|
Exonuclease V
Exodeoxyribonuclease V (EC 3.1.11.5, RecBCD, Exonuclease V, ''Escherichia coli'' exonuclease V, ''E. coli'' exonuclease V, gene recBC endoenzyme, RecBC deoxyribonuclease, gene recBC DNase, gene recBCD enzymes) is an enzyme of ''E. coli'' that initiates recombinational repair from potentially lethal double strand breaks in DNA which may result from ionizing radiation, replication errors, endonucleases, oxidative damage, and a host of other factors. The RecBCD enzyme is both a helicase that unwinds, or separates the strands of DNA, and a nuclease that makes single-stranded nicks in DNA. It catalyses exonucleolytic cleavage (in the presence of ATP) in either 5′- to 3′- or 3′- to 5′-direction to yield 5′-phosphooligonucleotides. Structure The enzyme complex is composed of three different subunits called RecB, RecC, and RecD and hence the complex is named RecBCD (Figure 1). Before the discovery of the ''recD'' gene, the enzyme was known as “RecBC.” Each subunit is en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-loop
In molecular biology, a displacement loop or D-loop is a DNA structure where the two strands of a double-stranded DNA molecule are separated for a stretch and held apart by a third strand of DNA. An R-loop is similar to a D-loop, but in that case the third strand is RNA rather than DNA. The third strand has a base sequence which is complementary to one of the main strands and pairs with it, thus displacing the other complementary main strand in the region. Within that region the structure is thus a form of triple-stranded DNA. A diagram in the paper introducing the term illustrated the D-loop with a shape resembling a capital "D", where the displaced strand formed the loop of the "D". D-loops occur in a number of particular situations, including in DNA repair, in telomeres, and as a semi-stable structure in mitochondrial circular DNA molecules. In mitochondria Researchers at Caltech discovered in 1971 that the circular mitochondrial DNA from growing cells included a sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EC 3
EC3 can refer to: People * Ethan Carter III (EC3) (born 1983), American professional wrestler Places * EC3, a district in the London EC postcode area Groups, organizations, companies * European Cybercrime Centre * EarthCheck, formerly EC3 Global; international tourism advisory group Transportation * BJEV ''EC3'', a Chinese electric vehicle * KUR ''EC3 class'', a class of steam locomotive * EC-3 radar, Italian WWII radar Other uses * Dolby Digital Plus, also known as EC-3 * Hydrolase enzymes (EC 3); see List of EC numbers (EC 3) See also * ECCC (other) {{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
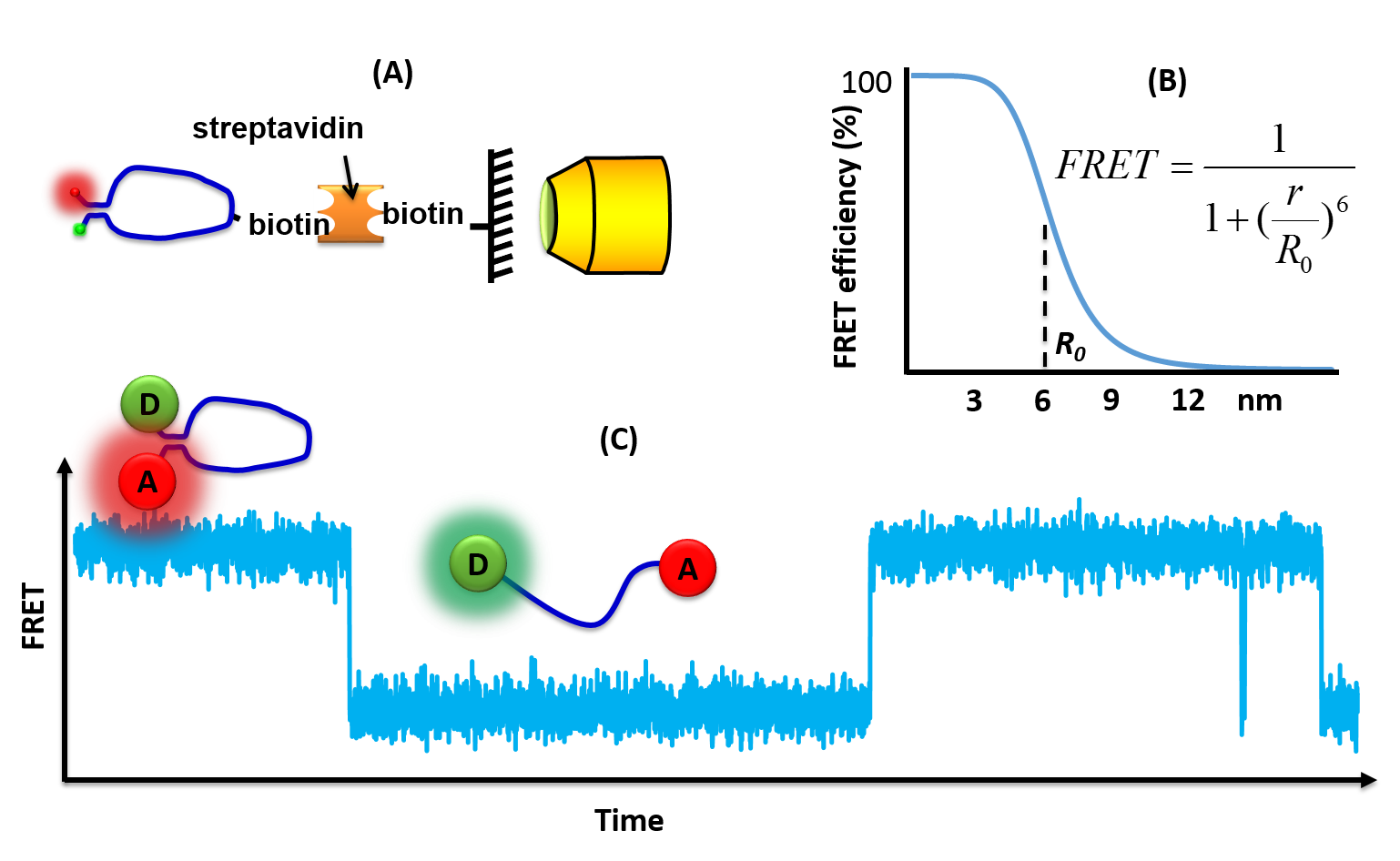
Single-molecule FRET
Single-molecule fluorescence (or Förster) resonance energy transfer (or smFRET) is a Biophysics, biophysical Outline of biophysics#Biophysical techniques, technique used to measure distances at the 1-10 nanometer scale in single molecules, typically biomolecules. It is an application of Förster resonance energy transfer, FRET wherein a pair of donor and acceptor fluorophores are excited and detected at a single molecule level. In contrast to "ensemble FRET" which provides the FRET signal of a high number of molecules, single-molecule FRET is able to resolve the FRET signal of each individual molecule. The variation of the smFRET signal is useful to reveal kinetic information that an ensemble measurement cannot provide, especially when the system is under equilibrium with no ensemble/bulk signal change. Heterogeneity among different molecules can also be observed. This method has been applied in many measurements of intramolecular dynamics such as DNA/RNA/protein folding/unfolding an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Subtilis
''Bacillus subtilis'' (), known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus ''Bacillus'', ''B. subtilis'' is rod-shaped, and can form a tough, protective endospore, allowing it to tolerate extreme environmental conditions. ''B. subtilis'' has historically been classified as an obligate aerobe, though evidence exists that it is a facultative anaerobe. ''B. subtilis'' is considered the best studied Gram-positive bacterium and a model organism to study bacterial chromosome replication and cell differentiation. It is one of the bacterial champions in secreted enzyme production and used on an industrial scale by biotechnology companies. Description ''Bacillus subtilis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, rod-shaped and catalase-positive. It was originally named ''Vibrio subtilis'' by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Recombination
Genetic recombination (also known as genetic reshuffling) is the exchange of genetic material between different organisms which leads to production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent. In eukaryotes, genetic recombination during meiosis can lead to a novel set of genetic information that can be further passed on from parents to offspring. Most recombination occurs naturally and can be classified into two types: (1) ''interchromosomal'' recombination, occurring through independent assortment of alleles whose loci are on different but homologous chromosomes (random orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I); & (2) ''intrachromosomal'' recombination, occurring through crossing over. During meiosis in eukaryotes, genetic recombination involves the pairing of homologous chromosomes. This may be followed by information transfer between the chromosomes. The information transfer may occur without physical exchange (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deinococcus Radiodurans
''Deinococcus radiodurans'' is a bacterium, an extremophile and one of the most radiation-resistant organisms known. It can survive cold, dehydration, vacuum, and acid, and therefore is known as a polyextremophile. ''The Guinness Book Of World Records'' listed it in January 1998 as the world's most radiation-resistant bacterium or lifeform. Several bacteria of comparable radioresistance are known, including some species of the genus '' Chroococcidiopsis'' (phylum cyanobacteria) and some species of '' Rubrobacter'' (phylum Actinomycetota); among the archaea, the species '' Thermococcus gammatolerans'' shows comparable radioresistance. Name and classification The name ''Deinococcus radiodurans'' derives from the Ancient Greek δεινός () and κόκκος () meaning "terrible grain/berry" and the Latin and , meaning "radiation-surviving". The species was formerly called ''Micrococcus radiodurans''. As a consequence of its hardiness, it has been nicknamed “Conan the Bacteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homologous Recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in Cell (biology), cellular organisms but may be also RNA in viruses). Homologous recombination is widely used by cells to accurately DNA repair, repair harmful DNA breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks (DSB), in a process called homologous recombinational repair (HRR). Homologous recombination also produces new combinations of DNA sequences during meiosis, the process by which eukaryotes make gamete cells, like sperm and ovum, egg cells in animals. These new combinations of DNA represent genetic variation in offspring, which in turn enables populations to Adaptation, adapt during the course of evolution. Homologous recombination is also used in horizontal gene transfer to exchange genetic material between different strains and species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RuvABC
RuvABC is a complex of three proteins that mediate branch migration and resolve the Holliday junction created during homologous recombination in bacteria. As such, RuvABC is critical to bacterial DNA repair. RuvA and RuvB bind to the four strand DNA structure formed in the Holliday junction intermediate, and migrate the strands through each other, using a putative spooling mechanism. The RuvAB complex can carry out DNA helicase activity, which helps unwind the duplex DNA. The binding of the RuvC protein to the RuvAB complex is thought to cleave the DNA strands, thereby resolving the Holliday junction. Protein complex The RuvABC is a complex of three proteins that resolve the Holliday junction formed during bacterial homologous recombination. In ''Escherichia coli'', DNA replication forks stall at least once per cell cycle, so that DNA replication must be restarted if the cell is to survive. Replication restart is a multi-step process in ''E. coli'' that requires the sequential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holliday Junction
A Holliday junction is a branched nucleic acid structure that contains four double-stranded arms joined. These arms may adopt one of several conformations depending on buffer salt concentrations and the sequence of nucleobases closest to the junction. The structure is named after Robin Holliday, the molecular biologist who proposed its existence in 1964. In biology, Holliday junctions are a key intermediate in many types of genetic recombination, as well as in double-strand break repair. These junctions usually have a symmetrical sequence and are thus mobile, meaning that the four individual arms may slide through the junction in a specific pattern that largely preserves base pairing. Additionally, four-arm junctions similar to Holliday junctions appear in some functional RNA molecules. Immobile Holliday junctions, with asymmetrical sequences that lock the strands in a specific position, were artificially created by scientists to study their structure as a model for natura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RecA
RecA is a 38 kilodalton protein essential for the repair and maintenance of DNA in bacteria. Structural and functional homologs to RecA have been found in all kingdoms of life. RecA serves as an archetype for this class of homologous DNA repair proteins. The homologous protein is called RAD51 in eukaryotes and RadA in archaea. RecA has multiple activities, all related to DNA repair. In the bacterial SOS response, it functions as a co-protease in the autocatalytic cleavage of the LexA repressor and the λ repressor. Function Homologous recombination The RecA protein binds strongly and in long clusters to ssDNA to form a nucleoprotein filament. The protein has multiple DNA binding sites, and thus can hold a single strand and double strand together. This feature makes it possible to catalyze a DNA synapsis reaction between a DNA double helix and a complementary region of single-stranded DNA. The RecA-ssDNA filament searches for sequence similarity along the dsDNA. A disordere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |