|
Eye Injury
Physical or chemical injuries of the eye can be a serious threat to vision if not treated appropriately and in a timely fashion. The most obvious presentation of ocular (eye) injuries is redness and pain of the affected eyes. This is not, however, universally true, as tiny metallic projectiles may cause neither symptom. Tiny metallic projectiles should be suspected when a patient reports ''metal on metal'' contact, such as with hammering a metal surface. Corneal foreign bodies are one of the most common preventable occupational hazards. Intraocular foreign bodies do not cause pain because of the lack of nerve endings in the vitreous humour and retina that can transmit pain sensations. As such, general or emergency department doctors should refer cases involving the posterior segment of the eye or intraocular foreign bodies to an ophthalmologist. Ideally, ointment would not be used when referring to an ophthalmologist, since it diminishes the ability to carry out a thorough ey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiology
Physiology (; ) is the science, scientific study of function (biology), functions and mechanism (biology), mechanisms in a life, living system. As a branches of science, subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organ (biology), organs, cell (biology), cells, and biomolecules carry out chemistry, chemical and physics, physical functions in a living system. According to the classes of organisms, the field can be divided into clinical physiology, medical physiology, Zoology#Physiology, animal physiology, plant physiology, cell physiology, and comparative physiology. Central to physiological functioning are biophysics, biophysical and biochemical processes, homeostasis, homeostatic control mechanisms, and cell signaling, communication between cells. ''Physiological state'' is the condition of normal function. In contrast, ''pathology, pathological state'' refers to abnormality (behavior), abnormal conditions, including human diseases. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archives Of Ophthalmology
An archive is an accumulation of historical records or materials, in any medium, or the physical facility in which they are located. Archives contain primary source documents that have accumulated over the course of an individual or organization's lifetime, and are kept to show the history and function of that person or organization. Professional archivists and historians generally understand archives to be records that have been naturally and necessarily generated as a product of regular legal, commercial, administrative, or social activities. They have been metaphorically defined as "the secretions of an organism", and are distinguished from documents that have been consciously written or created to communicate a particular message to posterity. In general, archives consist of records that have been selected for permanent or long-term preservation on the grounds of their enduring cultural, historical, or evidentiary value. Archival records are normally unpublished and alm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Injury
Physical or chemical injuries of the eye can be a serious threat to vision if not treated appropriately and in a timely fashion. The most obvious presentation of ocular (eye) injuries is redness and pain of the affected eyes. This is not, however, universally true, as tiny metallic projectiles may cause neither symptom. Tiny metallic projectiles should be suspected when a patient reports ''metal on metal'' contact, such as with hammering a metal surface. Corneal foreign bodies are one of the most common preventable occupational hazards. Intraocular foreign bodies do not cause pain because of the lack of nerve endings in the vitreous humour and retina that can transmit pain sensations. As such, general or emergency department doctors should refer cases involving the posterior segment of the eye or intraocular foreign bodies to an ophthalmologist. Ideally, ointment would not be used when referring to an ophthalmologist, since it diminishes the ability to carry out a thorough ey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Care Physician
A primary care physician (PCP) is a physician who provides both the first contact for a person with an undiagnosed health concern as well as continuing care of varied medical conditions, not limited by cause, organ system, or diagnosis. The term is primarily used in the United States. In the past, the equivalent term was 'general practitioner' in the US; however in the United Kingdom and other countries the term general practitioner is still used. With the advent of nurses as PCPs, the term PCP has also been expanded to denote primary care providers. A core element in general practice is continuity that bridges episodes of various illnesses. Greater continuity with a general practitioner has been shown to reduce the need for out-of-hours services and acute hospital admittance. Furthermore, continuity by a general practitioner reduces mortality. All physicians first complete medical school ( MD, MBBS, or DO). To become primary care physicians, medical school graduates then under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical History
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and eventually people close to them, so to collect reliable/objective information for managing the medical diagnosis and proposing efficient medical treatments. The medically relevant complaints reported by the patient or others familiar with the patient are referred to as symptoms, in contrast with clinical signs, which are ascertained by direct examination on the part of medical personnel. Most health encounters will result in some form of history being taken. Medical histories vary in their depth and focus. For example, an ambulance paramedic would typically limit their history to important details, such as name, history of presenting complaint, allergies, etc. In contrast, a psychiatric history is frequently lengthy and in depth, as man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proxymetacaine
Proxymetacaine (INN) or proparacaine (USAN) is a topical anesthetic drug of the aminoester group. Clinical pharmacology Proxymetacaine is a local anesthetic which on topical application penetrates sensory nerve endings in the corneal tissue. Mechanism of action Proxymetacaine is believed to act as an antagonist on voltage-gated sodium channels to affect the permeability of neuronal membranes; how this inhibits pain sensations and the exact mechanism of action of proxymetacaine are, however, unknown. Indications and usage Proxymetacaine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution (eye drops) is indicated for procedures such as tonometry, gonioscopy, removal of foreign bodies, or other similar procedures requiring topical anesthesia of the cornea and conjunctiva. Warnings Proxymetacaine is for topical ophthalmic use only, and it is specifically not intended for injection. Prolonged use of this or any other topical ocular anesthetic may produce permanent corneal opacification with accompan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topical Anesthetic
A topical anesthetic is a local anesthetic that is used to numb the surface of a body part. They can be used to numb any area of the skin as well as the front of the eyeball, the inside of the nose, ear or throat, the anus and the genital area. Topical anesthetics are available in creams, ointments, aerosols, sprays, lotions, and jellies. Examples include benzocaine, butamben, dibucaine, lidocaine, oxybuprocaine, pramoxine, proxymetacaine (proparacaine), and tetracaine (also named amethocaine). Usage Topical anesthetics are used to relieve pain and itching caused by conditions such as sunburn or other minor burns, insect bites or stings, poison ivy, poison oak, poison sumac, and minor cuts and scratches. Topical anesthetics are used in ophthalmology and optometry to numb the surface of the eye (the outermost layers of the cornea and conjunctiva) to: * Perform a contact/applanation tonometry. * Perform a Schirmer's test (The Schirmer's test is sometimes used with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment is a condition where the retina pulls away from the tissue underneath it. It may start in a small area, but without quick treatment, it can spread across the entire retina, leading to serious vision loss and possibly blindness. Retinal detachment is a medical emergency that requires surgery. The retina is a thin layer at the back of the eye that processes visual information and sends it to the brain. When the retina detaches, common symptoms include seeing floaters, flashing lights, a dark shadow in vision, and sudden blurry vision. The most common type of retinal detachment is rhegmatogenous, which occurs when a tear or hole in the retina lets fluid from the center of the eye get behind it, causing the retina to pull away. Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is most commonly caused by posterior vitreous detachment, a condition where the gel inside the eye breaks down and pulls on the retina. Risk factors include older age, nearsightedness ( myopia), eye injury, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitreous Hemorrhage
Vitreous hemorrhage is the extravasation, or leakage, of blood into the areas in and around the vitreous humor of the eye. The vitreous humor is the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eye. A variety of conditions can result in blood leaking into the vitreous humor, which can cause impaired vision, floaters, and photopsia. Symptoms Common symptoms of vitreous hemorrhage include: *Blurred vision * Floaters – faint cobweb-like apparitions floating through the field of vision *Reddish tint to vision *Photopsia – brief flashes of light in the peripheral vision Small vitreous hemorrhage often manifests itself as "floaters." A moderate case will often result in dark streaks in the vision, while dense vitreous hemorrhage can significantly inhibit vision. Causes There are many factors known to cause vitreous hemorrhage. Diabetic retinopathy The most common cause found in adults is diabetic retinopathy. Abnormal blood vessels can form in the back of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
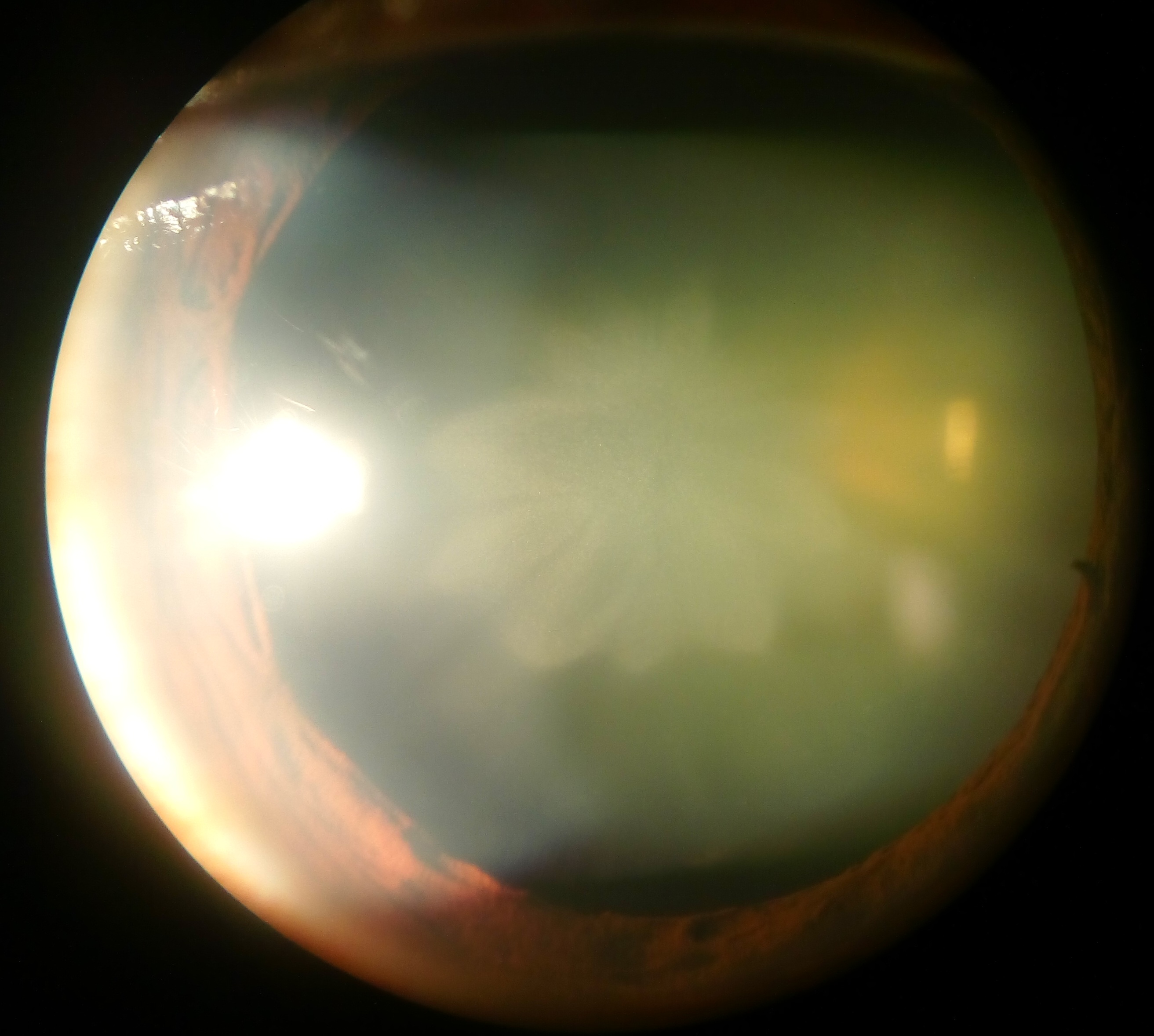
Cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens (anatomy), lens of the eye that leads to a visual impairment, decrease in vision of the eye. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and Nyctalopia, difficulty seeing at night. This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognizing faces. Poor vision caused by cataracts may also result in an increased risk of Falling (accident), falling and Depression (mood), depression. Cataracts cause 51% of all cases of blindness and 33% of visual impairment worldwide. Cataracts are most commonly due to senescence, aging but may also occur due to Trauma (medicine), trauma or radiation exposure, be congenital cataract, present from birth, or occur following eye surgery for other problems. Risk factors include diabetes mellitus, diabetes, longstanding use of corticosteroid medication, smoking tobacco, prolonged exposu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis is described anatomically, by the part of the eye affected, as anterior, intermediate or posterior, or panuveitic if all parts are involved. Anterior uveitis ( iridocyclitis) is the most common, with the incidence of uveitis overall affecting approximately 1:4500, most commonly those between the ages of 20–60. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, floaters and blurred vision, and ophthalmic examination may show dilated ciliary blood vessels and the presence of cells in the anterior chamber. Uveitis may arise spontaneously, have a genetic component, or be associated with an autoimmune disease or infection. While the eye is a relatively protected environment, its immune mecha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
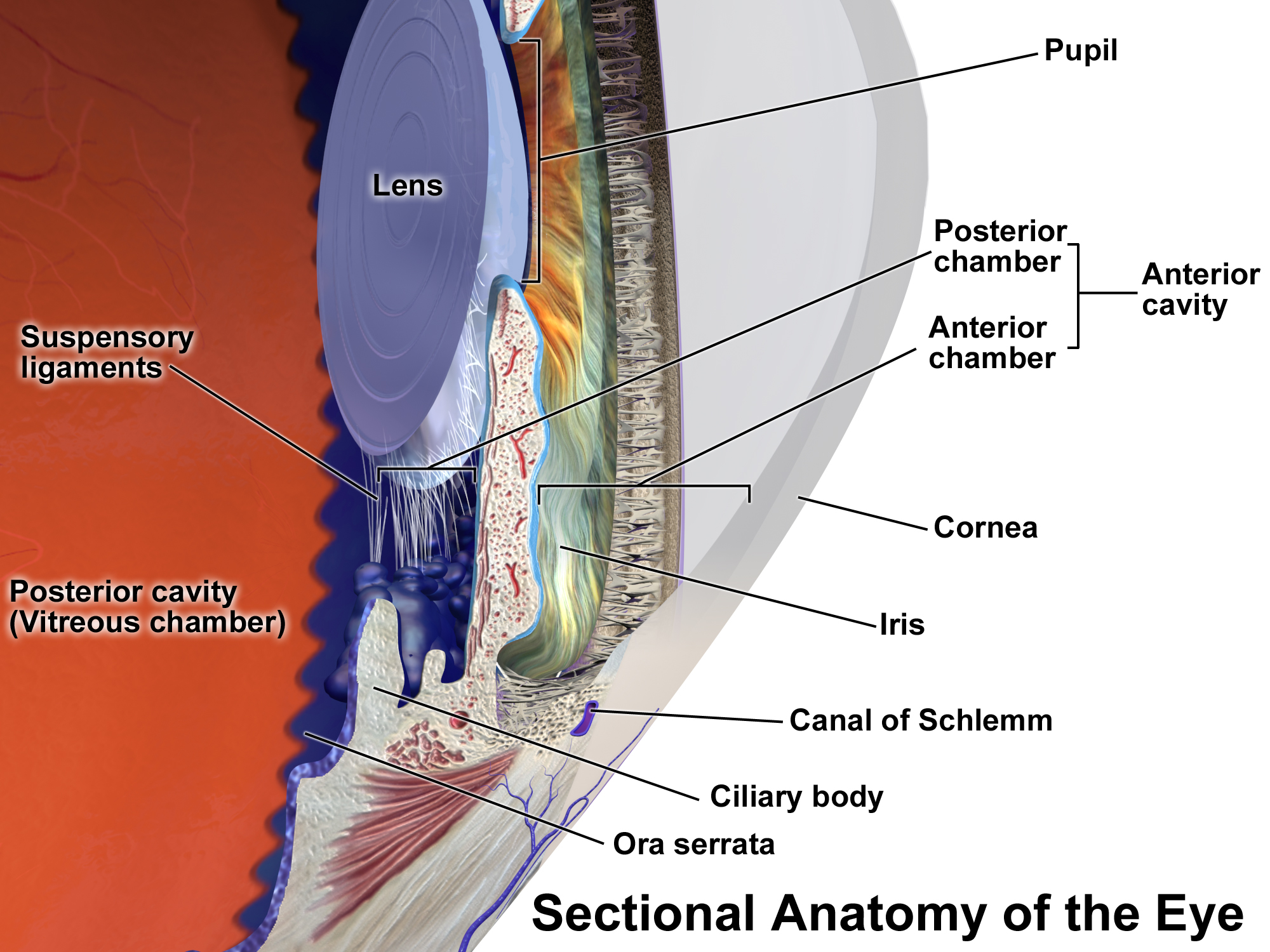
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to damage of the optic nerve. The optic nerve transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma may cause vision loss if left untreated. It has been called the "silent thief of sight" because the loss of vision usually occurs slowly over a long period of time. A major risk factor for glaucoma is increased pressure within the eye, known as Intraocular pressure, intraocular pressure (IOP). It is associated with old age, a family history of glaucoma, and certain medical conditions or the use of some medications. The word ''glaucoma'' comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning 'gleaming, blue-green, gray'. Of the different types of glaucoma, the most common are called open-angle glaucoma and closed-angle glaucoma. Inside the eye, a liquid called Aqueous humour, aqueous humor helps to maintain shape and provides nutrients. The aqueous humor normally drains through the trabecular meshwork. In open-angle glaucoma, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |