|
Exeter Traction Maintenance Depot
Exeter Traction Maintenance Depot (or Exeter TMD) is a railway Traction Maintenance Depot situated in Exeter, Devon, United Kingdom and is next to the city's main St Davids station. The depot is operated by Great Western Railway and has an allocation of diesel multiple units. The first engine shed on the site opened in 1844 and had an allocation of locomotives until 1963. It was rebuilt in 1976 but a larger three-road maintenance building and staff accommodation was opened in 2021. History An engine shed was opened at Exeter by the Bristol and Exeter Railway when it opened the line to here in 1844. A second facility was added a few years later by the South Devon Railway and the two were combined under the Great Western Railway (GWR) in 1876. The Bristol and Exeter had been worked by the GWR until 1849 but then purchased its own locomotives. Temporary workshops for these were built at Exeter but a permanent facility at Bristol was opened in 1851. When British Railways intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exeter
Exeter ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and the county town of Devon in South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol. In Roman Britain, Exeter was established as the base of Legio II Augusta under the personal command of Vespasian. Exeter became a religious centre in the Middle Ages. Exeter Cathedral, founded in the mid 11th century, became Anglicanism, Anglican in the 16th-century English Reformation. Exeter became an affluent centre for the wool trade, although by the First World War the city was in decline. After the Second World War, much of the city centre was rebuilt and is now a centre for education, business and tourism in Devon and Cornwall. It is home to two of the constituent campuses of the University of Exeter: Streatham Campus, Streatham and St Luke's Campus, St Luke's. The administrative area of Exeter has the status of a non-metropolitan district under the administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
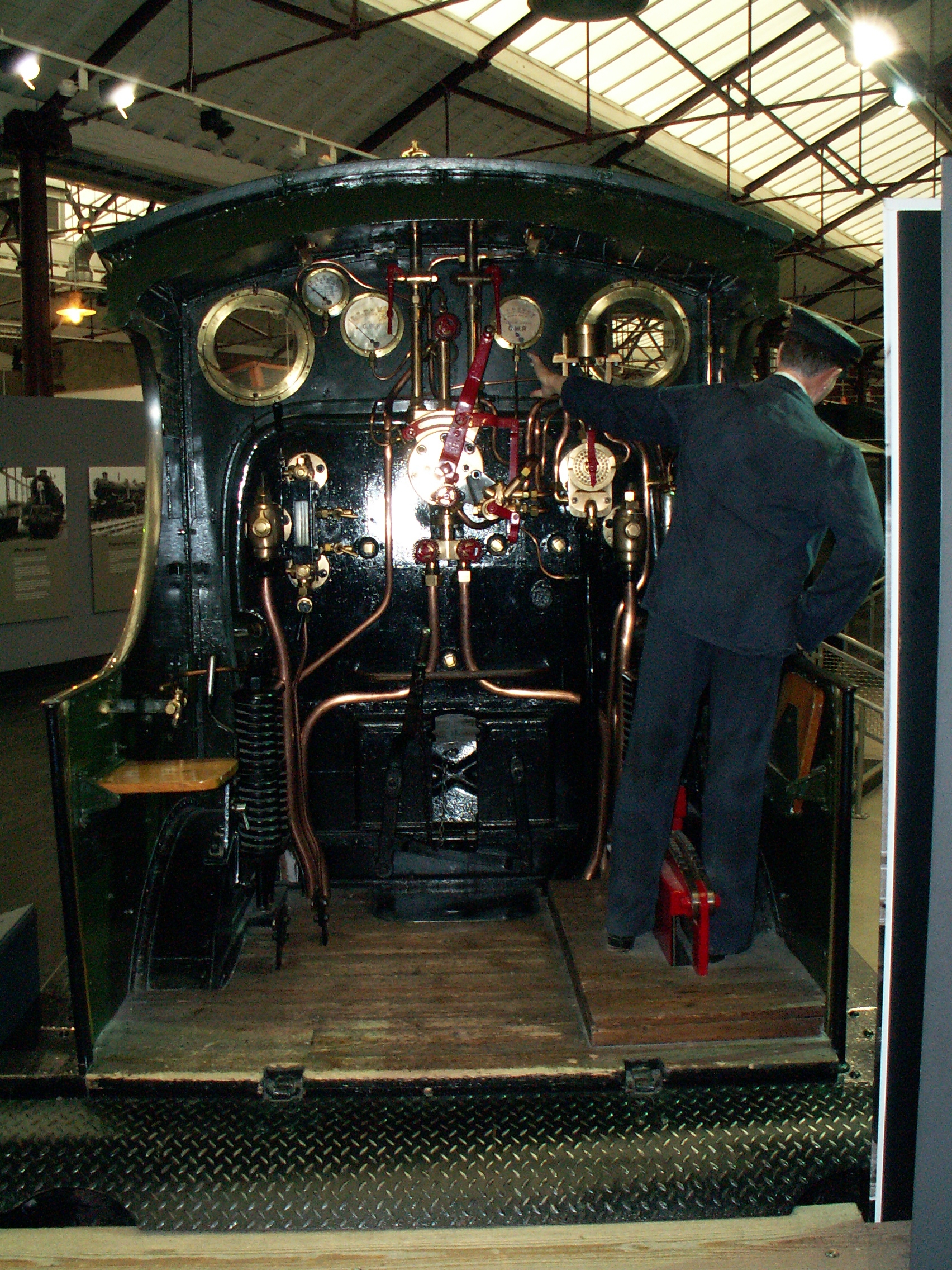
GWR 2301 Class
The Great Western Railway (GWR) 2301 Class or Dean Goods Class is a class of British 0-6-0 steam locomotives. Swindon Works built 260 of these goods locomotives between 1883 and 1899 to a design of William Dean. The 2301 class broke with previous GWR tradition in having inside frames only and changes were made in the boiler design during the period that they were being built. The first twenty engines were originally domeless though all were provided with domed boilers in due course. They were numbered 2301–2360 and 2381–2580 (2361–2380 were of the 2361 class, which were similar visually but had outside frames). Construction Rebuild as 3901 class In 1907, twenty Dean Goods (numbers 2491-2510) were rebuilt as 2-6-2T 'Prairie' tank locos, forming the new 3901 class numbers 3901-3920. War Service In 1917, 62 engines were taken over by the Railway Operating Division and sent to France. 46 of these engines returned to England in the early summer of 1919, but the other 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exmouth Junction
Exmouth Junction is the railway junction where the Exmouth branch line diverges from the London Waterloo to Exeter main line in Exeter, Devon, England. It was for many years the location for one of the largest engine sheds in the former London and South Western Railway. The sidings served the railway's concrete casting factory as well as a goods yard. History The London and South Western Railway (LSWR) opened its main line from to Exeter Queen Street on 19 July 1860, and a branch line from Exeter to on 1 May the following year. The junction of the two lines was from Queen Street, just east of the Blackboy Tunnel. An engine shed was initially provided at Queen Street but as the number of trains serviced grew too many for the cramped site, a new shed was opened at Exmouth Junction in 1887 on land to the north of the main line. It was rebuilt in brick and concrete in the 1920s by the Southern Railway (SR, which had taken over the LSWR in 1923), and at its peak in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Networker (train)
The Networker is a family of multiple-unit passenger trains which operate on the British railway system. They were built in the late 1980s and early 1990s by British Rail Engineering Limited (which became part of ABB in September 1992) and Metro Cammell. The trains were built for the Network SouthEast (NSE) sector of British Rail, which is where their name comes from. History At the launch of Network SouthEast in 1986, the 'Networker' series of trains was announced. It would be a new family of trains that would be introduced as a key part of NSE's wider plan to modernise their network. Specifically, it would replace various older types of trains, typically locomotive-hauled rakes of 'slam-door' carriages.Green and Vincent 2014, pp. 75–85. Unlike previous contemporary rolling stock units in Britain, Networker trains would use aluminium bodies to save weight. Furthermore, electric units would feature modern AC traction motors and air conditioning. The design was to cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol To Taunton Line
Bristol () is a cathedral city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, the most populous city in the region. Built around the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. The county is in the West of England combined authority area, which includes the Greater Bristol area ( eleventh most populous urban area in the United Kingdom) and nearby places such as Bath. Bristol is the second largest city in Southern England, after the capital London. Iron Age hillforts and Roman villas were built near the confluence of the rivers Frome and Avon. Bristol received a royal charter in 1155 and was historically divided between Gloucestershire and Somerset until 1373 when it became a county corporate. From the 13th to the 18th century, Bristol was among the top three English cities, after London, in tax receipts. A major port, Bristol was a starting place for early voyages of exploration to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |