|
Euromyth
A euromyth is an exaggerated or invented story about the European Union (EU) and the activities of its institutions, such as purportedly nonsensical EU legislation. Conversely, the same term has been applied by Eurosceptics to purportedly misleading or exaggerated claims by the European Commission, and some assert that the term (in the former sense) is falsely applied to true stories. Debate as to whether a particular claim is true sometimes continues long after the original story appeared. On occasions, Euromyths may arise when the actions of a different European organisation, such as the Council of Europe, are erroneously attributed to the EU.. In 2000, the British government announced a policy of publicly rebutting such myths and accused journalists of failing in their mission to inform. Accusations of distorted or untruthful reporting are most commonly directed at conservative and Eurosceptic sections of the British media. Stories can present the European civil service' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurosceptics
Euroscepticism, also spelled as Euroskepticism or EU-scepticism, is a political position involving criticism of the European Union (EU) and European integration. It ranges from those who oppose some EU institutions and policies and seek reform (''Eurorealism'', ''Eurocritical'', or ''soft Euroscepticism''), to those who oppose EU membership and see the EU as unreformable (''anti-European Unionism'', ''anti-EUism'', or ''hard Euroscepticism''). The opposite of Euroscepticism is known as ''pro-Europeanism''. The main drivers of Euroscepticism have been beliefs that integration undermines national sovereignty and the nation state, that the EU is elitist and lacks democratic legitimacy and transparency, that it is too bureaucratic and wasteful,(Op-Ed that it encourages high levels of immigration, or perceptions that it is a neoliberal organisation serving the big business elite at the expense of the working class, that it is responsible for austerity, and drives privatization. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commission Directive 91/71/EEC
Directive 91/71/EEC is an EU directive that was passed by the European Commission in 1991 regarding the level of sweeteners, flavourings and additives used in foods by states within the European Union and banning foods that did not comply. The directive was repealed in 2011. Regulations The directive required that all foodstuffs containing colouring, additives or flavouring, within member states in the EU had to be identified clearly on the packaging. The directive was an attempt to harmonise the identification of sweeteners and prohibit additives within certain foods. The directive would come into force in 1994, when all foods that did not conform would be banned from sale in the EU. Prawn cocktail crisps One particular Euromyth about the directive was that it would lead to a ban of prawn cocktail-flavoured crisps in the United Kingdom. The source of the myth was a proposal by EU Commissioner Martin Bangemann to ban artificial sweeteners in crisps, thus leading to news repo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fake News
Fake news or information disorder is false or misleading information (misinformation, disinformation, propaganda, and hoaxes) claiming the aesthetics and legitimacy of news. Fake news often has the aim of damaging the reputation of a person or entity,Schlesinger, Robert (April 14, 2017)"Fake news in reality" '' U.S. News & World Report''. or making money through advertising revenue. Although false news has always been spread throughout history, the term ''fake news'' was first used in the 1890s when sensational reports in newspapers were common. Nevertheless, the term does not have a fixed definition and has been applied broadly to any type of false information presented as news. It has also been used by high-profile people to apply to any news unfavorable to them. Further, disinformation involves spreading false information with harmful intent and is sometimes generated and propagated by hostile foreign actors, particularly during elections. In some definitions, fake news i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated population of over 449million as of 2024. The EU is often described as a ''sui generis'' political entity combining characteristics of both a federation and a confederation. Containing 5.5% of the world population in 2023, EU member states generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around €17.935 trillion in 2024, accounting for approximately one sixth of global economic output. Its cornerstone, the European Union Customs Union, Customs Union, paved the way to establishing European Single Market, an internal single market based on standardised European Union law, legal framework and legislation that applies in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
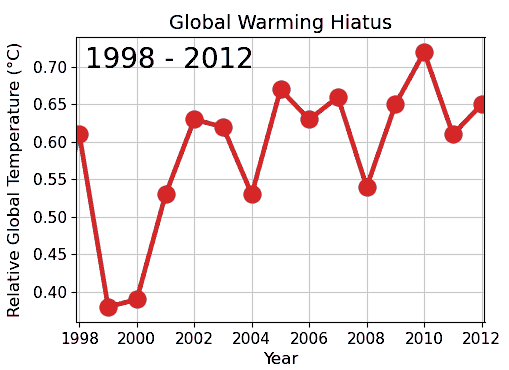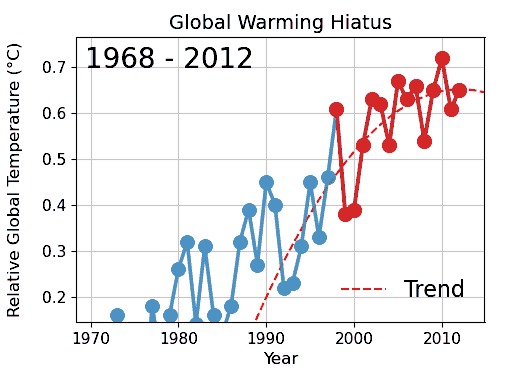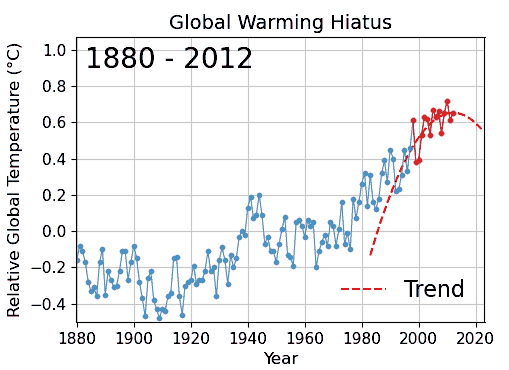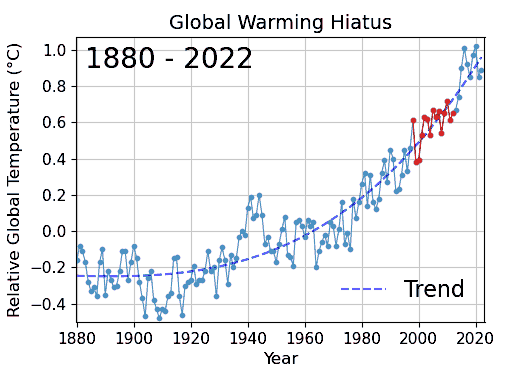
Card Stacking
Cherry picking, suppressing evidence, or the fallacy of incomplete evidence is the act of pointing to individual cases or data that seem to confirm a particular position while ignoring a significant portion of related and similar cases or data that may contradict that position. Cherry picking may be committed intentionally or unintentionally. The term is based on the perceived process of harvesting fruit, such as cherries. The picker would be expected to select only the ripest and healthiest fruits. An observer who sees only the selected fruit may thus wrongly conclude that most, or even all, of the tree's fruit is in a likewise good condition. This can also give a false impression of the quality of the fruit (since it is only a sample and is not a representative sample). A concept sometimes confused with cherry picking is the idea of gathering only the fruit that is easy to harvest, while ignoring other fruit that is higher up on the tree and thus more difficult to obtain (see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Committee For Standardization
The European Committee for Standardization (CEN, ) is a public standards organization whose mission is to foster the economy of the European Single Market and the wider European continent in global trading, the welfare of European citizens and the environment by providing an efficient infrastructure to interested parties for the development, maintenance and distribution of coherent sets of standards and specifications. The CEN was founded in 1961. Its thirty-four national members work together to develop European Standards (ENs) in various sectors to build a European internal market for goods and services and to position Europe in the global economy. CEN is officially recognized as a European standards body by the European Union, European Free Trade Association and the United Kingdom; the other official European standards bodies are the European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization ( CENELEC) and the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). More tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Legend
Urban legend (sometimes modern legend, urban myth, or simply legend) is a genre of folklore concerning stories about an unusual (usually scary) or humorous event that many people believe to be true but largely are not. These legends can be entertaining but often concern mysterious peril or troubling events, such as disappearances and strange objects or entities. Urban legends may confirm moral standards, reflect prejudices, or be a way to make sense of societal anxieties. In the past, urban legends were most often circulated orally, at gatherings and around the Campfire story, campfire for instance. Now, they can be spread by any media, including newspapers, mobile news apps, e-mail, and most often, social media. Some urban legends have passed through the years/decades with only minor changes, in where the time period takes place. Generic urban legends are often altered to suit regional variations, but the lesson or moral generally remains the same. Origin and structure Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin (propaganda)
In public relations and politics, spin is a form of propaganda, achieved through knowingly providing a biased interpretation of an event. While traditional public relations and advertising may manage their presentation of facts, "spin" often implies the use of disingenuous, deceptive, and manipulative tactics. Because of the frequent association between spin and press conferences (especially government press conferences), the room in which these conferences take place is sometimes described as a " spin room". Public relations advisors, pollsters and media consultants who develop deceptive or misleading messages may be referred to as "spin doctors" or "spinmeisters". A standard tactic used in "spinning" is to reframe or modify the perception of an issue or event to reduce any negative impact it might have on public opinion. For example, a company whose top-selling product is found to have a significant safety problem may "reframe" the issue by criticizing the safety of its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reputation Management
Reputation management, refers to the Social influence, influencing, controlling, enhancing, or concealing of an individual's or group's reputation. It is a marketing technique used to modify a person's or a company's reputation in a positive way. The growth of the internet and social media led to growth of reputation management companies, with Search engine results page, search results as a core part of a client's reputation. Online reputation management (ORM) involves overseeing and influencing the search engine results related to products and services. Ethical grey areas include Mug shot publishing industry, mug shot removal sites, astroturfing customer review Website, sites, censoring complaints, and using search engine optimization tactics to game the system, influence results. In other cases, the ethical lines are clear; some reputation management companies are closely connected to websites that publish unverified and libelous statements about people. Such unethical companies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-truth Politics
Post-truth politics, also described as post-factual politics or post-reality politics, amidst varying academic and dictionary definitions of the term, refer to a recent historical period where political culture is marked by public anxiety about what claims can be publicly accepted facts. It suggests that the public (not scientific or philosophical) distinction between truth and Deception, falsity—as well as honesty and Lie, lying—have become a focal concern of public life, and are viewed by popular commentators and academic researchers alike as having a consequential role in how politics operates in the early 21st century. It is regarded as especially being influenced by the arrival of new communication and media technologies. Popularized as a term in news media and a dictionary definition, post-truth has developed from a short-hand label for the abundance and influence of misleading or false political claims into a concept empirically studied and theorized by academic resear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Apathy
In political science, political apathy is a lack of interest or apathy towards politics. This includes voter apathy, information apathy and lack of interest in elections, political events, public meetings, and voting. Voter apathy is a lack of interest among voters in the elections of representative democracies. Political apathy or lack of interest is often cited as a cause of low turnout among eligible voters in jurisdictions where voting is optional, and the donkey vote where voting is compulsory. This phenomenon occurs to some extent across all countries or entities where citizens are able to vote. Political apathy has led to increased concerns regarding representative democracies because election results do not encompass the entire population who are eligible to vote. Political alienation Political apathy is sometimes considered distinct from political alienation, "the sense that voters feel like the political system does not work for them and any attempt to influence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |