|
Eupholus Chevrolati
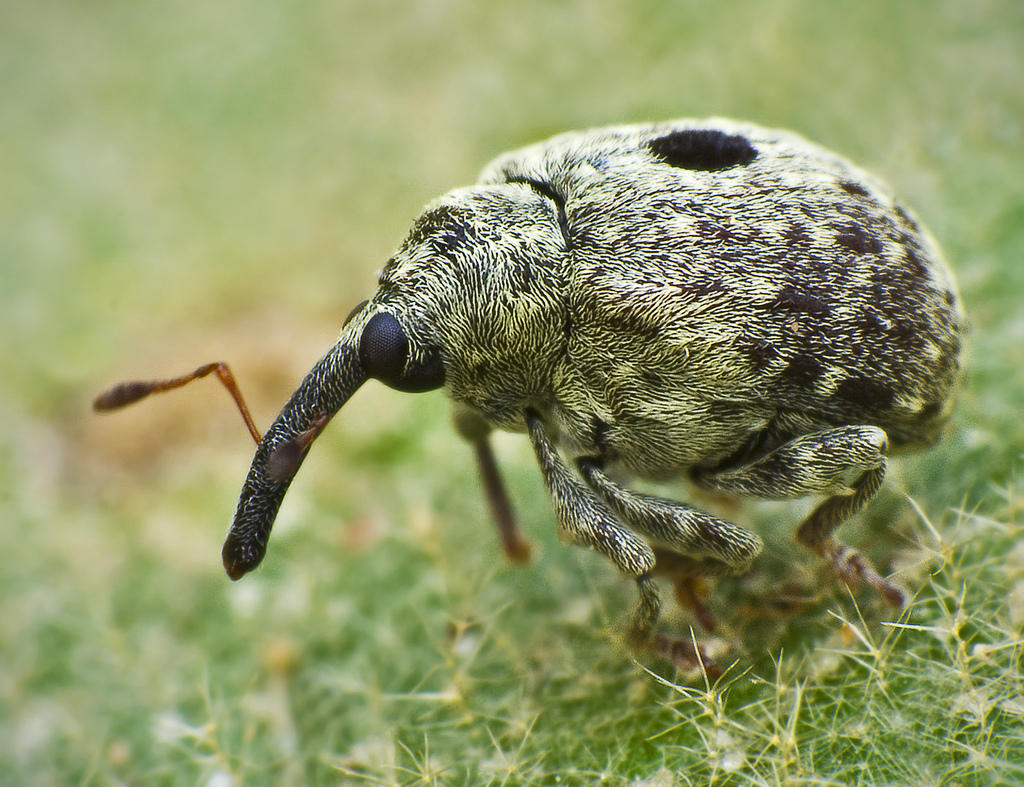
''Eupholus chevrolati'' is a species of beetle belonging to the family Curculionidae. Description ''Eupholus chevrolati'' can reach a length of about . The basic colour of this quite variable species is metallic blue-green, with some transversal irregular black bands along the elytra. The blue-green colour derives from very small scales. The top of rostrum and the end of the antennae are black. Distribution This species can be found in Aru Islands (Indonesia) Etymology The name honours the French entomologist Louis Alexandre Auguste Chevrolat Louis Alexandre Auguste Chevrolat was a French entomologist, born 29 March 1799 in Paris and died 16 December 1884 in Paris. In government service in Paris, this amateur entomologist studied mainly beetles and birds. He published nearly 250 note ... References Universal Biological IndexerEupholus chevrolatiWorld Field Guide Entiminae Insects of Indonesia Fauna of the Aru Islands Fauna of the Lesser Sunda Islands Taxa named b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
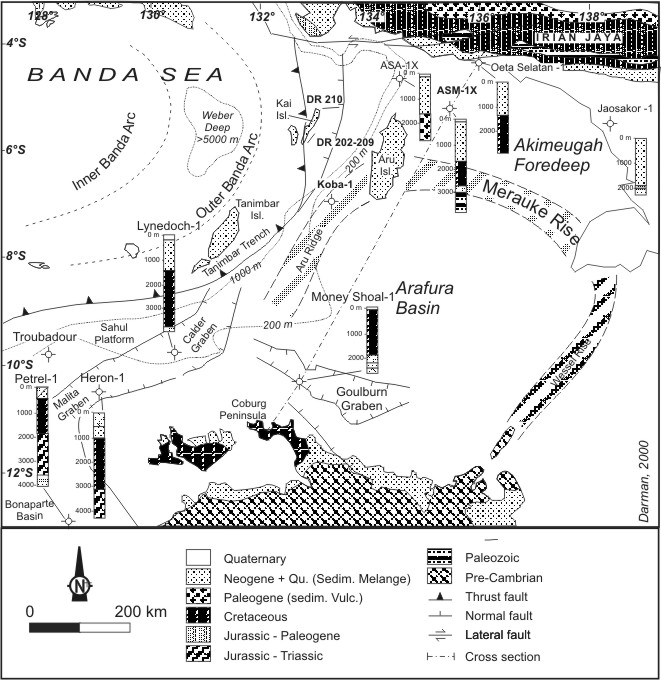
Aru Islands
The Aru Islands Regency ( id, Kabupaten Kepulauan Aru) is a group of about 95 low-lying islands in the Maluku Islands of eastern Indonesia. It also forms a regency of Maluku Province, with a land area of . At the 2011 Census the Regency had a population of 84,138;Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011. the 2020 Census produced a total of 102,237. Some sources regard the archipelago as part of Asia, while others regard it as part of Melanesia. Administration At the time of the 2010 Census, the regency was divided into seven districts (''kecamatan''), but subsequently an additional three districts have been created by the splitting of existing districts. The districts are tabulated below with their areas (in km2) and their populations at the 2010 Census and 2020 Census. The table also includes the locations of the district administrative centres, the number of villages (''desa'') in each district, and its postal code. Notes: (a) the 2010 population of Aru Utara Timur Batuley and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea. Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the 14th-largest country by area, at . With over 275 million people, Indonesia is the world's fourth-most populous country and the most populous Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population. Indonesia is a presidential republic with an elected legislature. It has 38 provinces, of which nine have special status. The country's capital, Jakarta, is the world's second-most populous urban area. Indonesia shares land borders with Papua New Guinea, East Timor, and the East Malaysia, eastern part of Malaysia, as well as maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Australia, Palau, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Félix Édouard Guérin-Méneville
Félix Édouard Guérin-Méneville, also known as F. E. Guerin, (12 October 1799, in Toulon – 26 January 1874, in Paris) was a French entomologist. Life and work Guérin-Méneville changed his surname from Guérin in 1836. He was the author of the illustrated work ''Iconographie du Règne Animal de G. Cuvier 1829–1844'', a complement to the work of the zoologists Georges Cuvier and Pierre André Latreille, '' Le Règne Animal'', which illustrated only a selection of the animals covered. Cuvier was delighted with the work, saying that it would be very useful to readers, and that the illustrations were "as accurate as they were elegant". He also introduced silkworm The domestic silk moth (''Bombyx mori''), is an insect from the moth family Bombycidae. It is the closest relative of ''Bombyx mandarina'', the wild silk moth. The silkworm is the larva or caterpillar of a silk moth. It is an economically imp ...s to France, so they could be bred for the production of silk. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curculionidae
The Curculionidae are a family of weevils, commonly called snout beetles or true weevils. They are one of the largest animal families, with 6,800 genera and 83,000 species described worldwide. They are the sister group to the family Brentidae. They include the bark beetles as the subfamily Scolytinae, which are modified in shape in accordance with their wood-boring lifestyle. They do not much resemble other weevils, so they were traditionally considered a distinct family, Scolytidae. The family also includes the ambrosia beetles, of which the present-day subfamily Platypodinae was formerly considered the distinct family Platypodidae. Description Adult Curculionidae can be recognised by the well-developed, downwards-curved snout (Rostrum (anatomy), rostrum) possessed by many species, though the rostrum is sometimes short (e.g. Entiminae). They have elbowed Antenna (biology), antennae that end in clubs, and the first antennal segment often fits into a groove in the side of the ros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Alexandre Auguste Chevrolat
Louis Alexandre Auguste Chevrolat was a French entomologist, born 29 March 1799 in Paris and died 16 December 1884 in Paris. In government service in Paris, this amateur entomologist studied mainly beetles and birds. He published nearly 250 notes and papers and was the author of more than 2,000 species. He was one of the founders of the Société entomologique de France The Société entomologique de France, or French Entomological Society, is devoted to the study of insects. The society was founded in 1832 in Paris, France. The society was created by eighteen Parisian entomologists on January 31, 1832. The first ... in 1832. On his death, his collection was dispersed. Part of his collection is now in the Natural History Museum in London along with some manuscripts. Works (Selection) * 1833a. Description de Buprestis analis. ''Magasin de Zoologie'' 1833. Insectes, Nr. 60, 1 color plat* 1833b. ''Coléoptères du Mexique'', Fascicle 5 pp. Oct. 1833. Strasbourg. * 1834. ''Colé ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entiminae
The Entiminae are a large subfamily in the weevil family Curculionidae, containing most of the short-nosed weevils, including such genera as '' Entimus'', '' Otiorhynchus'', '' Phyllobius'', '' Sitona'', and '' Pachyrrhynchus''. In comparison with their stunning diversity, only a few of these weevils are notorious pests of major economic importance. Entimines are commonly encountered in the field, including urban environments, and abundant in entomological collections. Diversity There are over 12000 described species worldwide, distributed in over 1370 genera, nearly 14000 by more recent counts. Most tribes are represented in only one biogeographic region of the world. The current classification within the subfamily has been recognized as artificial rather than reflecting natural groups. General morphology Besides the shape of their broad and short rostrum, most entimines are easily recognized by the presence of a mandibular scar that appears when a deciduous process falls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insects Of Indonesia
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes and one pair of antennae. Their blood is not totally contained in vessels; some circulates in an open cavity known as the haemocoel. Insects are the most diverse group of animals; they include more than a million described species and represent more than half of all known living organisms. The total number of extant species is estimated at between six and ten million; In: potentially over 90% of the animal life forms on Earth are insects. Insects may be found in nearly all environments, although only a small number of species reside in the oceans, which are dominated by another arthropod group, crustaceans, which recent research has indicated insects are nested within. Nearly all insects hatch from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna Of The Aru Islands
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is ''funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as ''biota''. Zoologists and paleontologists use ''fauna'' to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. The study of animals of a particular region is called faunistics. Etymology ''Fauna'' comes from the name Fauna, a Roman goddess of earth and fertility, the Roman god Faunus, and the related forest spirits called Fauns. All three words are cognates of the name of the Greek god Pan, and ''panis'' is the Greek equivalent of fauna. ''Fauna'' is also the word for a book that catalogues the animals in such a manner. The term was first used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Félix Édouard Guérin-Méneville
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |