|
Eugene Sadowski
Eugene Ivanovich Sadowski (August 30, 1911 – August 1987) was a Ukrainian-born Soviet-American author, translator, Nazi collaborator, and mathematics professor. Lauded by Soviet and Russian authorities as a writer who died during World War II, it was discovered in January 2011 that Sadowski had not died but had instead collaborated with the Germans, where he wrote for Rech in Oryol. Early life and literary career Yevgeny Ivanovich Sadovsky was born on August 30, 1911, in the city of Mariupol, then part of the Russian Empire (now located in south-eastern Ukraine) into an ethnically Russian family. According to an autobiography which he dictated to German authorities, he moved to Moscow in 1926, studying and eventually (in 1932) graduating from the German department of the faculty for literary translation at the Institute for New Languages. He described himself as having been fascinated with languages from an early age, and, in addition to his native Ukrainian and Russian, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mariupol
Mariupol is a city in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. It is situated on the northern coast (Pryazovia) of the Sea of Azov, at the mouth of the Kalmius, Kalmius River. Prior to the Russian invasion of Ukraine, it was the tenth-largest city in the country and the second-largest city in Donetsk Oblast, with an estimated population of 425,681 people in January 2022; as of August 2023, Ukrainian authorities estimate the population of Mariupol at approximately 120,000. Mariupol has been occupied by Russian forces since May 2022. Historically, the city of Mariupol was a centre for trade and manufacturing, and played a key role in the development of higher education and many businesses and also served as a coastal resort on the Sea of Azov. In 1948, Mariupol was renamed Zhdanov () after Andrei Zhdanov, a native of the city who had become a high-ranking official of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union and a close ally to Joseph Stalin. The name was part of a larger effort to rename cities a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Defense (Soviet Union)
The Ministry of Defense (Minoboron; ) was a government ministry in the Soviet Union, which supervised the Soviet Armed Forces. The first Minister of Defense was Nikolai Bulganin, starting 1953. History The Ministry of Defence was renamed a number of times. From 1917 to 1934 it was the People's Commissariat for Military and Naval Affairs, from 1934 to 1946 it was the People's Commissariat of Defense of the Soviet Union, and in 1946 the People's Commissariat for the Armed Forces. On February 25, 1946 the People's Commissariat of Defense of the Soviet Union and the People's Commissariat of the Navy of the Soviet Union were amalgamated into a Ministry of the Armed Forces of the Soviet Union (). The ministry became responsible for: "developing long-term plans for the development of the army and navy and improving organization and logistics fall types and branches of troops of the Armed Forces, which were controlled through the corresponding main commands in accordance with the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babruysk
Babruysk (, ) or Bobruysk (, ; , ) is a city in Mogilev Region, Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Babruysk District, though it is administratively separated from the district. It is situated on the Berezina, Berezina River. Babruysk occupies an area of , and comprises over 450 streets whose combined length stretches for over . , it has a population of 207,351.Babruysk is located at the intersection of railroads to Asipovichy, Zhlobin, Aktsyabrski and roads to Minsk, Gomel, Mogilev, Kalinkavichy, Slutsk, and Rahachow. It has the biggest timber mill in Belarus, and is also known for its chemical, machine building and metal-working industries. In 2021, there were 38 public schools in Babruysk, with over 24,000 students. There are three schools specializing in music, dance and visual arts. Additionally, there is a medical school and numerous professional technical schools. Etymology The name ''Babruysk'' (as well as that of the Babruyka, Babruyka River) probably or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
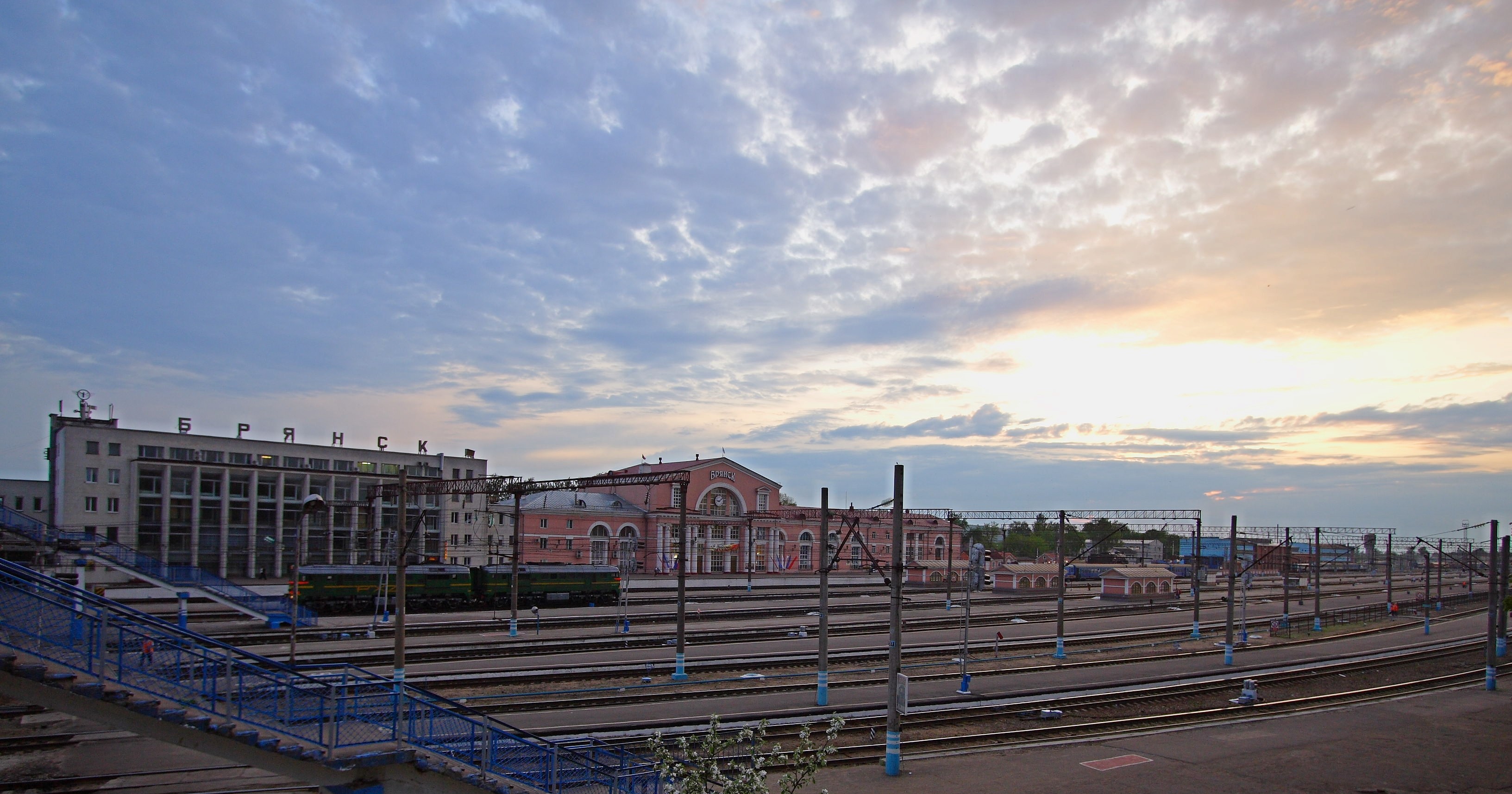
Bryansk
Bryansk (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Bryansk Oblast, Russia, situated on the Desna (river), Desna River, southwest of Moscow. It has a population of 379,152 at the 2021 census. Bryansk is one of the oldest cities in the oblast, with 985 regarded as the year of foundation. It was part of the Kievan Rus', Mongol Empire and Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuania during the Middle Ages, medieval period, then was contested by Grand Duchy of Moscow, Moscow and Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Poland–Lithuania in the early modern period, before ultimately passing to Russia, within which it was a major regional trading center. History Medieval period Based on excavations at the end of the 20th century, information was found on the birth of the city in the 10th century on the Chashin Kurgan. For ease of perception, the conventional date of birth was chosen as 985 AD. The first written mention of Bryansk, as Debryansk, dates t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisoner-of-war Camp
A prisoner-of-war camp (often abbreviated as POW camp) is a site for the containment of enemy fighters captured as Prisoner of war, prisoners of war by a belligerent power in time of war. There are significant differences among POW camps, internment camps, and military prisons. Purpose-built prisoner-of-war camps appeared at Norman Cross Prison, Norman Cross in England in 1797 during the French Revolutionary Wars and HM Prison Dartmoor, constructed during the Napoleonic Wars, and they have been in use in all the main conflicts of the last 200 years. The main camps are used for marines, sailors, soldiers, and more recently, airmen of an enemy power who have been captured by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. Civilians, such as Merchant navy, merchant mariners and war correspondents, have also been imprisoned in some conflicts. Per the Geneva Convention on Prisoners of War (1929), 1929 Geneva Convention on Prisoners of War, later superseded by the T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Samarin
Vladimir Dmitriyevich Sokolov (2 March 1913 – 19 January 1992), also known under the pen name of Samarin, was a Russian Nazi collaborator, journalist, writer, researcher and educator. Following his work as a propagandist for Nazi Germany as one of the writers of the Rech newspaper, he fled to the United States and became a senior lector of Russian language studies at Yale University from 1949 to 1976. In 1982, he was targeted by the United States Department of Justice for deportation, bringing him national notoriety. Following the revocation of his citizenship, he fled to an Orthodox monastery in Montreal, Canada, where he died in 1992. Early life Vladimir Dmitriyevich Sokolov was born to the family of a nobleman and landlord in Oryol, in what was then the Russian Empire, on 2 March 1913. In 1921, as a student, he witnessed the crushing of the Tambov rebellion by the Red Army with the usage of chemical weapons, an experience which had a great effect on his personal views. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Holocaust Memorial Museum
The United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM) is the United States' official memorial to the Holocaust, dedicated to the documentation, study, and interpretation of the Holocaust. Opened in 1993, the museum explores the Holocaust through permanent and traveling exhibitions, educational programs, survivor testimonies and archival collections. The USHMM was created to help leaders and citizens of the world confront hatred, prevent genocide, promote human dignity, and strengthen democracy. Overview In 2008, the museum had an operating budget of $120.6 million, a staff of about 400 employees, 125 contractors, 650 volunteers, 91 Holocaust survivors, and 175,000 members. It has local offices in New York City, Boston, Boca Raton, Chicago, Los Angeles, and Dallas. Since its dedication on April 22, 1993, the museum has had nearly 40 million visitors, including more than 10 million school children, 120 heads of state, and more than 3,500 foreign officials from over 132 countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Oktan
Mikhail Aleksandrovich Ilinich (; ; – after 1945), better known by the pseudonym of Mikhail Oktan (; ) was a Russian Nazi collaborator during World War II who served as ''de facto'' mayor of the city of Oryol under Nazi occupation, as well as an important Russian collaborationist in Bobruisk. He was active in Russia, Belarus, and Poland. Early life Little is known about Oktan's early life save for the fact that he was born in the city of Odessa. He described himself to German officers as an engineer, and was, according to historian Alexander Dallin, said by some peers to have studied economics. It was claimed by a newspaperman close to Oktan that he had been a member of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union prior to World War II, possibly as a propagandist or local functionary. This claim was also repeated in intelligence from Soviet partisans, which stated Oktan had been head of the Oryol Oblast education department prior to the outbreak of the war. According to a 1943 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian State Archive Of Literature And Art
Russian State Archive of Literature and Art (, or RGALI) is one of the largest state archives in Russia. It preserves documents of national literature, music, theatre, cinema, painting and architecture. History As a centralized archive for documentation in the cultural sphere, RGALI was founded in 1941 under the name of TsGLA, on the basis of the collected manuscript holdings of the State Literary Museum (Goslitmuzei—GLM) and designated fonds from other museums and archives. *1941–1954 – ''Central State Literary Archive (TsGLA)'' () *1954-VI.1992 – ''Central State Archive of Literature and Art of the USSR (TsGALI SSSR)'' () *1992–present – ''Russian State Archive of Literature and Art (RGALI)'' () External linksOfficial websiteOfficial website Archives in Russia Russia Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainer Maria Rilke
René Karl Wilhelm Johann Josef Maria Rilke (4 December 1875 – 29 December 1926), known as Rainer Maria Rilke, was an Austrian poet and novelist. Acclaimed as an Idiosyncrasy, idiosyncratic and expressive poet, he is widely recognized as a significant writer in the German language.Biography: Rainer Maria Rilke 1875–1926 Poetry Foundation website. Retrieved 2 February 2013. His work is viewed by critics and scholars as possessing undertones of mysticism, exploring themes of Subjectivity, subjective experience and disbelief. His writings include one novel, several collections of poetry, several volumes of correspondence and a few early novellas. Rilke traveled extensively throughout Europe, finally settling in Switzerland, which provided the inspiration for many of his poems. While Rilke is best ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes R
Johannes is a Medieval Latin form of the personal name that usually appears as "John" in English language contexts. It is a variant of the Greek and Classical Latin variants (Ιωάννης, '' Ioannes''), itself derived from the Hebrew name '' Yehochanan'', meaning "YHWH is gracious". The name became popular in Northern Europe, especially in Germany because of Christianity. Common German variants for Johannes are ''Johann'', ''Hannes'', '' Hans'' (diminutized to ''Hänschen'' or ''Hänsel'', as known from "''Hansel and Gretel''", a fairy tale by the Grimm brothers), '' Jens'' (from Danish) and '' Jan'' (from Dutch, and found in many countries). In the Netherlands, Johannes was without interruption the most common masculine birth name until 1989. The English equivalent for Johannes is John. In other languages *Joan, Jan, Gjon, Gjin and Gjovalin in Albanian *'' Yoe'' or '' Yohe'', uncommon American form''Dictionary of American Family Names'', Oxford University Press, 2013. *Ya� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literaturnaya Gazeta
''Literaturnaya Gazeta'' (, ''Literary Gazette'') is a weekly cultural and political newspaper published in Russia and the Soviet Union. It was published for two periods in the 19th century, and was revived in 1929. Overview The current newspaper shares its title with a 19th century publication, and claims to be a continuation of the original publication. The first paper to bear the name of ''Literaturnaya Gazeta'' was founded by a literary group led by Anton Delvig and Alexander Pushkin, whose profile to this day adorns the paper's masthead.Историческая справка (in Russian) The first issue appeared on January 1, 1830. The paper appeared regularly until June 30, 1831, reappearing in 1840–1849. Pushkin himself published some of his most famous works in this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |