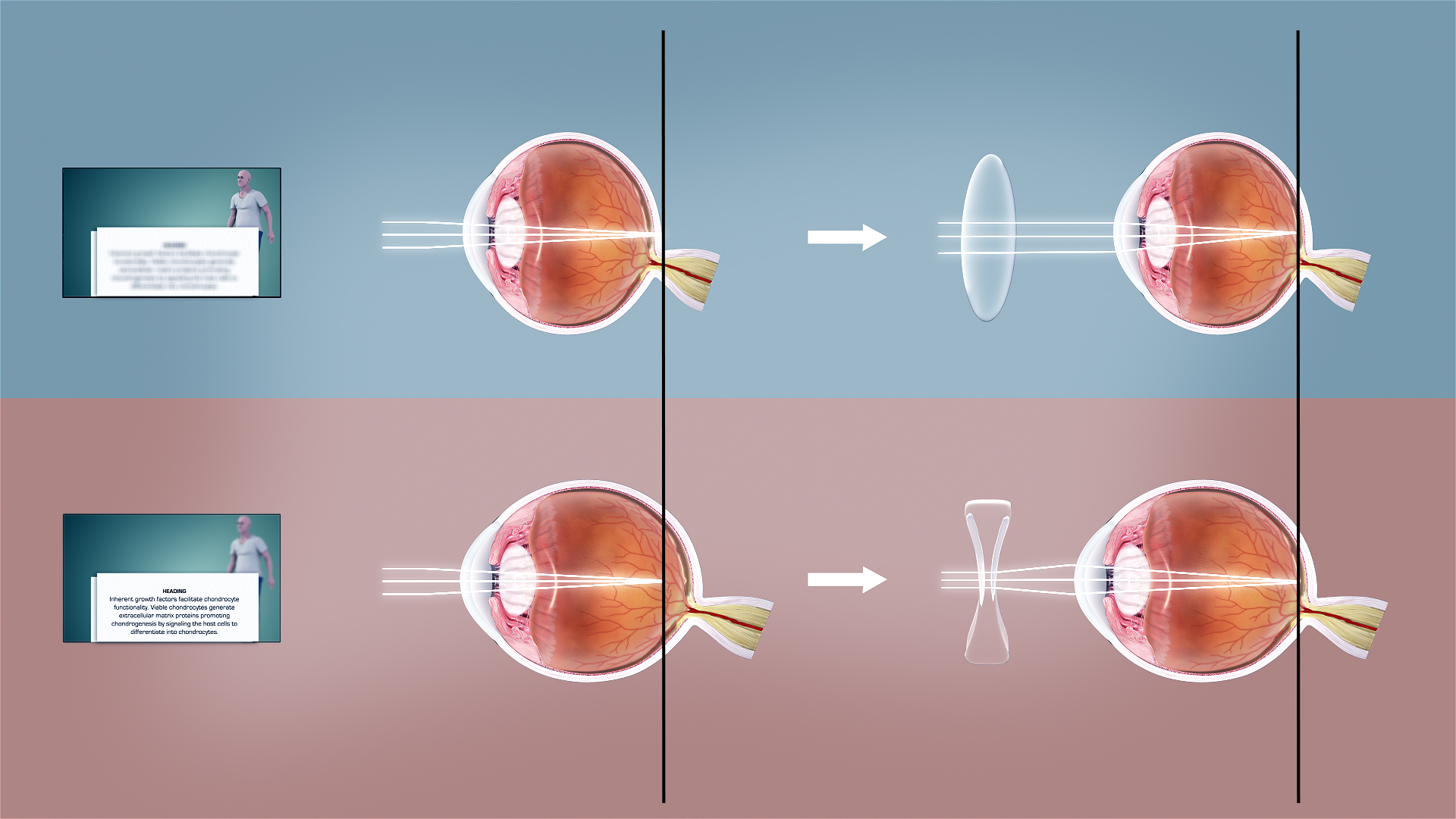
Refractive Error
Refractive error is a problem with focus (optics), focusing light accurately on the retina due to the shape of the eye and/or cornea. The most common types of refractive error are myopia, near-sightedness, hyperopia, far-sightedness, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Near-sightedness results in far away objects being blurred vision, blurry, far-sightedness and presbyopia result in close objects being blurry, and astigmatism causes objects to appear stretched out or blurry. Other symptoms may include double vision, headaches, and eye strain. Near-sightedness is due to the length of the eyeball being too long; far-sightedness the eyeball too short; astigmatism the cornea being the wrong shape, while presbyopia results from aging of the lens of the eye such that it cannot change shape sufficiently. Some refractive errors occur more often among those whose parents are affected. Diagnosis is by eye examination. Refractive errors are corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Perception
Visual perception is the ability to detect light and use it to form an image of the surrounding Biophysical environment, environment. Photodetection without image formation is classified as ''light sensing''. In most vertebrates, visual perception can be enabled by photopic vision (daytime vision) or scotopic vision (night vision), with most vertebrates having both. Visual perception detects light (photons) in the visible spectrum reflected by objects in the environment or emitted by light sources. The light, visible range of light is defined by what is readily perceptible to humans, though the visual perception of non-humans often extends beyond the visual spectrum. The resulting perception is also known as vision, sight, or eyesight (adjectives ''visual'', ''optical'', and ''ocular'', respectively). The various physiological components involved in vision are referred to collectively as the visual system, and are the focus of much research in linguistics, psychology, cognitive s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utrecht
Utrecht ( ; ; ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city of the Netherlands, as well as the capital and the most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of Utrecht (province), Utrecht. The municipality of Utrecht is located in the eastern part of the Randstad conurbation, in the very centre of mainland Netherlands, and includes Haarzuilens, Vleuten and De Meern. It has a population of 376,435 as of . Utrecht's ancient city centre features many buildings and structures, several dating as far back as the High Middle Ages. It has been the religious centre of the Netherlands since the 8th century. In 1579, the Union of Utrecht was signed in the city to lay the foundations for the Dutch Republic. Utrecht was the most important city in the Netherlands until the Dutch Golden Age, when it was surpassed by Amsterdam as the country's cultural centre and most populous city. Utrecht is home to Utrecht University, the largest university ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herman Snellen
Herman Snellen (, February 19, 1834 – January 18, 1908) was a Dutch ophthalmologist who in 1862 introduced the Snellen chart to study visual acuity. He took over directorship of the Netherlands Hospital for Eye Patients (Nederlandsch Gasthuis voor Ooglijders), after Franciscus Donders. He was elected an International Member of the American Philosophical Society in 1894. Early life Herman Snellen studied medicine at Utrecht University under Donders, Gerardus Johannes Mulder and Jacobus Schroeder van der Kolk. He earned his medical degree in 1858 from Leiden University. He specialized in ophthalmology and worked as an assistant physician at the Netherlands Hospital for Eye Patients after he had completed his degree. Director He was named to succeed Donders as the institute's director in 1884, a position he served until 1903. In 1877, he was appointed as a professor of ophthalmology at Utrecht University. He did research on astigmatism, glaucoma and other eye diseases as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard Jäger Von Jaxtthal
Eduard Jäger von Jaxtthal (25 June 1818 in Vienna – 5 July 1884 in Vienna) was an Austrian ophthalmologist who was a native of Vienna. He was a professor at the University of Vienna, and was son to oculist Friedrich Jäger von Jaxtthal (1784-1871), and grandson to Georg Joseph Beer (1763-1821). Jäger is remembered for his work involving eye operations, and for his research of ophthalmic disorders. He was an early practitioner of the ophthalmoscope, and was among the first to use ophthalmoscopy to determine refractive error in the eye. Also, he is credited with providing the first description of retinal appearances associated with diabetes. In the 1850s Jäger made improvements to eye chart test types that were earlier developed by Heinrich Küchler (1811-1873). In 1862 Dutch ophthalmologist Hermann Snellen introduced the popular "Snellen chart" for testing visual acuity.H. Snellen, Probebuchstaben zur Bestimmung der Sehschärfe, Utrecht 1862. Selected writings * ''Bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Küchler
Heinrich Georg Küchler (23 April 1811, Darmstadt – 29 March 1873, Darmstadt) was a German ophthalmologist. From 1828 he studied medicine at the University of Giessen, and after graduation visited Paris for study. In 1834 he returned to Darmstadt, where he started a private ophthalmic practice. In 1836 he was arrested unexpectedly because of his actions in association with a ''Burschenschaft'' (fraternal organization) at Giessen. For nearly three years he was imprisoned, obtaining his freedom in January 1839. After his release, he resumed his ophthalmic practice in Darmstadt.ADB:Küchler, Heinrich – Wikisource at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franciscus Donders
Franciscus (Franz) Cornelius Donders FRS FRSE (27 May 1818 – 24 March 1889) was a Dutch ophthalmologist. During his career, he was a professor of physiology in Utrecht, and was internationally regarded as an authority on eye diseases, directing the Netherlands Hospital for Eye Patients. Along with Graefe and Helmholtz, he was one of the primary founders of scientific ophthalmology. Life He was born in Tilburg, the son of Jan Franz Donders and Agnes Elizabeth Hegh. Education Franciscus Donders was first educated at Duizel School and seminaries in both Tilburg and Boxmeer. By the age of seventeen, he had started studying medicine in the School of Military in Utrecht. It was here that he discovered his passion for experimental study, specifically in the field of chemistry. By the age of twenty-two he entered the junior military in order to become a surgeon For several years, the young Donders studied at the Royal Dutch Hospital for Military Medicine in Utrecht, then earning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |