|
Exudates
An exudate is a fluid released by an organism through pores or a wound, a process known as exuding or exudation. ''Exudate'' is derived from ''exude'' 'to ooze' from Latin 'to (ooze out) sweat' (' 'out' and ' 'to sweat'). Medicine An exudate is any fluid that filters from the circulatory system into lesions or areas of inflammation. It can be a pus-like or clear fluid. When an injury occurs, leaving skin exposed, it leaks out of the blood vessels and into nearby tissues. The fluid is composed of serum, fibrin, and leukocytes. Exudate may ooze from cuts or from areas of infection or inflammation. Types * Purulent or suppurative exudate consists of plasma with both active and dead neutrophils, fibrinogen, and necrotic parenchymal cells. This kind of exudate is consistent with more severe infections, and is commonly referred to as pus. * Fibrinous exudate is composed mainly of fibrinogen and fibrin. It is characteristic of rheumatic carditis, but is seen in all seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transudate
Transudate is extravascular fluid with low protein content and a low specific gravity (< 1.012). It has low nucleated cell counts (less than 500 to 1000 per microliter) and the primary cell types are mononuclear leukocyte, mononuclear cells: macrophages, lymphocytes and mesothelial cells. For instance, an ultrafiltrate of blood plasma is transudate. It results from increased fluid pressures or diminished colloid oncotic forces in the plasma. Transudate vs. exudate There is an important distinction between transudates and exudates. Transudates are caused by disturbances of hydrostatic or colloid osmotic pressure, not by inflammation. They have a low protein content in comparison to exudates and thus appear clearer.The University of Utah • Spencer S. Eccles Health Sciences Library; WebPath images Levels of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) or a Rivalta test can be used to distinguish ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivalta Test
Certain diseases can cause excessive accumulations of fluid in areas of the body such as the abdomen (ascites) or the pleural space around the lungs (pleural effusion) or the pericardial space around the heart. An estimate of the concentration of protein in such fluids can narrow the differential diagnosis and assist the clinician in establishing a diagnosis. For example, fluid accumulations due to congestive heart failure and liver failure (cirrhosis) are typically lower in protein content and are called transudates whereas fluid accumulations due to cancer and tuberculosis are typically higher in protein content and are called exudates. The Rivalta Test is a simple, inexpensive method that can be used in resource-limited settings to differentiate a transudate from an exudate. It is a simple, inexpensive method that does not require special laboratory equipment and can be easily performed in private practice. The test was originally developed by the Italian researcher Rivalta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transudates
Transudate is extravascular fluid with low protein content and a low specific gravity (< 1.012). It has low nucleated cell counts (less than 500 to 1000 per microliter) and the primary cell types are mononuclear cells: s, s and mesothelial cells. For instance, an ultrafiltrate of is transudate. It results from increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrotic
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who is often regarded as one of the founders of modern pathology. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated digestion of cell components. In contrast, ''apoptosis'' is a naturally occurring programmed and targeted cause of cellular death. While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal. Cellular death due to necrosis does not follow the apoptotic signal transduction pathway, but rather various receptors are activated and result in the loss of cell membrane integrity and an uncontrolled release of products of cell death into the extracellular space. This initiates an inflammatory response in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strep Throat
Streptococcal pharyngitis, also known as streptococcal sore throat (strep throat), is pharyngitis (an infection of the pharynx, the back of the throat) caused by ''Streptococcus pyogenes'', a Gram-positive bacteria, gram-positive, group A streptococcal infection, group A streptococcus. Common symptoms include fever, sore throat, red Palatine tonsil, tonsils, and enlarged Cervical lymph nodes, lymph nodes in the front of the neck. A headache and nausea or vomiting may also occur. Some develop a sandpaper-like rash which is known as scarlet fever. Symptoms typically begin one to three days after exposure and last seven to ten days. Strep throat is spread by respiratory droplets from an infected person, spread by talking, coughing or sneezing, or by touching something that has droplets on it and then touching the mouth, nose, or eyes. It may be spread directly through touching infected sores. It may also be spread by contact with skin infected with group A strep. The diagnosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have been proposed to define what an organism is. Among the most common is that an organism has autonomous reproduction, Cell growth, growth, and metabolism. This would exclude viruses, despite the fact that they evolution, evolve like organisms. Other problematic cases include colonial organisms; a colony of eusocial insects is organised adaptively, and has Germ-Soma Differentiation, germ-soma specialisation, with some insects reproducing, others not, like cells in an animal's body. The body of a siphonophore, a jelly-like marine animal, is composed of organism-like zooids, but the whole structure looks and functions much like an animal such as a jellyfish, the parts collaborating to provide the functions of the colonial organism. The evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Gum
Natural gums are polysaccharides of natural origin, capable of causing a large increase in a solution's viscosity, even at small concentrations. They are mostly gum (botany), botanical gums, found in the woody elements of plants or in seed coatings. Human uses Gums are used in the food industry as thickening agents, gelling agents, Emulsion, emulsifying agents, and Food additive#Categories , stabilizers, and in other industrial adhesives, Excipient#Types, binding agents, crystal inhibitors, Brewing#Ingredients, clarifying agents, encapsulating agents, Flocculation , flocculating agents, swelling agents, foam stabilizers, etc. When consumed by humans, many of these gums are fermented by the microbes that inhabit the lower gastrointestinal tract (microbiome) and may influence the ecology and functions of these microscopic communities. Commercial significance Humans have used natural gums for various purposes, including chewing gum , chewing and the manufacturing of a wide rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Saps
Sap is a fluid transported in the xylem cells (vessel elements or tracheids) or phloem sieve tube elements of a plant. These cells transport water and nutrients throughout the plant. Sap is distinct from latex, resin, or cell sap; it is a separate substance, separately produced, and with different components and functions. Insect honeydew is called sap, particularly when it falls from trees, but is only the remains of eaten sap and other plant parts. Types of sap Saps may be broadly divided into two types: xylem sap and phloem sap. Xylem sap Xylem sap (pronounced ) consists primarily of a watery solution of hormones, mineral elements and other nutrients. Transport of sap in xylem is characterized by movement from the roots toward the leaves. Over the past century, there has been some controversy regarding the mechanism of xylem sap transport; today, most plant scientists agree that the cohesion-tension theory best explains this process, but multiforce theories that h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Cavity
A body cavity is any space or compartment, or potential space, in an animal body. Cavities accommodate organs and other structures; cavities as potential spaces contain fluid. The two largest human body cavities are the ventral body cavity, and the dorsal body cavity. In the dorsal body cavity the brain and spinal cord are located. The membranes that surround the central nervous system organs (the brain and the spinal cord, in the cranial and spinal cavities) are the three meninges. The differently lined spaces contain different types of fluid. In the meninges for example the fluid is cerebrospinal fluid; in the abdominal cavity the fluid contained in the peritoneum is a serous fluid. In amniotes and some invertebrates the peritoneum lines their largest body cavity called the coelom. Mammals Mammalian embryos develop two body cavities: the intraembryonic coelom and the extraembryonic coelom (or chorionic cavity). The intraembryonic coelom is lined by somatic and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Permeability
Vascular permeability, often in the form of capillary permeability or microvascular permeability, characterizes the permeability of a blood vessel wall–in other words, the blood vessel wall's capacity to allow for the flow of small molecules (such as drugs, nutrients, water, or ions) or even whole cells (such as lymphocytes on their way to a site of inflammation) in and out of the vessel. Blood vessel walls are lined by a single layer of endothelial cells. The gaps between endothelial cells (cell junctions) are strictly regulated depending on the type and physiological state of the tissue. There are several techniques to measure vascular permeability to certain molecules. For instance, the cannulation of a single microvessel with a micropipette: the microvessel is perfused with a certain pressure, occluded downstream, and then the velocity of some cells will be related to the permeability.Michel, C. C., Mason, J. C., Curry, F. E. & Tooke, J. E. Development of Landis Techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
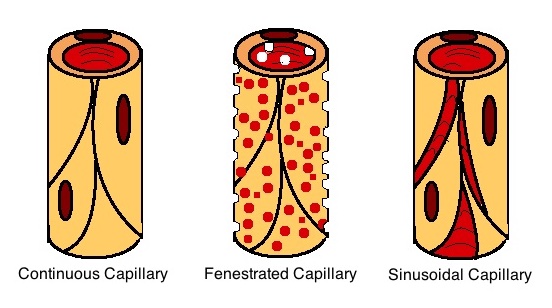
Capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the innermost layer of an artery or vein), consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the site of the exchange of many substances from the surrounding interstitial fluid, and they convey blood from the smallest branches of the arteries (arterioles) to those of the veins (venules). Other substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in microcirculation. Etymology ''Capillary'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "of or resembling hair", with use in English beginning in the mid-17th century. The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Gravity
Relative density, also called specific gravity, is a dimensionless quantity defined as the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for solids and liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water at its densest (at ); for gases, the reference is air at room temperature (). The term "relative density" (abbreviated r.d. or RD) is preferred in SI, whereas the term "specific gravity" is gradually being abandoned. If a substance's relative density is less than 1 then it is less dense than the reference; if greater than 1 then it is denser than the reference. If the relative density is exactly 1 then the densities are equal; that is, equal volumes of the two substances have the same mass. If the reference material is water, then a substance with a relative density (or specific gravity) less than 1 will float in water. For example, an ice cube, with a relative density of about 0.91, will float. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |