|
Expressivity (genetics)
In genetics, expressivity is the degree to which a phenotype is expressed by individuals having a particular genotype. Alternatively, it may refer to the expression of a particular gene by individuals having a certain phenotype. Expressivity is related to the ''intensity'' of a given phenotype; it differs from penetrance, which refers to the ''proportion'' of individuals with a particular genotype that share the same phenotype. Variable expressivity Variable expressivity refers to the phenomenon by which individuals with a shared genotype exhibit varying phenotypes. This can be further described as a spectrum of associated traits that can range in size, colour, intensity, and so forth. Variable expressivity can be seen in plants and animals, such as differences in hair colour, leaf size, and severity of diseases. Mechanisms influencing expressivity This variation in expression can be affected by modifier genes, epigenetic factors or the environment. # Modifier genes can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Phenotypic trait, Trait inheritance and Molecular genetics, molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the Cell (bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatin Variant
A chromatin variant (also known as an epigenetic lesion, epimutation or epigenetic alteration) corresponds to a section of the genome that differs in chromatin states across cell types/states within an individual (intra-individual) or between individuals for a given cell type/state (inter-individual). Chromatin variants distinguish DNA sequences that differ in their function in one cell type/state versus another. Chromatin variants are found across the genome, inclusive of repetitive and non-repetitive DNA sequences. Chromatin variants range in sizes. The smallest chromatin variants cover a few hundred DNA base pairs, such as seen at promoters, enhancers or insulators. The largest chromatin variants capture a few thousand DNA base pairs, such as seen at Large Organized Chromatin Lysine domains (LOCKs) and Clusters Of Cis-Regulatory Elements (COREs), such as super-enhancer Cell differentiation in multicellular organism A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis (NF) refers to a group of three distinct genetic conditions in which tumors grow in the nervous system. The tumors are non-cancerous (benign) and often involve the skin or surrounding bone. Although symptoms are often mild, each condition presents differently. neurofibromatosis type I, Neurofibromatosis type I (NF1) is typically characterized by Café au lait spot, café au lait spots (light-brown flat patches of skin), Neurofibroma, neurofibromas (small bumps in or under the skin), scoliosis (side-way curvature of the back), and Headache, headaches. neurofibromatosis type II, Neurofibromatosis type II (NF2), on the other hand, may present with early-onset hearing loss, cataracts, tinnitus, difficulty walking or maintaining balance, and muscle atrophy. The third type is called schwannomatosis and often presents in early adulthood with widespread pain, numbness, or tingling due to nerve compression. The cause is a genetic mutation in certain oncogenes. These c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Der Woude Syndrome
Van der Woude syndrome (VDWS) is a genetic disorder characterized by the combination of lower lip pits, cleft lip with or without cleft palate (CL/P), and cleft palate only (CPO). The frequency of orofacial clefts ranges from 1:1000 to 1:500 births worldwide, and there are more than 400 syndromes that involve CL/P. VWS is distinct from other clefting syndromes due to the combination of cleft lip and palate (CLP) and CPO within the same family. Other features frequently associated with VWS include hypodontia in 10-81% of cases, narrow arched palate, congenital heart disease, heart murmur and cerebral abnormalities, syndactyly of the hands, polythelia, ankyloglossia, and adhesions between the upper and lower gum pads. The association between lower lip pits and cleft lip and/or palate was first described by Anne Van der Woude in 1954. The worldwide disease incidence ranges from 1:100,000 to 1:40,000. Genetics Van der Woude syndrome is inherited as an autosomal dominant disease ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marfan Syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with dolichostenomelia, long arms, legs, Arachnodactyly, fingers, and toes. They also typically have hypermobility (joints), exceptionally flexible joints and scoliosis, abnormally curved spines. The most serious complications involve the heart and aorta, with an increased risk of mitral valve prolapse and aortic aneurysm. The lungs, eyes, bones, and the dura mater, covering of the spinal cord are also commonly affected. The severity of the symptoms is variable. MFS is caused by a mutation in ''FBN1'', one of the genes that make fibrillin, which results in abnormal connective tissue. It is an autosomal dominant disorder. In about 75% of cases, it is inherited from a parent with the condition, while in about 25% it is a new mutation. Diagnosis is often based on the Ghent criteria, family history and genetic testing (DNA analysis). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marfan Thumb Sign
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with long arms, legs, fingers, and toes. They also typically have exceptionally flexible joints and abnormally curved spines. The most serious complications involve the heart and aorta, with an increased risk of mitral valve prolapse and aortic aneurysm. The lungs, eyes, bones, and the covering of the spinal cord are also commonly affected. The severity of the symptoms is variable. MFS is caused by a mutation in ''FBN1'', one of the genes that make fibrillin, which results in abnormal connective tissue. It is an autosomal dominant disorder. In about 75% of cases, it is inherited from a parent with the condition, while in about 25% it is a new mutation. Diagnosis is often based on the Ghent criteria, family history and genetic testing (DNA analysis). There is no known cure for MFS. Many of those with the disorder have a normal l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incomplete Cleft Lip
{{disambigu ...
Incomplete may refer to: * Unfinished creative work * An incomplete formal system, see Completeness (logic) * Gödel's incompleteness theorems, a specification of logic * "Incomplete" (Bad Religion song), 1994 * "Incomplete" (Sisqó song), 1999 * "Incomplete" (Backstreet Boys song), 2005 * "Incomplete" (Hoobastank song), 2013 * ''Incomplete'' (Nembrionic album), or the title track * ''Incomplete'' (Diaura album), 2015 * Incomplete pass, a gridiron football term * Incomplete abortion (or incomplete miscarriage), a medical term * "Incomplete", a song by Alanis Morissette on the 2008 album ''Flavors of Entanglement'' * “Incomplete”, an episode of ''The Good Doctor'' See also * Completeness (other) Complete may refer to: Logic * Completeness (logic) * Completeness of a theory, the property of a theory that every formula in the theory's language or its negation is provable Mathematics * The completeness of the real numbers, which implies t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominance (genetics)
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second is called recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance, such as incomp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonic Hedgehog Protein
Sonic hedgehog protein (SHH) is a major signaling molecule of embryonic development in humans and animals, encoded by the ''SHH'' gene. This signaling molecule is key in regulating embryonic morphogenesis in all animals. SHH controls organogenesis and the organization of the central nervous system, limbs, digits and many other parts of the body. Sonic hedgehog is a morphogen that patterns the developing embryo using a concentration gradient characterized by the French flag model. This model has a non-uniform distribution of SHH molecules which governs different cell fates according to concentration. Mutations in this gene can cause holoprosencephaly, a failure of splitting in the cerebral hemispheres, as demonstrated in an experiment using SHH knock-out mice in which the forebrain midline failed to develop and instead only a single fused telencephalic vesicle resulted. Sonic hedgehog still plays a role in differentiation, proliferation, and maintenance of adult tissues. Abn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polydactyl Cat
A polydactyl cat is a cat with a congenital physical anomaly called polydactyly (also known as polydactylism or hyperdactyly), which causes the cat to be born with more than the usual number of toes on one or more of its paws. Cats with this genetically inherited trait are most commonly found along the East Coast of North America (in the United States and Canada) and in South West England and Wales. Occurrence Polydactyly is a congenital abnormality that can be inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Some cases of polydactyly are caused by mutations in the ZRS, a genetic enhancer that regulates expression of the sonic hedgehog (SHH) gene in the limb. The SHH protein is an important signalling molecule involved in patterning of many body elements, including limbs and digits. Normal cats have a total of 18 toes, with five toes on each fore paw, and four toes on each hind paw; polydactyl cats may have as many as nine digits on their front or hind paws. Both Jake, a Canadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
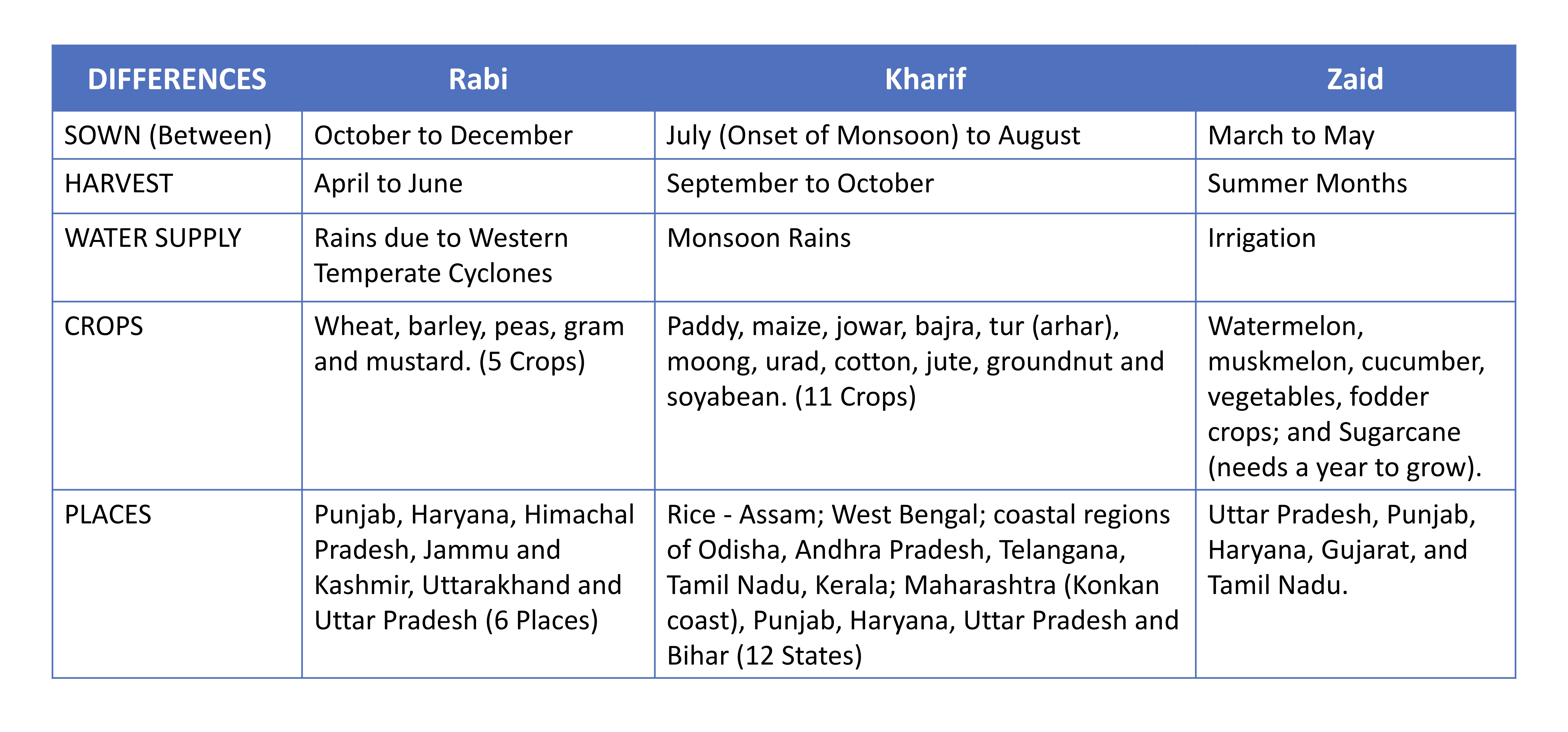
Rabi Crop
Rabi crops or the rabi harvest, also known as winter crops, are crop, agricultural crops that are sown in winter and harvested in the spring in India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh. Complementary to the rabi crop is the kharif crop, which is grown after the rabi and zaid crops are harvested one after another respectively. The word rabi was borrowed from . Etymology The words ''kharif'' and ''rabi'' have their origins in Arabic. These came to be used in India with the ascent of the Mughal Empire, Mughal empire in the Indian subcontinent and have been widely used ever since. The term is derived from the Arabic word for "spring (season), spring", which is used in the Indian subcontinent, where it is the spring harvest (also known as the "winter crop"). Rabi season in India Rabi crops are sown around mid-November, preferably after the monsoon rains are over, and harvesting begins in April / May. The crops are grown either with rainwater that has percolation, percolated into the ground ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorghum
''Sorghum bicolor'', commonly called sorghum () and also known as great millet, broomcorn, guinea corn, durra, imphee, jowar, or milo, is a species in the Poaceae, grass genus ''Sorghum (genus), Sorghum'' cultivated for its grain. The grain is used as food by humans, while the plant is used for animal feed and ethanol production. Sorghum originated in Africa, and is widely cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions. Sorghum is the world's fifth-most important cereal crop after rice, wheat, maize, and barley. Sorghum is typically an annual, but some cultivars are perennial. It grows in clumps that may reach over high. The grain is small, in diameter. Sweet sorghums are cultivars grown for forage, syrup production, and ethanol. They are taller than those grown for grain. Description Sorghum is a large stout grass that grows up to tall. It has large bushy flowerheads or panicles that provide an edible starchy grain with up to 3,000 seeds in each flowerhead. It grows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |