|
Everun Note
The Everun Note is a subnotebook / netbook computer designed by Raon Digital. At the time of its introduction, it was noted for the performance of its Turion 64 X2 dual core processor, getting high scores in benchmark testing. The Everun Note is also noted for being particularly small, given the relatively high resolution of the screen (1024x600 pixels) and taking the approach of using a touch screen instead of the touchpad that is commonly found on budget netbooks. Retailers in the U.S. are offering the Linux model pre-installed with an unspecified Ubuntu Ubuntu ( ) is a Linux distribution based on Debian and composed mostly of free and open-source software. Ubuntu is officially released in three editions: ''Desktop'', ''Server'', and ''Core'' for Internet of things devices and robots. All the ... release. External links Manufacturer's WebsiteEverun Note Information and SupportForum (Appointed by Manufacturer) References {{reflist, 3 Subnotebooks Netbooks Compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subnotebook
Subnotebook, also called ultraportable, superportable, or mini notebook, was a marketing term for laptop computers that are smaller and lighter than a typical notebook-sized laptop. Types and sizes As typical laptop sizes have decreased over the course of the 2010s, and other distinguishing features have become mainstream, the distinction between regular-size and 'subnotebook' laptops has largely disappeared. To the extent that it still exists, 'subnotebook' could be defined as machines with screen smaller than 13" but with a permanently-attached keyboard intended for two-handed typing. Prior to this convergence, subnotebooks were also distinguished from netbooks and ultra-mobile PCs, based on both size and market position. Classic subnotebooks were smaller than full sized laptops but larger than handheld computers. They were distinguished by smaller screens and bodies and lighter weights relative to contemporaneous laptops. The savings in size and weight were often achieve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
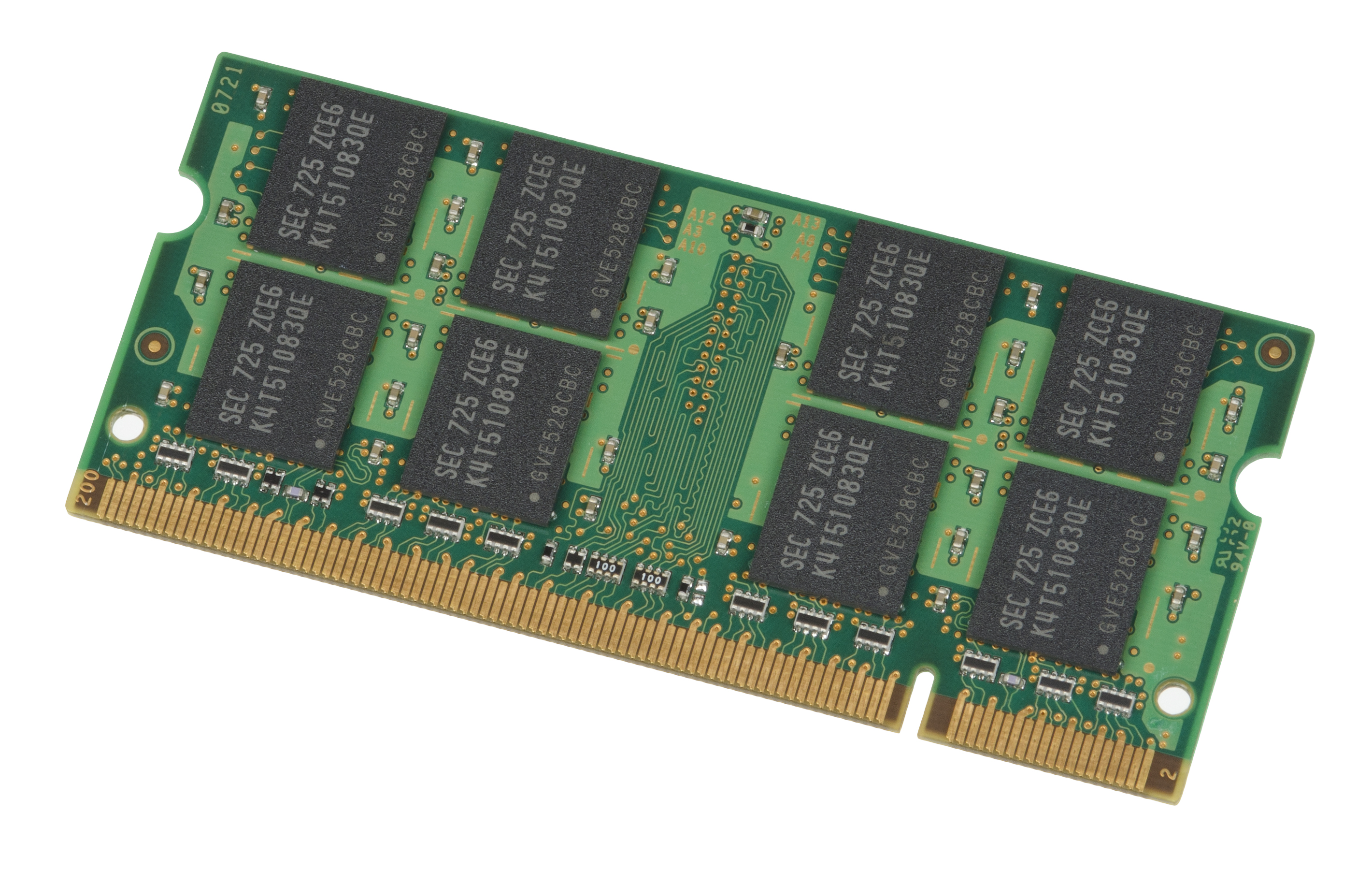
DDR2 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR2 SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) interface. It superseded the original DDR SDRAM specification, and was itself superseded by DDR3 SDRAM (launched in 2007). DDR2 DIMMs are neither forward compatible with DDR3 nor backward compatible with DDR. In addition to double pumping the data bus as in DDR SDRAM (transferring data on the rising and falling edges of the bus clock signal), DDR2 allows higher bus speed and requires lower power by running the internal clock at half the speed of the data bus. The two factors combine to produce a total of four data transfers per internal clock cycle. Since the DDR2 internal clock runs at half the DDR external clock rate, DDR2 memory operating at the same external data bus clock rate as DDR results in DDR2 being able to provide the same bandwidth but with better latency. Alternatively, DDR2 memory operating at twice the external d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subnotebooks
Subnotebook, also called ultraportable, superportable, or mini notebook, was a marketing term for laptop computers that are smaller and lighter than a typical notebook-sized laptop. Types and sizes As typical laptop sizes have decreased over the course of the 2010s, and other distinguishing features have become mainstream, the distinction between regular-size and 'subnotebook' laptops has largely disappeared. To the extent that it still exists, 'subnotebook' could be defined as machines with screen smaller than 13" but with a permanently-attached keyboard intended for two-handed typing. Prior to this convergence, subnotebooks were also distinguished from netbooks and ultra-mobile PCs, based on both size and market position. Classic subnotebooks were smaller than full sized laptops but larger than handheld computers. They were distinguished by smaller screens and bodies and lighter weights relative to contemporaneous laptops. The savings in size and weight were often achieved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Touchpad
A touchpad or trackpad is a pointing device featuring a tactile sensor, a specialized surface that can translate the motion and position of a user's fingers to a relative position on the operating system that is made output to the screen. Touchpads are a common feature of laptop computers as opposed to using a mouse on a desktop, and are also used as a substitute for a mouse where desk space is scarce. Because they vary in size, they can also be found on personal digital assistants (PDAs) and some portable media players. Wireless touchpads are also available as detached accessories. Operation and function Touchpads operate in one of several ways, including capacitive sensing or resistive touchscreen. The most common technology used in the 2010s senses the change of capacitance where a finger touches the pad. Capacitance-based touchpads will not sense the tip of a pencil or other similar ungrounded or non-conducting implements. Fingers insulated by a glove may also be prob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Touch Screen
A touchscreen or touch screen is the assembly of both an input ('touch panel') and output ('display') device. The touch panel is normally layered on the top of an electronic visual display of an information processing system. The display is often an LCD, AMOLED or OLED display while the system is usually used in a laptop, tablet, or smartphone. A user can give input or control the information processing system through simple or multi-touch gestures by touching the screen with a special stylus or one or more fingers. Some touchscreens use ordinary or specially coated gloves to work while others may only work using a special stylus or pen. The user can use the touchscreen to react to what is displayed and, if the software allows, to control how it is displayed; for example, zooming to increase the text size. The touchscreen enables the user to interact directly with what is displayed, rather than using a mouse, touchpad, or other such devices (other than a stylus, which is optio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benchmark (computing)
In computing, a benchmark is the act of running a computer program, a set of programs, or other operations, in order to assess the relative performance of an object, normally by running a number of standard tests and trials against it. The term ''benchmark'' is also commonly utilized for the purposes of elaborately designed benchmarking programs themselves. Benchmarking is usually associated with assessing performance characteristics of computer hardware, for example, the floating point operation performance of a CPU, but there are circumstances when the technique is also applicable to software. Software benchmarks are, for example, run against compilers or database management systems (DBMS). Benchmarks provide a method of comparing the performance of various subsystems across different chip/system architectures. Purpose As computer architecture advanced, it became more difficult to compare the performance of various computer systems simply by looking at their specificatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual Core
A multi-core processor is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit with two or more separate processing units, called cores, each of which reads and executes program instructions. The instructions are ordinary CPU instructions (such as add, move data, and branch) but the single processor can run instructions on separate cores at the same time, increasing overall speed for programs that support multithreading or other parallel computing techniques. Manufacturers typically integrate the cores onto a single integrated circuit die (known as a chip multiprocessor or CMP) or onto multiple dies in a single chip package. The microprocessors currently used in almost all personal computers are multi-core. A multi-core processor implements multiprocessing in a single physical package. Designers may couple cores in a multi-core device tightly or loosely. For example, cores may or may not share caches, and they may implement message passing or shared-memory inter-core comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raon Digital
Raon Digital was a Korea Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...n company that manufactured Ultra-Mobile PCs (UMPCs) such as the Raon Vega, Raon Everun and Everun Note. The company closed in 2009. References External links * Reviews of Raon Vega1 * Review of Everun Note 1 Electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netbook
Netbook was a commonly used term that identified a product class of small and inexpensive laptops which were sold from 2007 to around 2013. These machines were designed primarily as cost-effective tools for consumers to access the Internet from any location before the widespread advent of smartphones, and as a result, generally had lower-end hardware specifications than consumer laptops of the time, being primarily intended as clients for Internet services. While ''netbook'' has fallen out of use, these machines evolved into other products including Google's Chromebook, and mobile devices, particularly tablet computers, often running mobile operating systems such as iOS or Android. At their inception in late 2007, as smaller-than-typical laptop computers optimized for low weight and low cost, netbooks began appearing without certain then-standard laptop features (such as an optical drive), and with less computing power than in full-sized laptops. Later netbooks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subnotebook
Subnotebook, also called ultraportable, superportable, or mini notebook, was a marketing term for laptop computers that are smaller and lighter than a typical notebook-sized laptop. Types and sizes As typical laptop sizes have decreased over the course of the 2010s, and other distinguishing features have become mainstream, the distinction between regular-size and 'subnotebook' laptops has largely disappeared. To the extent that it still exists, 'subnotebook' could be defined as machines with screen smaller than 13" but with a permanently-attached keyboard intended for two-handed typing. Prior to this convergence, subnotebooks were also distinguished from netbooks and ultra-mobile PCs, based on both size and market position. Classic subnotebooks were smaller than full sized laptops but larger than handheld computers. They were distinguished by smaller screens and bodies and lighter weights relative to contemporaneous laptops. The savings in size and weight were often achieve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backlight
A backlight is a form of illumination used in liquid crystal displays (LCDs). As LCDs do not produce light by themselves—unlike, for example, cathode ray tube (CRT), plasma (PDP) or OLED displays—they need illumination ( ambient light or a special light source) to produce a visible image. Backlights illuminate the LCD from the side or back of the display panel, unlike frontlights, which are placed in front of the LCD. Backlights are used in small displays to increase readability in low light conditions such as in wristwatches, and are used in smart phones, computer displays and LCD televisions to produce light in a manner similar to a CRT display. A review of some early backlighting schemes for LCDs is given in a report ''Engineering and Technology History'' by Peter J. Wild. Simple types of LCDs such as in pocket calculators are built without an internal light source, requiring external light sources to convey the display image to the user. Most LCD screens, however, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-emitting Diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. Later developments produced LEDs available in visible, ultraviolet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |