|
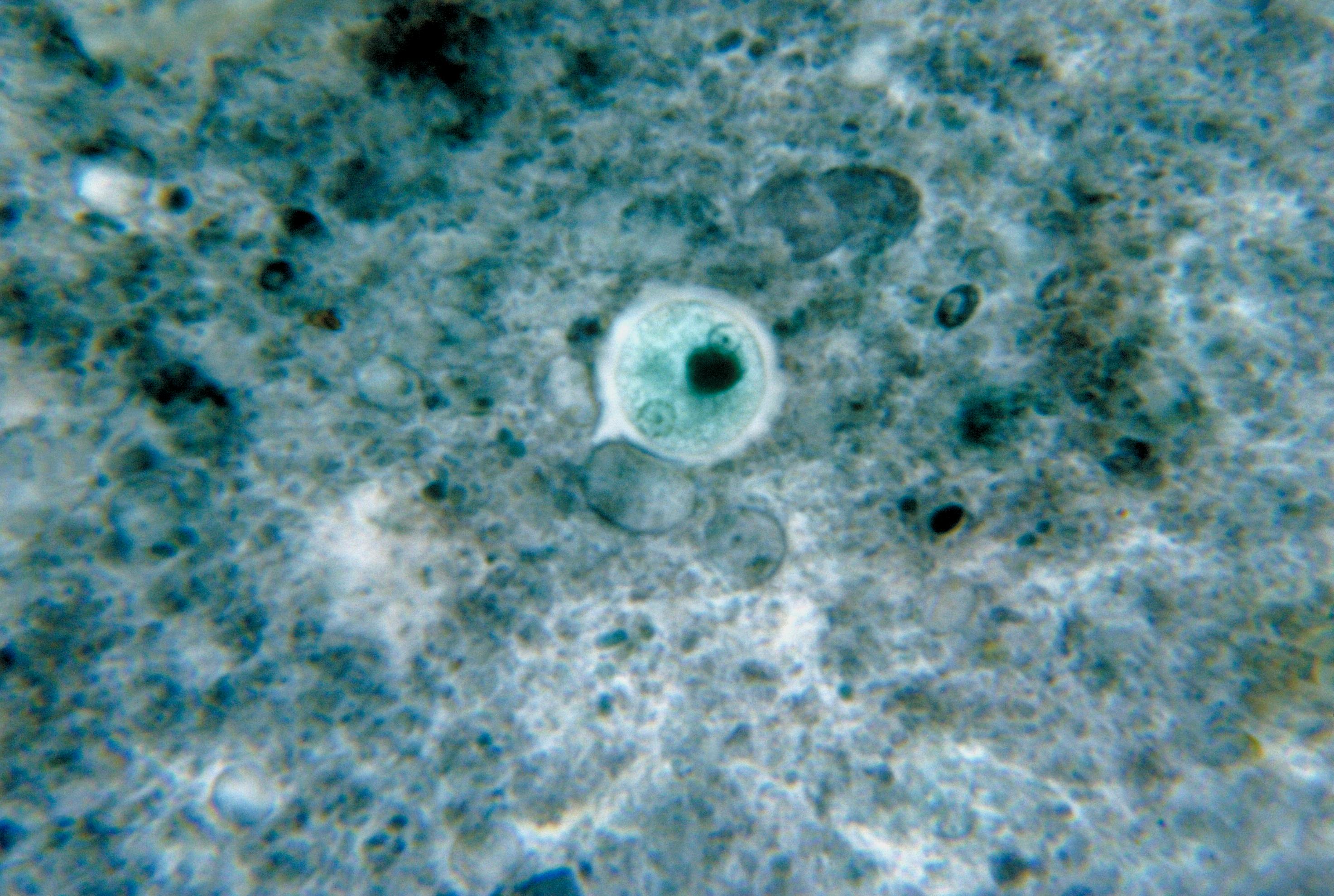
Euglena Viridis
''Euglena viridis'' is a single-celled species of euglenoid, a type of microalgae. It is one of the oldest-known species of ''Euglena'', and was first seen by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1764. It is found in freshwater habitats worldwide. ''Euglena viridis'', along with other ''Euglena'' species, are well-studied. Cells of ''E. viridis'' have a secondary chloroplast. The chloroplast is bounded by three layers of membrane without a nucleomorph. Taxonomy ''Euglena viridis'' is one of the first ''Euglena'' species named when Ehrenberg established the genus ''Euglena''. ''Euglena viridis'' is also the type species of this genus. The whole group of Euglenozoa was originally placed in a group called Excavata. However, Excavata has been thought not monophyletic and is divided into several groups. Now, Euglenozoa is placed below a group in Discoba. Phylogeny According to molecular evidence, phylogenetic relationships between ''Euglena viridis'' and its close relatives are as follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg (19 April 1795 – 27 June 1876) was a German Natural history, naturalist, zoologist, Botany, botanist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopy, microscopist. He is considered to be one of the most famous and productive scientists of his time. Early collections The son of a judge, Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg was born in Delitzsch, near Leipzig. He first studied theology at the University of Leipzig, then medicine and natural sciences in Humboldt University of Berlin, Berlin and became a friend of the famous List of explorers, explorer Alexander von Humboldt. In 1818, he completed his doctoral dissertation on fungi, ''Sylvae mycologicae Berolinenses.'' In 1820–1825, on a scientific expedition to the Middle East with his friend Wilhelm Hemprich, he collected thousands of specimens of plants and animals. He investigated parts of Egypt, the Libyan Desert, the Nile, Nile valley and the northern coasts of the Red Sea, where he made a special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagella
A flagellum (; : flagella) (Latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hair-like appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores ( zoospores), and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are known as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium '' Helicobacter pylori'', for example, uses its flagella to propel itself through the stomach to reach the mucous lining where it may colonise the epithelium and potentially cause gastritis, and ulcers – a risk factor for stomach cancer. In some swarming bacteria, the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota, the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means " whip" to describe its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euglena Pseudoviridis
''Euglena'' is a genus of single-celled, flagellate eukaryotes. It is the best-known and most widely studied member of the class Euglenoidea, a diverse group containing some 54 genera and at least 200 species. Species of ''Euglena'' are found in fresh water and salt water. They are often abundant in quiet inland waters where they may bloom in numbers sufficient to color the surface of ponds and ditches green ('' E. viridis'') or red ('' E. sanguinea''). The species ''Euglena gracilis'' has been used extensively in the laboratory as a model organism. Most species of ''Euglena'' have photosynthesizing chloroplasts within the body of the cell, which enable them to feed by autotrophy, like plants. However, they can also take nourishment heterotrophically, like animals. Since ''Euglena'' have features of both animals and plants, early taxonomists, working within the Linnaean two-kingdom system of biological classification, found them difficult to classify. It was the quest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister Species
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree. Definition The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram: Taxon A and taxon B are sister groups to each other. Taxa A and B, together with any other extant or extinct descendants of their most recent common ancestor (MRCA), form a monophyletic group, the clade AB. Clade AB and taxon C are also sister groups. Taxa A, B, and C, together with all other descendants of their MRCA form the clade ABC. The whole clade ABC is itself a subtree of a larger tree which offers yet more sister group relationships, both among the leaves and among larger, more deeply rooted clades. The tree structure shown connects through its root to the rest of the universal tree of life. In cladistic standards, taxa A, B, and C may represent specimens, species, genera, or any other taxonomic units. If A and B are at the same taxonomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutral Red
Neutral red (toluylene red, Basic Red 5, or C.I. 50040) is a eurhodin dye used for staining in histology. It stains lysosomes red. It is used as a general stain in histology, as a counterstain in combination with other dyes, and for many staining methods. Together with Janus Green B, it is used to stain embryonal tissues and supravital staining of blood. It can be used for staining the Golgi apparatus in cells and Nissl granules in neurons. In microbiology, it is used in the MacConkey agar to differentiate bacteria for lactose fermentation.Neutral redcan be used as a vital stain. The Neutral Red Cytotoxicity Assay was first developed by Ellen Borenfreund in 1984. In the Neutral Red Assay live cells incorporate neutral red into their lysosomes. As cells begin to die, their ability to incorporate neutral red diminishes. Thus, loss of neutral red uptake corresponds to loss of cell viability. The neutral red is also used to stain cell cultures for plate titration of viruses. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euglena Cantabrica
''Euglena'' is a genus of single-celled, flagellate eukaryotes. It is the best-known and most widely studied member of the class Euglenoidea, a diverse group containing some 54 genera and at least 200 species. Species of ''Euglena'' are found in fresh water and salt water. They are often abundant in quiet inland waters where they may bloom in numbers sufficient to color the surface of ponds and ditches green ('' E. viridis'') or red ('' E. sanguinea''). The species ''Euglena gracilis'' has been used extensively in the laboratory as a model organism. Most species of ''Euglena'' have photosynthesizing chloroplasts within the body of the cell, which enable them to feed by autotrophy, like plants. However, they can also take nourishment heterotrophically, like animals. Since ''Euglena'' have features of both animals and plants, early taxonomists, working within the Linnaean two-kingdom system of biological classification, found them difficult to classify. It was the quest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbial Cyst
A microbial cyst is a resting or dormant stage of a microorganism, that can be thought of as a state of suspended animation in which the metabolic processes of the cell are slowed and the cell ceases all activities like feeding and locomotion. Many groups of single-celled, microscopic organisms, or microbes, possess the ability to enter this dormant state. Encystment, the process of cyst formation, can function as a method for dispersal and as a way for an organism to survive in unfavorable environmental conditions. These two functions can be combined when a microbe needs to be able to survive harsh conditions between habitable environments (such as between hosts) in order to disperse. Cysts can also be sites for nuclear reorganization and cell division, and in parasitic species they are often the infectious stage between hosts. When the encysted microbe reaches an environment favorable to its growth and survival, the cyst wall breaks down by a process known as excystation. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaboly
Spirocuta () is a clade of euglenids, single-celled eukaryotes or protists belonging to the phylum Euglenozoa. They are distinguished from other euglenids by active deformation of their cell shape, a process called euglenid motion or metaboly. This is made possible by a high number of spirally arranged protein strips that run below their cell membrane and confer the cell with flexibility. These strips compose the helicoidal pellicle (biology), pellicle, a trait referenced by the alternative name Helicales. Description Spirocuta is a group of flagellates, unicellular eukaryotes or protists with one or two flagella for locomotion in the anterior region of the cell. The move through a gliding motility, gliding motion in contact with the substrate to propel the cell forward. Like other members of the Euglenida, their cells are lined by a pellicle (biology), pellicle composed of proteinaceous strips that interlock with each other, and are spirally arranged underneath the cell membran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyespot Apparatus
The eyespot apparatus (or '' stigma'') is a photoreceptive organelle found in the flagellate or (motile) cells of green algae and other unicellular photosynthetic organisms such as euglenids. It allows the cells to sense light direction and intensity and respond to it, prompting the organism to either swim towards the light (positive phototaxis), or away from it (negative phototaxis). A related response ("photoshock" or photophobic response) occurs when cells are briefly exposed to high light intensity, causing the cell to stop, briefly swim backwards, then change swimming direction. Eyespot-mediated light perception helps the cells in finding an environment with optimal light conditions for photosynthesis. Eyespots are the simplest and most common "eyes" found in nature, composed of photoreceptors and areas of bright orange-red red pigment granules. Signals relayed from the eyespot photoreceptors result in alteration of the beating pattern of the flagella, generating a photo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramylon
Paramylon is a carbohydrate similar to starch. The chloroplasts found in ''Euglena'' contain chlorophyll which aids in the synthesis of carbohydrates to be stored as starch granules and paramylon. Overview Paramylon is made in the pyrenoids of ''Euglena''. The euglenoids have chlorophylls a and b and they store their photosynthate in an unusual form called paramylon starch, a β-1,3 polymer of glucose. The paramylon is stored in rod like bodies throughout the cytoplasm, called paramylon bodies, which are often visible as colorless or white particles in light microscopy. Their shape is often characteristic of the ''Euglena'' species that produces them. Paramylon is also reportedly made in granuales by Pavlovophyceae haptophytes. Paramylon was named and first described in detail by Johann Gottlieb Johann Gottlieb (February 15, 1815 – March 4, 1875) was an Austrian chemist who first synthesized Propionic acid. He is also known for describing and naming Paramylon. Biog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |