|
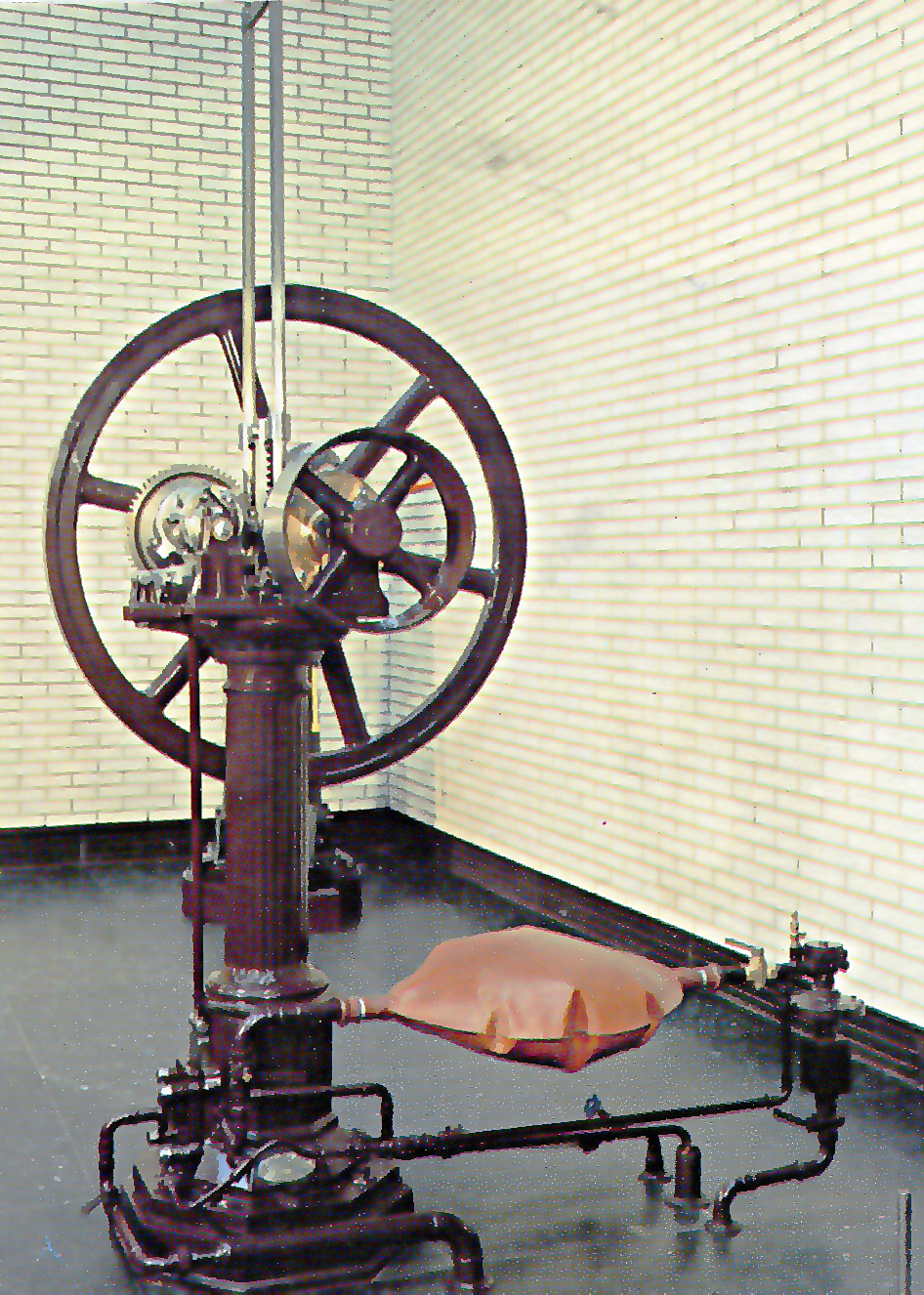
Eugenio Barsanti
Eugenio Barsanti (12 October 1821 – 19 April 1864), also named Nicolò, was an Italian engineer and Catholic priest who, together with Felice Matteucci, invented the first internal combustion engine in 1853. Their patent request was granted in London on June 12, 1854, and published in London's ''Morning Journal'' under the title "Specification of Eugene Barsanti and Felix Matteucci, Obtaining Motive Power by the Explosion of Gasses", as documented by the Fondazione Barsanti e Matteucci. Biography Barsanti was born in Pietrasanta, Grand Duchy of Tuscany, Tuscany. Lean and short of stature, he studied in a Catholic scientific-oriented institute near Lucca, in Tuscany, and entered the novitiate of the Piarist Fathers or Scolopi, who were known for being open to scientific study, in Florence in 1838. In 1841 Barsanti began teaching in the ''Collegio San Michele'', situated in Volterra. Here, during a lecture describing the explosion of mixed hydrogen and air, he realised the poten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Cockerill (industrialist)
John Cockerill (3 August 1790 – 9 June 1840) was an English-born industrialist who became a prominent businessman in Belgium. Born at Haslingden, Lancashire, England, he was brought by his father (British entrepreneur William Cockerill) to the Liège region, where he continued the family tradition of building wool-processing machinery. He founded an ironworks named John Cockerill & Cie. (English: John Cockerill & Company). Life and career At the age of twelve, John Cockerill was brought to Verviers (subsequently part of Belgium) by his father William Cockerill, who was successful as a machine builder there. In 1807, aged 17, he and his brother Charles James Cockerill took over the management of a factory in Liege. Their father retired in 1813, leaving the management of his business to his sons.Chamber's Edinburgh Journal, Vol.8 In September 1813, he married Jeanne Frédérique Pastor, the same day her sister Caroline married Charles James Cockerill. After the victory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1821 Births
Events January–March * January 21 – Peter I Island in the Antarctic is first sighted, by Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen. * January 26 – Congress of Laibach convenes to deal with outstanding international issues, particularly the outbreak of a revolution in southern Italy. * January 28 – Alexander Island, the largest in Antarctica, is first discovered by Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen. * February 9 – Columbian College in the District of Columbia is chartered by President James Monroe (it becomes George Washington University). * February 10 – In Mexico, the Embrace of Acatempan takes place between Agustín de Iturbide and Vicente Guerrero, which seals the peace between the viceroyalty troops and the insurgents. * February 28 – Congress of Laibach formally comes to an end. However the leading participants remain as fresh uprisings break out in Northern Italy and Greece. * March 7 – The Battle of Rieti is fought in Italy between intervening Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Roman Catholic Scientist-clerics
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but lists are frequently written down on paper, or maintained electronically. Lists are "most frequently a tool", and "one does not ''read'' but only ''uses'' a list: one looks up the relevant information in it, but usually does not need to deal with it as a whole".Lucie Doležalová,The Potential and Limitations of Studying Lists, in Lucie Doležalová, ed., ''The Charm of a List: From the Sumerians to Computerised Data Processing'' (2009). Purpose It has been observed that, with a few exceptions, "the scholarship on lists remains fragmented". David Wallechinsky, a co-author of '' The Book of Lists'', described the attraction of lists as being "because we live in an era of overstimulation, especially in terms of information, and lists help us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Internal Combustion Engine
Internal combustion engines date back to between the 10th and 13th centuries, when the first rocket engines were invented in China. Following the first commercial steam engine (a type of external combustion engine) by Thomas Savery in 1698, various efforts were made during the 18th century to develop equivalent internal combustion engines. In 1791, the English inventor John Barber patented a gas turbine. In 1794, Thomas Mead patented a gas engine. Also in 1794, Robert Street patented an internal-combustion engine, which was also the first to use liquid fuel (petroleum) and built an engine around that time. In 1798, John Stevens designed the first American internal combustion engine. In 1807, French engineers Nicéphore and Claude Niépce ran a prototype internal combustion engine, using controlled dust explosions, the Pyréolophore. This engine powered a boat on the river in France. The same year, the Swiss engineer François Isaac de Rivaz built and patented a hydrogen an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Combustion Engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons (reciprocating engine, piston engine), turbine blades (gas turbine), a Wankel engine, rotor (Wankel engine), or a propulsive nozzle, nozzle (jet engine). This force moves the component over a distance. This process transforms chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to. The first commercially successful internal combustion engines were invented in the mid-19th century. The first modern internal combustion engine, the Otto engine, was designed in 1876 by the German engineer Nicolaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-stroke Cycle
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes of the piston, one up and one down, in one revolution of the crankshaft in contrast to a four-stroke engine which requires four strokes of the piston in two crankshaft revolutions to complete a power cycle. During the stroke from bottom dead center to top dead center, the end of the exhaust/intake (or scavenging) is completed along with the compression of the mixture. The second stroke encompasses the combustion of the mixture, the expansion of the burnt mixture and, near bottom dead center, the beginning of the scavenging flows. Two-stroke engines often have a higher power-to-weight ratio than a four-stroke engine, since their power stroke occurs twice as often. Two-stroke engines can also have fewer moving parts, and thus be cheaper to manufacture and weigh less. In countries and regions with stringent emissions regulation, two-stroke engines have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reciprocating Engine
A reciprocating engine, more often known as a piston engine, is a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the Stirling engine for niche applications. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected then or earlier.''Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach'' by Yunus A. Cengal and Michael A. Boles Common features in all types There may be one or more pistons. Each piston is inside a cylinder, into which a gas is introduced, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museo Galileo
Museo Galileo (formerly ''Istituto e Museo di Storia della Scienza''; Institute and Museum of the History of Science) is located in Florence, Italy, in Piazza dei Giudici, along the River Arno and close to the Uffizi Gallery. The museum, dedicated to astronomer and scientist Galileo Galilei, is housed in Palazzo Castellani, an 11th-century building which was then known as the Castello d'Altafronte. Museo Galileo owns one of the world's major collection of scientific instruments, which bears evidence of the role that the Medici and Lorraine Grand Dukes attached to science and scientists. The Museo di Storia della Scienza has re-opened to the public under the new name ''Museo Galileo'' since June 10, 2010, after a two-year closure due to redesigning and renovation work. Its name change celebrates the 400-year anniversary of Galileo's '' Sidereus Nuncius'' (''The Starry Messenger''), first published in March of 1610. The museum The museum features the valuable scientific instru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolaus Otto
Nicolaus August Otto (10 June 1832 – 26 January 1891) was a German engineer who successfully developed the compressed charge internal combustion engine which ran on petroleum gas and led to the modern internal combustion engine. The Association of German Engineers (VDI) created DIN standard 1940 which says "Otto Engine: internal combustion engine in which the ignition of the compressed fuel-air mixture is initiated by a timed spark", which has been applied to all engines of this type since. Biography Nicolaus August Otto was born on 10 June 1832 in Holzhausen an der Haide, Germany. He was the youngest of six children. His father died in 1832. He began school in 1838. After six years of good performance he moved to the high school in Bad Schwalbach, Langenschwalbach until 1848. He did not complete his studies but was cited for good performance. His main interest in school had been in science and technology but he graduated after three years as a business apprentice in a sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulics
Hydraulics () is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counterpart of pneumatics, which concerns gases. Fluid mechanics provides the theoretical foundation for hydraulics, which focuses on applied engineering using the properties of fluids. In its fluid power applications, hydraulics is used for the generation, control, and transmission of Power (physics), power by the use of pressure, pressurized liquids. Hydraulic topics range through some parts of science and most of engineering modules, and they cover concepts such as pipe Volumetric flow rate, flow, dam design, fluidics, and fluid control circuitry. The principles of hydraulics are in use naturally in the human body within the vascular system and erectile tissue. ''Free surface hydraulics'' is the branch of hydraulics dealing with free surface flow, such as occurring in rivers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever, also known simply as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella enterica'' serotype Typhi bacteria, also called ''Salmonella'' Typhi. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. This is commonly accompanied by weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, and mild vomiting. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases, people may experience confusion. Without treatment, symptoms may last weeks or months. Diarrhea may be severe, but is uncommon. Other people may carry it without being affected, but are still contagious. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever, along with paratyphoid fever. ''Salmonella enterica'' Typhi is believed to infect and replicate only within humans. Typhoid is caused by the bacterium ''Salmonella enterica'' subsp. ''enterica'' serovar Typhi growing in the intestines, Peyer's patches, mesen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |