|
Eucalyptus Stricklandii
''Eucalyptus stricklandii'', commonly known as Strickland's gum, is a species of small tree that is endemic to Western Australia, but possibly also naturalised in Victoria. It has rough, crumbly to flaky bark near the base of the trunk, smooth reddish brown to grey bark above, lance-shaped adult leaves, flower buds in groups of seven, yellow flowers and bell-shaped fruit. Description ''Eucalyptus stricklandii'' is a tree that typically grows to a height of and does not form a lignotuber. It has rough, crumbly to flaky bark on the lower part of the trunk, smooth reddish brown to grey bark above. Young plants and coppice regrowth have thick, dull green to greyish egg-shaped leaves that are long and wide. Adult leaves are thick, glossy green, lance-shaped to curved, long and wide, tapering to a petiole long. The flower buds are arranged in leaf axils in groups of seven on a, glaucous, flattened, unbranched peduncle long, the individual buds more or less sessile. Mature buds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norseman, Western Australia
Norseman is a town located in the Goldfields-Esperance region of Western Australia along the Coolgardie-Esperance Highway, east of Perth and above sea level. It is also the starting point of the Eyre Highway, and the last major town in Western Australia before the South Australian border to the east. At the 2021 census, Norseman had a population of 562, of which 17% were Australian Aboriginal. History The quest for gold led to the establishment of Norseman, on the traditional land of the Ngadju. Today there are a number of small goldmining operations in the area but only the Central Norseman Gold Corporation can be considered a major producer. Gold was first found in the Norseman area in 1892, about 10 km south of the town, near Dundas. The "Dundas Field" was proclaimed in August 1893 and a townsite gazetted there. In August 1894, Lawrence Sinclair, his brother George Sinclair, and Jack Alsopp discovered a rich gold reef which Sinclair named after his horse, Hardy No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Western Australia
The Royal Society of Western Australia (RSWA) promotes science in Western Australia. The RSWA was founded in 1914. It publishes the ''Journal of the Royal Society of Western Australia'', and has awarded the Medal of the Royal Society of Western Australia (also known incorrectly as the Kelvin Medal) on an occasional basis since 1924. Journal The ''Journal of the Royal Society of Western Australia'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering scientific research carried out in Western Australia, or on topics related to Western Australia.. It is the official journal of Royal Society of Western Australia and traces its roots to the ''Journal and Proceedings of the Mueller Botanic Society of Western Australia'' published from 1899 to 1903. The Mueller Botanic Society became the West Australian Natural History Society in 1903, and from 1904 to 1909, the journal was published as ''Journal of the West Australian Natural History Society''. In 1909 the society again changed it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myrtales Of Australia
The Myrtales are an order of flowering plants placed as a sister to the eurosids II clade as of the publishing of the ''Eucalyptus grandis'' genome in June 2014. The APG III system of classification for angiosperms still places it within the eurosids. This finding is corroborated by the placement of the Myrtales in the Malvid clade by the One Thousand Plant Transcriptomes Initiative. The following families are included as of APGIII: * Alzateaceae S. A. Graham * Combretaceae R. Br. ( leadwood family) * Crypteroniaceae A. DC. * Lythraceae J. St.-Hil. ( loosestrife and pomegranate family) * Melastomataceae Juss. (including Memecylaceae DC.) * Myrtaceae Juss. (myrtle family; including Heteropyxidaceae Engl. & Gilg, Psiloxylaceae Croizat) * Onagraceae Juss. ( evening primrose and Fuchsia family) * Penaeaceae Sweet ex Guill. (including Oliniaceae Arn., Rhynchocalycaceae L. A. S. Johnson & B. G. Briggs) * Vochysiaceae A. St.-Hil. The Cronquist system gives essentially the same c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of Flowering plant, flowering trees, shrubs or Mallee (habit), mallees in the Myrtaceae, myrtle Family (biology), family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the Tribe (biology), tribe Eucalypteae, including ''Corymbia'', they are commonly known as eucalypts. Plants in the genus ''Eucalyptus'' have bark that is either smooth, fibrous, hard or stringy, leaves with oil Gland (botany), glands, and sepals and petals that are fused to form a "cap" or Operculum (botany), operculum over the stamens. The fruit is a woody Capsule (botany), capsule commonly referred to as a "gumnut". Most species of ''Eucalyptus'' are Indigenous (ecology), native to Australia, and every state and territory has representative species. About three-quarters of Australian forests are eucalypt forests. Wildfire is a feature of the Australian landscape and many eucalypt species are adapted to fire, and resprout after fire or have seeds which sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trees Of Australia
The flora of Australia comprises a vast assemblage of plant species estimated to over 30,000 vascular and 14,000 non-vascular plants, 250,000 species of fungi and over 3,000 lichens. The flora has strong affinities with the flora of Gondwana, and below the family level has a highly endemic angiosperm flora whose diversity was shaped by the effects of continental drift and climate change since the Cretaceous. Prominent features of the Australian flora are adaptations to aridity and fire which include scleromorphy and serotiny. These adaptations are common in species from the large and well-known families Proteaceae (''Banksia''), Myrtaceae (''Eucalyptus'' - gum trees), and Fabaceae (''Acacia'' - wattle). The arrival of humans around 50,000 years ago and the settlement by Europeans from 1788, has had a significant impact on the flora. The use of fire-stick farming by Aboriginal people led to significant changes in the distribution of plant species over time, and the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucalypts Of Western Australia
Eucalypt is a descriptive name for woody plants with capsule fruiting bodies belonging to seven closely related genera (of the tribe Eucalypteae) found across Australasia: ''Eucalyptus'', ''Corymbia'', ''Angophora'', '' Stockwellia'', '' Allosyncarpia'', '' Eucalyptopsis'' and ''Arillastrum''. Taxonomy For an example of changing historical perspectives, in 1991, largely genetic evidence indicated that some prominent ''Eucalyptus'' species were actually more closely related to ''Angophora'' than to other eucalypts; they were accordingly split off into the new genus ''Corymbia''. Although separate, all of these genera and their species are allied and it remains the standard to refer to the members of all seven genera ''Angophora'', ''Corymbia'', ''Eucalyptus'', ''Stockwellia'', ''Allosyncarpia'', ''Eucalyptopsis'' and ''Arillastrum'' as "eucalypts" or as the eucalypt group. The extant genera ''Stockwellia'', ''Allosyncarpia'', ''Eucalyptopsis'' and ''Arillastrum'' comprise six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Eucalyptus Species
The following is an alphabetical list of ''Eucalyptus'' species accepted by the Australian Plant Census as at February 2019. Several species only occurring outside Australia, including '' E. orophila'', '' E. urophylla'' and '' E. wetarensis'' are listed at the World Checklist of Selected Plant Families. A * '' Eucalyptus abdita'' Brooker & Hopper * ''Eucalyptus absita'' Grayling & Brooker – Badgingarra box * '' Eucalyptus acaciiformis'' H.Deane & Maiden – wattle-leaved peppermint * ''Eucalyptus accedens'' W.Fitzg. – powderbark wandoo * '' Eucalyptus acies'' Brooker – Woolburnup mallee * ''Eucalyptus acmenoides'' Schauer in W.G.Walpers – white mahogany * '' Eucalyptus acroleuca'' L.A.S.Johnson & K.D.Hill – Lakefield coolibah * '' Eucalyptus adesmophloia'' (Brooker & Hopper) D.Nicolle & M.E.French * '' Eucalyptus aequioperta'' Brooker & Hopper – Welcome Hill gum * ''Eucalyptus agglomerata'' Maiden – blue-leaved stringybark * ''Eucalyptus aggregata'' H.Deane & Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Parks And Wildlife (Western Australia)
The Department of Parks and Wildlife (DPaW) was the department of the Government of Western Australia responsible for managing lands described in the ''Conservation and Land Management Act 1984'' and implementing the state's conservation and environment legislation and regulations. The minister responsible for the department was the Minister for the Environment (Western Australia), Minister for the Environment. History The Department of Environment and Conservation (Western Australia), Department of Environment and Conservation (DEC) was separated on 30 June 2013, forming the Department of Parks and Wildlife (DPaW) and the Department of Environment Regulation (DER), both of which commenced operations on 1 July 2013. DPaW focused on managing multiple use state forests, national parks, marine parks and reserves. DER focused on environmental regulation, approvals and appeals processes, and pollution prevention. It was announced on 28 April 2017 that the Department of Parks and Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBRA
The Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) is a biogeographic regionalisation of Australia developed by the Australian government's Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population, and Communities. It was developed for use as a planning tool, for example for the establishment of a national reserve system. The first version of IBRA was developed in 1993–94 and published in 1995. Within the broadest scale, Australia is a major part of the Australasia biogeographic realm, as developed by the World Wide Fund for Nature The World Wide Fund for Nature Inc. (WWF) is an international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the Wor .... Based on this system, the world is also split into 14 terrestrial habitats, of which eight are shared by Australia. The Australian land mass is divided into 89 bioregions and 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murchison (biogeographic Region)
The Murchison is an interim Australian bioregion located within the Mid West of Western Australia. The bioregion is loosely related to the catchment area of the Murchison River and has an area of . Traditionally the region is known as ''The Murchison''. Geography The landscape is characterised by low hills and mesas, separated by colluvium flats and alluvial plains. The western portion of the bioregion is drained by the upper Murchison and Wooramel rivers, which drain westwards towards the coast.Anthony Desmond, Mark Cowan and Alanna Chant (2001). "Murchison 2 (MUR2 – Western Murchison subregion)", in ''A Biodiversity Audit of Western Australia’s 53 Biogeographical Subregions in 2002''. The Department of Conservation and Land Management, Government of Western Australia, November 2001/ref> Together with Gascoyne bioregion, it constitutes the Western Australian mulga shrublands ecoregion. Population is scattered; the largest population centres are Meekatharra, Mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
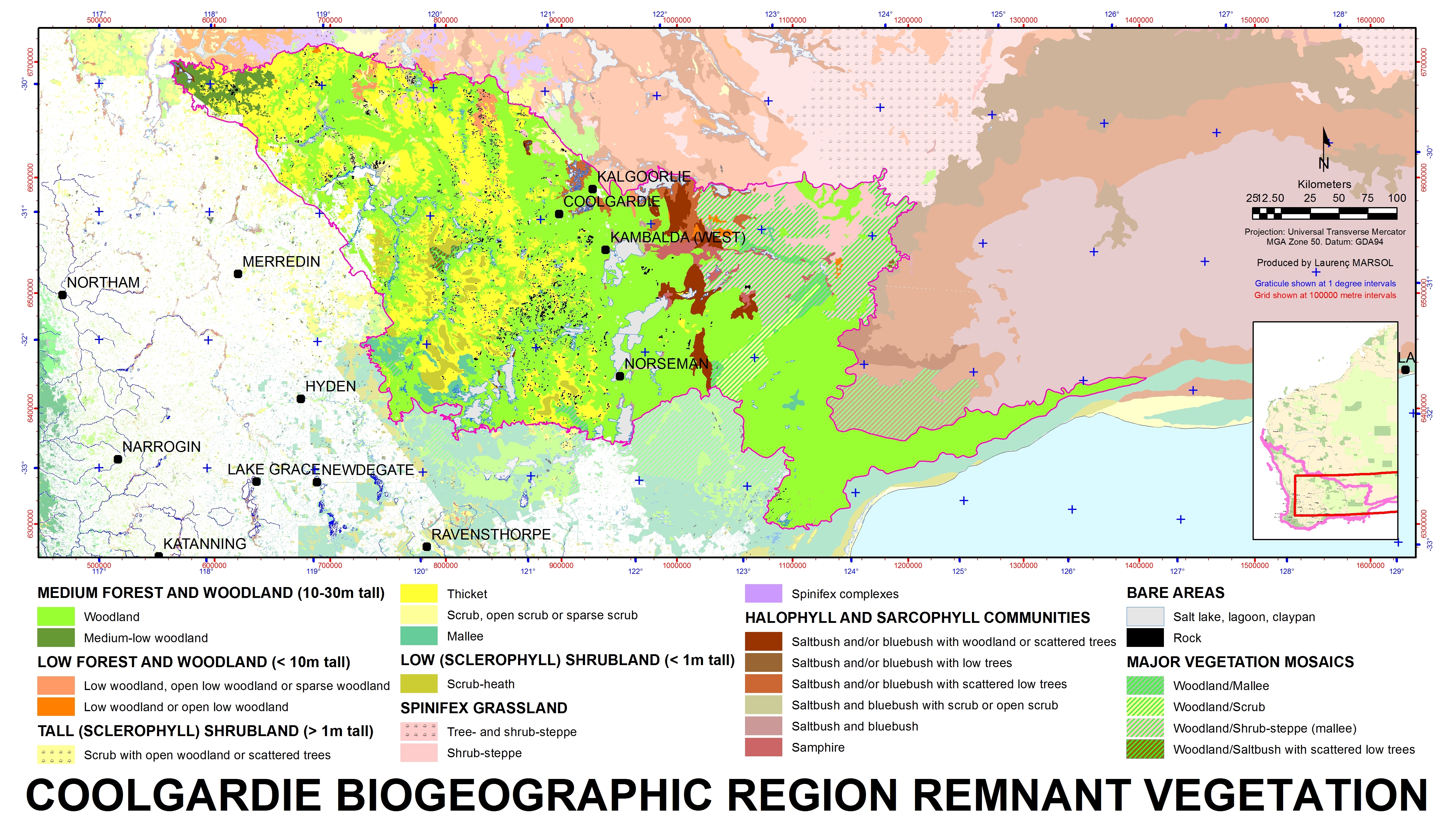
Coolgardie (biogeographic Region)
Coolgardie is an Australian bioregion consisting of an area of low hills and plains of infertile sandy soil in Western Australia. It has an area of . It includes much of the Great Western Woodlands. Location and description This is a transition zone between the Mediterranean climate of Australia's south-west coast and the country's dry interior. The poor soil makes it unsuitable for agriculture but Coolgardie has been a gold and nickel mining area. It is bounded on the north by the arid Murchison bioregion, characterised by open Mulga woodlands and steppe. The low shrublands of the arid Nullarbor Plain lie to the east. The Mallee bioregion adjoins Coolgardie on the south. The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is to the west. The Coolgardie bioregion, together with the coastal Hampton bioregion to the southeast, constitute the Coolgardie woodlands ecoregion defined by the World Wildlife Fund. Flora and fauna The low hills are home to woodland of endemic species of eucalyptus whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coolgardie, Western Australia
Coolgardie is a small town in Western Australia, east of the state capital, Perth. It has a population of approximately 850 people. Although Coolgardie is now known to most Western Australians as a tourist town and a mining ghost town, it was once the third largest town in Western Australia (after Perth and Fremantle). At this time, mining of alluvial gold was a major industry and supplied the flagging economy with new hope. Many miners suffered under the harsh conditions, but for a few, their find made the hard work worthwhile. Most men, however, left poorer than they had started off, with their hopes dashed. History Coolgardie was founded in 1892, when gold was discovered in the area known as Fly Flat by prospectors Arthur Wellesley Bayley and William Ford. Australia had seen several major gold rushes over the previous three decades, mostly centred on the east coast, but these had mostly been exhausted by the 1890s. With the discovery of a new goldfield, an entire new g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |