|
Eurotamanduidae
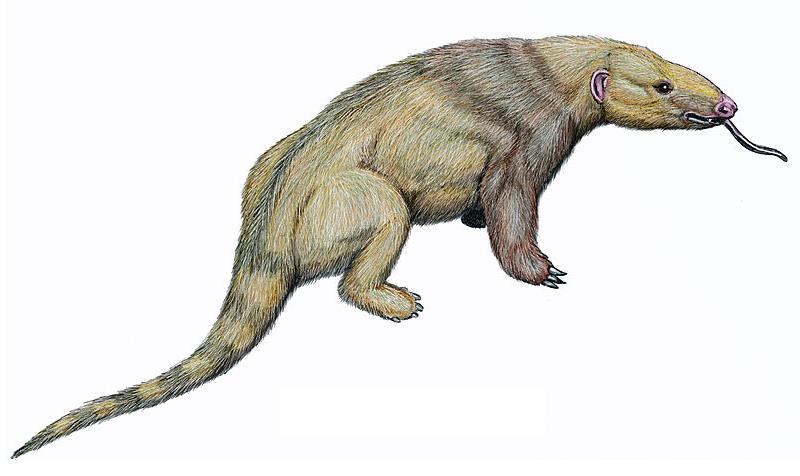
''Eurotamandua'' ("european ''Tamandua''") is an extinct genus of mammal from extinct family Eurotamanduidae that lived during the middle Eocene. A single fossil is known, coming from the Messel Pit in southwestern Germany. ''Eurotamandua'' was about long. Most palaeontologists now classify ''Eurotamandua'' as a pangolin. When its fossils were first discovered, ''Eurotamandua'' was originally thought to be an anteater, as it lacked the characteristic fused-hair scales of other pangolins. ''Eurotamandua'' placement within the pangolins was made primarily because of a lack of the characteristic "xenarthran" joints found in all xenarthrans, including tamanduas. There is still much ambiguity in the taxonomy of all mammals prior to the Eocene, so there is the possibility that ''Eurotamandua'' was a primitive xenarthran. However, this is highly unlikely because all known fossil evidence indicates that xenarthrans existed exclusively in South America from the beginning of the Cenozoic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pholidotamorpha
Pholidotamorpha ("pangolin-like forms") is a clade of placental, mostly ant- and termite-eating mammals that (partially) physically resemble anteaters and armadillos. However, those aforementioned species are now placed in the order Xenarthra, along with sloths; Pholidotamorpha is now classified under the mirorder Ferae, which includes the order Carnivora (carnivorous mammals) and the pangolins (Pholidota) as well as the prehistoric order Palaeanodonta, containing only extinct species. Classification and phylogeny History of taxonomy Both the Pholidota and Palaeanodonta orders were formerly placed with other orders of ant-eating mammals, most notably Xenarthra (armadillos, sloths, anteaters, which they superficially resemble); some palaeontologists, throughout the history of zoology, have placed pangolins and palaeanodonts as a suborder, Pholidota, in the greater order Cimolesta, alongside the extinct family Ernanodontidae as a separate suborder Ernanodonta near it. Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eupholidota
Eupholidota ("true pangolins") is a suborder of pangolins that includes two superfamilies: extant Manoidea and extinct Eomanoidea. Taxonomy * Suborder: Eupholidota (true pangolins) ** Superfamily: Manoidea (pangolins) *** Family: Manidae (pangolins) *** Family: †Patriomanidae *** ''Incertae sedis'' **** Genus: †''Necromanis'' ** Superfamily: † Eomanoidea *** Family: † Eomanidae Phylogeny Phylogenetic position of suborder Eupholidota within order Pholidota. See also * Mammal classification * Pangolin Pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, are mammals of the order Pholidota (). The one extant family, the Manidae, has three genera: '' Manis'', '' Phataginus'', and '' Smutsia''. ''Manis'' comprises four species found in Asia, while ' ... References Pangolins {{mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pholidota Sp
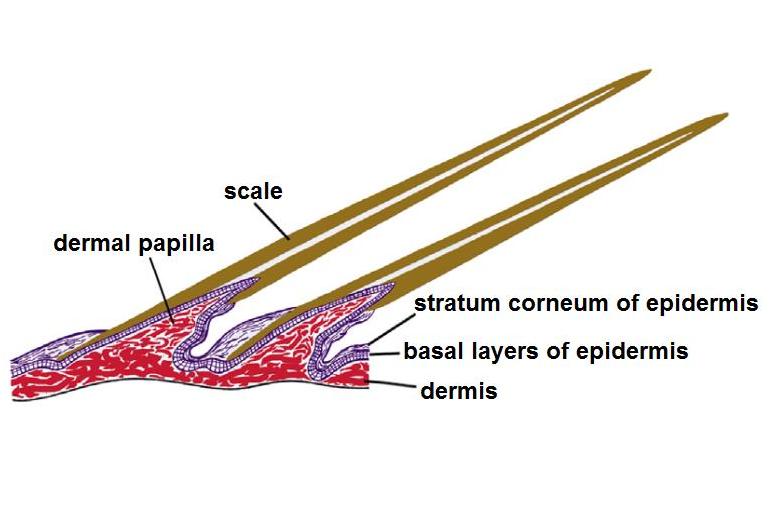
Pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, are mammals of the order Pholidota (). The one extant family, the Manidae, has three genera: ''Manis'', ''Phataginus'', and ''Smutsia''. ''Manis'' comprises four species found in Asia, while ''Phataginus'' and ''Smutsia'' include two species each, all found in sub-Saharan Africa. These species range in size from . Several extinct pangolin species are also known. In September 2023, nine species were reported. Pangolins have large, protective keratin scales, similar in material to fingernails and toenails, covering their skin; they are the only known mammals with this feature. Depending on the species, they live in hollow trees or burrows. Pangolins are nocturnal, and their diet consists of mainly ants and termites, which they capture using their long tongues. They tend to be solitary animals, meeting only to mate and produce a litter of one to three offspring, which they raise for about two years. Pangolins superficially resemble ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangolin
Pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, are mammals of the order Pholidota (). The one extant family, the Manidae, has three genera: '' Manis'', '' Phataginus'', and '' Smutsia''. ''Manis'' comprises four species found in Asia, while ''Phataginus'' and ''Smutsia'' include two species each, all found in sub-Saharan Africa. These species range in size from . Several extinct pangolin species are also known. In September 2023, nine species were reported. Pangolins have large, protective keratin scales, similar in material to fingernails and toenails, covering their skin; they are the only known mammals with this feature. Depending on the species, they live in hollow trees or burrows. Pangolins are nocturnal, and their diet consists of mainly ants and termites, which they capture using their long tongues. They tend to be solitary animals, meeting only to mate and produce a litter of one to three offspring, which they raise for about two years. Pangolins superficially resemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necromanis
''Necromanis'' ("extinct pangolin") is an extinct genus of pangolin from superfamily Manoidea. It lived from the middle Oligocene to middle Miocene in Europe. It was originally placed within family Manidae, but was eventually removed from it as more fossil pholidotids from outside that family were found and studied more extensively (i.e., with the discovery and study of ''Eomanis'' and ''Patriomanis'').Gaudin, Timothy J., Robert J. Emry, and Brandon Pogue. "A new genus and species of pangolin (Mammalia, Pholidota) from the late Eocene of Inner Mongolia, China." Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 26.1 (2006): 146-159. Currently, ''Necromanis'' is placed as ''incertae sedis'' within the pholidotid superfamily Manoidea, together with the families Manidae and Patriomanidae. ''N. quercyi'' was originally placed within ''Teutomanis'' by Ameghino in 1905, but was later subsumed into ''Necromanis''. A new fossil humerus attributed to ''N. franconica'' from Quercy, France lead researchers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eomanis
''Eomanis'' ("dawn pangolin") is the earliest known true (and scaled) pangolin from extinct family Eomanidae (and extinct superfamily Eomanoidea) within suborder Eupholidota. It lived during the Eocene in Europe. ''Eomanis'' fossils found in the Messel Pit in Germany are very similar in size and anatomy to living pangolins of the genus ''Manis'', indicating that pangolins have remained largely unchanged in morphology and behavior for 50 million years. However, unlike modern pangolins, its tail and legs did not bear scales. According to the stomach contents of the excellently preserved Messel specimens, ''Eomanis’'' diet consisted of both insects and plants. Another early mammal discovered in the Messel Pit that was similar in anatomy and likely also had an insectivorous diet was '' Eurotamandua''. Despite its name, ''Eurotamandua'' was almost certainly not a xenarthran because it lacked the characteristic xenarthran joints present in all living and extinct xenarthrans. In add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euromanis
''Euromanis'' ("european pangolin") is one of the earliest known pangolin genera. It lived during the middle Eocene in Europe. ''Euromanis'' fossils found in the Messel Pit in Germany. Unlike modern pangolins, it did not bear scales on its body. Phylogeny Phylogenetic position of genus ''Euromanis'' within order Pholidota. See also * Mammal classification * Pangolin Pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, are mammals of the order Pholidota (). The one extant family, the Manidae, has three genera: '' Manis'', '' Phataginus'', and '' Smutsia''. ''Manis'' comprises four species found in Asia, while ' ... References Prehistoric pangolins Eocene mammals Myrmecophagous mammals Prehistoric placental genera Cenozoic mammals of Europe Fossil taxa described in 1994 {{paleo-mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeanodonta
Palaeanodonta ("ancient toothless animals") is an extinct clade of stem-pangolins. They were insectivorous (Myrmecophagy, myrmecophagous), possibly fossorial, and lived from the middle Paleocene to early Oligocene in North America, Europe and Asia. While the taxonomic grouping of Palaeanodonta has been debated,Averianov, A. O. & Lopatin, A. V. (2014."High-level systematics of placental mammals: Current status of the problem."Biology Bulletin, 41(9), 801–816. it is widely thought that they are a sister group to pangolins. Anatomy Skull Palaeanodonts generally have low and caudally-broad skulls, with notable Lambdoid suture, lambdoid crests and inflated Tympanic part of the temporal bone, bullae and Squamosal bone, squamosals. Teeth Despite the name of the group and contrary to their pangolin relatives, palaeanodonts are known to have had teeth. Early palaeanodonts retained minimal Molar (tooth)#Tribosphenic, tribosphenic post-canines while later species had peglike or othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacheiromys DB152-2
''Metacheiromys'' ("next to ''Cheiromys''") is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct paraphyletic subfamily Metacheiromyinae within extinct paraphyletic family Metacheiromyidae in extinct order Palaeanodonta, that lived in North America (what is now Wyoming) from the early to middle Eocene. Etymology The generic name means "next to ''Cheiromys''" because the scientist who saw the bones mistakenly thought that the animal was a primate with hands like those of the lemurs from genus ''Daubentonia'', whose synonym is ''Cheiromys''. Characteristics of taxa ''Metacheiromys'' was a small creature, and measured around long. It had long claws and a narrow head similar in shape to that of an armadillo or an anteater (though it was actually related to the modern pangolins). The shape of its claws suggests that it probably dug through the soil in search of food, most likely small invertebrates. Unlike modern anteaters or pangolins, it had powerful canine teeth, but only a very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |