|
Evolutionary Rescue
Evolutionary rescue is a process by which a population—that would have gone extinct in the absence of evolution—persists due to natural selection acting on heritable variation. The term was first used in 1995 by Gomulkiewicz and Holt in the context of a sudden environmental change, but the process was studied long before in the context of continuous environmental change and, especially, drug resistance evolution. Theoretical framework After a sudden change in the environment, evolutionary rescue is predicted to create a U-shaped curve of population dynamics, as the original genotypes, which are unable to replace themselves, are replaced by genotypes that are able to increase in numbers. In a continuously changing environment, evolutionary rescue is predicted to appear as a stable lag of the mean trait value behind a moving environmental optimum, where the rate of evolution and rate of change in the environment are equal. The theory has been reviewed by Alexander et al in 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
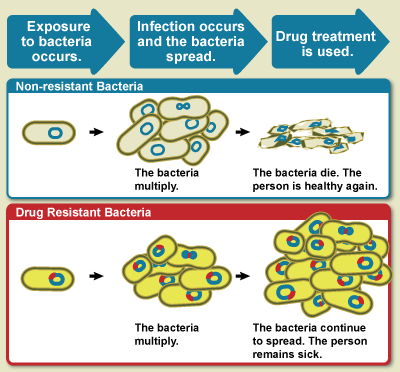
Drug Resistance
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is, resistance has evolved. Antimicrobial resistance and antineoplastic resistance challenge clinical care and drive research. When an organism is resistant to more than one drug, it is said to be multidrug-resistant. The development of antibiotic resistance in particular stems from the drugs targeting only specific bacterial molecules (almost always proteins). Because the drug is ''so'' specific, any mutation in these molecules will interfere with or negate its destructive effect, resulting in antibiotic resistance. Furthermore, there is mounting concern over the abuse of antibiotics in the farming of livestock, which in the European Union alone accounts for three times the volume dispensed to humans – leading to development of super-resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Depiction Of Evolutionary Rescue
A theory is a rational type of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the results of such thinking. The process of contemplative and rational thinking is often associated with such processes as observational study or research. Theories may be scientific, belong to a non-scientific discipline, or no discipline at all. Depending on the context, a theory's assertions might, for example, include generalized explanations of how nature works. The word has its roots in ancient Greek, but in modern use it has taken on several related meanings. In modern science, the term "theory" refers to scientific theories, a well-confirmed type of explanation of nature, made in a way consistent with the scientific method, and fulfilling the criteria required by modern science. Such theories are described in such a way that scientific tests should be able to provide empirical support for it, or empirical contradiction ("falsify") of it. Scientific theories are the most reliable, rigorous, and compreh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Rescue
Genetic rescue is seen as a mitigation strategy designed to restore genetic diversity and reduce extinction risks in small, isolated and frequently inbred populations. It is largely implemented through translocation, a type of demographic rescue and technical migration that adds individuals to a population to prevent its potential extinction. This demographic rescue may be similar to genetic rescue, as each increase population size and/or fitness. This overlap in meaning has led some researchers to consider a more detailed definition for each type of rescue that details 'assessment and documentation of pre- and post-translocation genetic ancestry'. Not every example of genetic rescue is clearly successful and the current definition of genetic rescue does not mandate that the process result in a 'successful' outcome. Despite an ambiguous definition, genetic rescue is viewed positively, with many perceived successes. History The conceptual foundation of genetic rescue can be traced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Review Of Plant Biology
''Annual Review of Plant Biology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Annual Reviews. It was first published in 1950 as the ''Annual Review of Plant Physiology''. Sabeeha Merchant has been the editor since 2005, making her the longest-serving editor in the journal's history after Winslow Briggs (1973–1993). As of 2022, ''Journal Citation Reports'' lists the journal's 2021 impact factor as 28.310, ranking it first of 238 journal titles in the category "Plant Sciences". History Beginning in 1947, the publishing nonprofit Annual Reviews began asking plant physiologists if it would be useful to have an annual journal that published review articles summarizing the recent literature in the field. Responses indicated that this would be very favorable, and the ''Annual Review of Plant Physiology'' published its first volume in 1950. Its founding editor was Daniel I. Arnon. It was thus the seventh journal title to be published by Annual Reviews. Its scope was somewh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Reviews (publisher)
Annual Reviews is an independent, non-profit academic publishing company based in San Mateo, California. As of 2021, it publishes 51 journals of review articles and ''Knowable Magazine'', covering the fields of life, biomedical, physical, and social sciences. Review articles are usually “peer-invited” solicited submissions, often planned one to two years in advance, which go through a peer-review process. The organizational structure has three levels: a volunteer board of directors, editorial committees of experts for each journal, and paid employees. Annual Reviews' stated mission is to synthesize and integrate knowledge "for the progress of science and the benefit of society". The first Annual Reviews journal, the ''Annual Review of Biochemistry'', was published in 1932 under the editorship of Stanford University chemist J. Murray Luck, who wanted to create a resource that provided critical reviews on contemporary research. The second journal was added in 1939. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pesticide Resistance
Pesticide resistance describes the decreased susceptibility of a pest population to a pesticide that was previously effective at controlling the pest. Pest species evolve pesticide resistance via natural selection: the most resistant specimens survive and pass on their acquired heritable changes traits to their offspring.PBS (2001)Pesticide resistance Retrieved on September 15, 2007. If a pest has ''resistance'' then the pesticide lacks ''efficacy'' efficacy and resistance are inversely related. Cases of resistance have been reported in all classes of pests (''i.e.'' crop diseases, weeds, rodents, ''etc.''), with 'crises' in insect control occurring early-on after the introduction of pesticide use in the 20th century. The Insecticide Resistance Action Committee (IRAC) definition of insecticide resistance is ''a heritable change in the sensitivity of a pest population that is reflected in the repeated failure of a product to achieve the expected level of control when used acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Ecology
Evolutionary ecology lies at the intersection of ecology and evolutionary biology. It approaches the study of ecology in a way that explicitly considers the evolutionary histories of species and the interactions between them. Conversely, it can be seen as an approach to the study of evolution that incorporates an understanding of the interactions between the species under consideration. The main subfields of evolutionary ecology are life history evolution, sociobiology (the evolution of social behavior), the evolution of interspecific interactions (e.g. cooperation, predator–prey interactions, parasitism, mutualism) and the evolution of biodiversity and of ecological communities. Evolutionary ecology mostly considers two things: how interactions (both among species and between species and their physical environment) shape species through selection and adaptation, and the consequences of the resulting evolutionary change. Evolutionary models A large part of evolutionary ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |