|
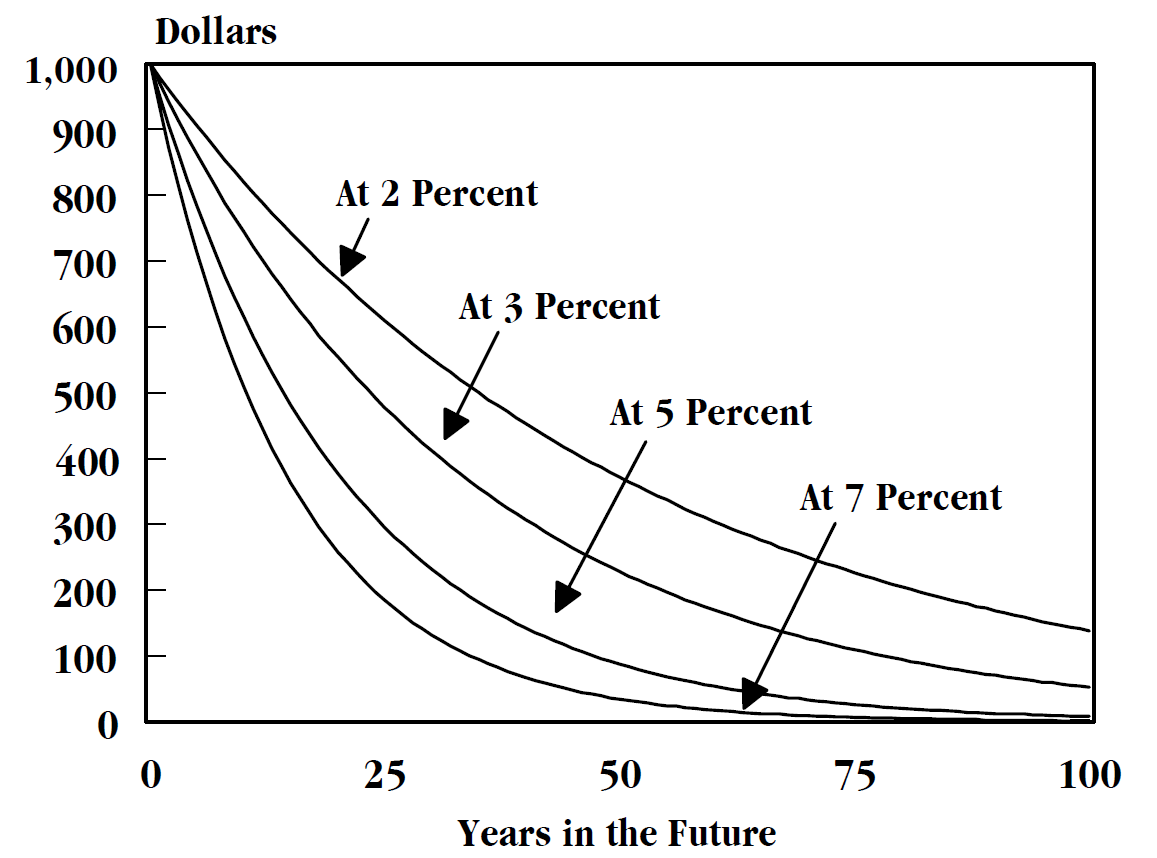
Exponential Discounting
In economics, exponential discounting is a specific form of the discount function, used in the analysis of choice over time (with or without uncertainty). Formally, exponential discounting occurs when total utility is given by U \Bigl(\_^ \Bigr) = \sum_^ \delta^(u(c_t)) where is consumption at time , is the exponential discount factor, and is the instantaneous utility function. In continuous time, exponential discounting is given by U \Bigl(\_^ \Bigl) = \int_^ e^u(c(t))\,dt Exponential discounting implies that the marginal rate of substitution between consumption at any pair of points in time depends only on how far apart those two points are. Exponential discounting is not dynamically inconsistent. A key aspect of the exponential discounting assumption is the property of dynamic consistency— preferences are constant over time. In other words, preferences do not change with the passage of time unless new information is presented. For example, consider an investment o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economy, economies, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and Expenditure, investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: Labour (human activity), labour, Capital (economics), capital, Land (economics), land, and Entrepreneurship, enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact gloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discount Function
In economics, a discount function is used in economic models to describe the weights placed on rewards received at different points in time. For example, if time is discrete and utility is time-separable, with the discount function having a negative first derivative and with (or in continuous time) defined as consumption at time , total utility from an infinite stream of consumption is given by: U\Bigl( \_^\infty \Bigr) = \sum_^\infty Total utility in the continuous-time case is given by: U \Bigl( \_^\infty \Bigr) = \int_^\infty {f(t)u(c(t)) dt} provided that this integral exists. Exponential discounting and hyperbolic discounting are the two most commonly used examples. See also *Discounted utility In economics, discounted utility is the utility (desirability) of some future event, such as consuming a certain amount of a good, as perceived at the present time as opposed to at the time of its occurrence. It is calculated as the present dis ... * Inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intertemporal Choice
In economics, intertemporal choice is the study of the relative value people assign to two or more payoffs at different points in time. This relationship is usually simplified to today and some future date. Intertemporal choice was introduced by Canadian economist John Rae in 1834 in the "Sociological Theory of Capital". Later, Eugen von Böhm-Bawerk in 1889 and Irving Fisher in 1930 elaborated on the model. Fisher model Assumptions of the model # consumer's income is constant # maximization of the utility # anything above the line is out of explanation # investments are generators of savings # any property is indivisible and unchangeable According to this model there are three types of consumption: past, present and future. When making decisions between present and future consumption, the consumer takes his/her previous consumption into account. This decision making is based on an '' indifference map with negative slope'' because if he consumes something today it means th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncertainty
Uncertainty or incertitude refers to situations involving imperfect or unknown information. It applies to predictions of future events, to physical measurements that are already made, or to the unknown, and is particularly relevant for decision-making. Uncertainty arises in partially observable or stochastic environments, as well as due to ignorance, Laziness, indolence, or both. It arises in any number of fields, including insurance, philosophy, physics, statistics, economics, finance, medicine, psychology, sociology, engineering, metrology, meteorology, ecology and information science. Concepts Although the terms are used in various ways among the general public, many specialists in decision theory, statistics and other quantitative fields have defined uncertainty, risk, and their measurement as: Uncertainty The lack of certainty, a state of limited knowledge where it is impossible to exactly describe the existing state, a future outcome, or more than one possible outcome. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility
In economics, utility is a measure of a certain person's satisfaction from a certain state of the world. Over time, the term has been used with at least two meanings. * In a normative context, utility refers to a goal or objective that we wish to maximize, i.e., an objective function. This kind of utility bears a closer resemblance to the original utilitarian concept, developed by moral philosophers such as Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill. * In a descriptive context, the term refers to an ''apparent'' objective function; such a function is revealed by a person's behavior, and specifically by their preferences over lotteries, which can be any quantified choice. The relationship between these two kinds of utility functions has been a source of controversy among both economists and ethicists, with most maintaining that the two are distinct but generally related. Utility function Consider a set of alternatives among which a person has a preference ordering. A utility fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumption (economics)
Consumption refers to the use of resources to fulfill present needs and desires. It is seen in contrast to investing, which is spending for acquisition of ''future'' income. Consumption is a major concept in economics and is also studied in many other social sciences. Different schools of economists define consumption differently. According to mainstream economics, mainstream economists, only the final purchase of newly produced Good (economics), goods and Service (economics), services by individuals for immediate use constitutes consumption, while other types of expenditure — in particular, fixed investment, intermediate consumption, and government spending — are placed in separate categories (see consumer choice). Other economists define consumption much more broadly, as the aggregate of all economic activity that does not entail the design, production and marketing of goods and services (e.g., the selection, adoption, use, disposal and recycling of goods and services). E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discount Factor
In finance, discounting is a mechanism in which a debtor obtains the right to delay payments to a creditor, for a defined period of time, in exchange for a charge or fee.See "Time Value", "Discount", "Discount Yield", "Compound Interest", "Efficient Market", "Market Value" and "Opportunity Cost" in Downes, J. and Goodman, J. E. ''Dictionary of Finance and Investment Terms'', Baron's Financial Guides, 2003. Essentially, the party that owes money in the present purchases the right to delay the payment until some future date.See "Discount", "Compound Interest", "Efficient Markets Hypothesis", "Efficient Resource Allocation", "Pareto-Optimality", "Price", "Price Mechanism" and "Efficient Market" in Black, John, ''Oxford Dictionary of Economics'', Oxford University Press, 2002. This transaction is based on the fact that most people prefer current interest to delayed interest because of mortality effects, impatience effects, and salience effects. The discount, or charge, is the dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Time
In mathematical dynamics, discrete time and continuous time are two alternative frameworks within which variables that evolve over time are modeled. Discrete time Discrete time views values of variables as occurring at distinct, separate "points in time", or equivalently as being unchanged throughout each non-zero region of time ("time period")—that is, time is viewed as a discrete variable. Thus a non-time variable jumps from one value to another as time moves from one time period to the next. This view of time corresponds to a digital clock that gives a fixed reading of 10:37 for a while, and then jumps to a new fixed reading of 10:38, etc. In this framework, each variable of interest is measured once at each time period. The number of measurements between any two time periods is finite. Measurements are typically made at sequential integer values of the variable "time". A discrete signal or discrete-time signal is a time series consisting of a sequence of quantities. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Rate Of Substitution
In economics, the marginal rate of substitution (MRS) is the rate at which a consumer can give up some amount of one good in exchange for another good while maintaining the same level of utility. At equilibrium consumption levels (assuming no externalities), marginal rates of substitution are identical. The marginal rate of substitution is one of the three factors from marginal productivity, the others being marginal rates of transformation and marginal productivity of a factor. As the slope of indifference curve Under the standard assumption of neoclassical economics that goods and services are continuously divisible, the marginal rates of substitution will be the same regardless of the direction of exchange, and will correspond to the slope of an indifference curve (more precisely, to the slope multiplied by −1) passing through the consumption bundle in question, at that point: mathematically, it is the implicit derivative. MRS of X for Y is the amount of Y which a consumer c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Discounting
In economics, hyperbolic discounting is a time inconsistency, time-''inconsistent'' model of delay discounting. It is one of the cornerstones of behavioral economics and its brain-basis is actively being studied by neuroeconomics researchers. According to the discounted utility approach, intertemporal choices are no different from other choices, except that some consequences are delayed and hence must be anticipated and discounted (i.e., reweighted to take into account the delay). Given two similar rewards, humans show a preference for one that arrives in a more prompt timeframe. Humans are said to ''discount'' the value of the later reward, by a factor that increases with the length of the delay. In the financial world, this process is normally modeled in the form of exponential discounting, a time-''consistent'' model of discounting. Many psychological studies have since demonstrated deviations in instinctive preference from the constant discount rate assumed in exponential disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Discounting
In behavioral economics, time preference (or time discounting,. delay discounting, temporal discounting, long-term orientation) is the current relative valuation placed on receiving a good at an earlier date compared with receiving it at a later date. Applications for these preferences include finance, health, and climate change. Time preferences are captured mathematically in the discount function. The main models of discounting include exponential, hyperbolic, and quasi hyperbolic. The higher the time preference, the higher the discount placed on returns receivable or costs payable in the future. Several factors correlate with an individual’s time preference, including age, income, race, risk, and temptation. On a larger level, ideas such as sign effects, sub-additivity, and the elicitation method can influence how people display time preference. Time preference can also inform wider preferences about real world behavior and attitudes, such as pro-social behavior. Cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |