|
Etravirine
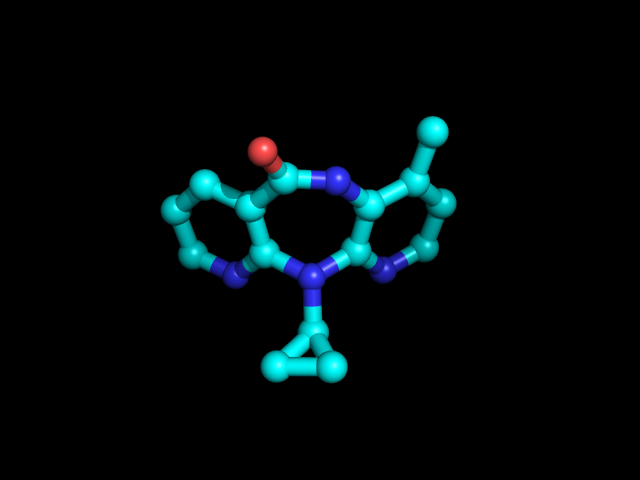
Etravirine (ETR,), sold under the brand name Intelence is an antiretroviral medication used for the treatment of HIV. Etravirine is a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI). Unlike agents in the class, resistance to other NNRTIs does not seem to confer resistance to etravirine. Etravirine is marketed by Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson. In January 2008, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved its use for people with established resistance to other drugs, making it the 30th anti-HIV drug approved in the United States and the first to be approved in 2008. It was also approved for use in Canada in April 2008. Etravirine is licensed in the United States, Canada, Israel, Russia, Australia, New Zealand, and the European Union, and is under regulatory review in Switzerland. Medical uses In the US, etravirine is indicated for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in treatment-experienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarylpyrimidine
Diarylpyrimidines (DAPY) and diaryltriazines (DATA) are two closely related classes of molecules resembling the pyrimidine nucleotides found in DNA. They show great potency in inhibiting the activity of HIV reverse transcriptase. Several compounds in this class are non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors used clinically in the treatment of HIV/AIDS, notably etravirine and rilpivirine.Steve MitchellHIV Market To Top 10 Billion Dollars United Press International. April 11, 2007. References Antiretroviral drugs Pyrimidines {{heterocyclic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP3A4
Cytochrome P450 3A4 (abbreviated CYP3A4) () is an important enzyme in the body, mainly found in the liver and in the intestine, which in humans is encoded by ''CYP3A4'' gene. It organic redox reaction, oxidizes small foreign organic molecules (xenobiotics), such as toxins or drugs, so that they can be removed from the body. It is highly homologous to CYP3A5, another important CYP3A enzyme. While many drugs are deactivated by CYP3A4, there are also some drugs that are ''activated'' by the enzyme. Some substances, such as some drugs and furanocoumarins present in grapefruit juice, interfere with the action of CYP3A4. These substances will, therefore, either amplify or weaken the action of those drugs that are modified by CYP3A4. CYP3A4 is a member of the cytochrome P450 family of oxidizing enzymes. Several other members of this family are also involved in drug metabolism, but CYP3A4 is the most common and the most versatile one. Like all members of this family, it is a hemoprote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiretroviral Medication
The management of HIV/AIDS normally includes the use of multiple antiretroviral drugs as a strategy to control HIV infection. There are several classes of antiretroviral agents that act on different stages of the HIV life-cycle. The use of multiple drugs that act on different viral targets is known as highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). HAART decreases the patient's total burden of HIV, maintains function of the immune system, and prevents opportunistic infections that often lead to death. HAART also prevents the transmission of HIV between serodiscordant same-sex and opposite-sex partners so long as the HIV-positive partner maintains an undetectable viral load. Treatment has been so successful that in many parts of the world, HIV has become a chronic condition in which progression to AIDS is increasingly rare. Anthony Fauci, former head of the United States National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, has written, "With collective and resolute action now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevirapine
Nevirapine (NVP), sold under the brand name Viramune among others, is a medication used to treat and prevent HIV/AIDS, specifically HIV-1. It is generally recommended for use with other antiretroviral medications. It may be used to prevent mother to child spread during birth but is not recommended following other exposures. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include rash, headache, nausea, feeling tired, and liver problems. The liver problems and skin rash may be severe and should be checked for during the first few months of treatment. It appears to be safe for use during pregnancy. It is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) and works by blocking the function of reverse transcriptase. Nevirapine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1996. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. Medical uses Nevirapine is used in people six years of age and older infected with H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stevens–Johnson Syndrome
Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS) is a type of severe skin reaction. Together with toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and #Classification, Stevens–Johnson/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN) overlap, they are considered febrile mucocutaneous drug reactions and probably part of the same spectrum of disease, with SJS being less severe. Erythema multiforme (EM) is generally considered a separate condition. Early symptoms of SJS include fever and flu-like symptoms. A few days later, the skin begins to blister and peel, forming painful raw areas. Mucous membranes, such as the mouth, are also typically involved. Complications include dehydration, sepsis, pneumonia and multiple organ failure. The most common cause is certain medications such as lamotrigine, carbamazepine, allopurinol, sulfonamide antibiotics and nevirapine. Other causes can include infections such as ''Mycoplasma pneumoniae'' and cytomegalovirus, or the cause may remain unknown. Risk factors include HIV/AIDS and syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
By Mouth
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes of administration, such as Injection (medicine), injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth". The expression is used in medicine to describe a treatment that is taken orally (but not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose-galactose Malabsorption
Glucose-galactose malabsorption is a rare condition in which the cells lining the intestine cannot take in the sugars glucose and galactose, which prevents proper digestion of these molecules and larger molecules made from them. Glucose and galactose are called simple sugars, or monosaccharides. Sucrose and lactose are called disaccharides because they are made from two simple sugars, and are broken down into these simple sugars during digestion. Sucrose is broken down into glucose and another simple sugar called fructose, and lactose is broken down into glucose and galactose. As a result, lactose, sucrose and other compounds made from carbohydrates cannot be digested by individuals with glucose-galactose malabsorption. Signs and symptoms Genetics The ''SLC5A1'' gene provides instructions for producing a sodium/glucose cotransporter protein called SGLT1. This protein is found mainly in the intestinal tract and, to a lesser extent, in the kidneys, where it is involved in transport ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Conformation
Protein structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule. Proteins are polymers specifically polypeptides formed from sequences of amino acids, which are the monomers of the polymer. A single amino acid monomer may also be called a ''residue'', which indicates a repeating unit of a polymer. Proteins form by amino acids undergoing condensation reactions, in which the amino acids lose one water molecule per reaction in order to attach to one another with a peptide bond. By convention, a chain under 30 amino acids is often identified as a peptide, rather than a protein. To be able to perform their biological function, proteins fold into one or more specific spatial conformations driven by a number of non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonding, ionic interactions, Van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic packing. To understand the functions of proteins at a molecular level, it is often necessary to determine their three-dimensional st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
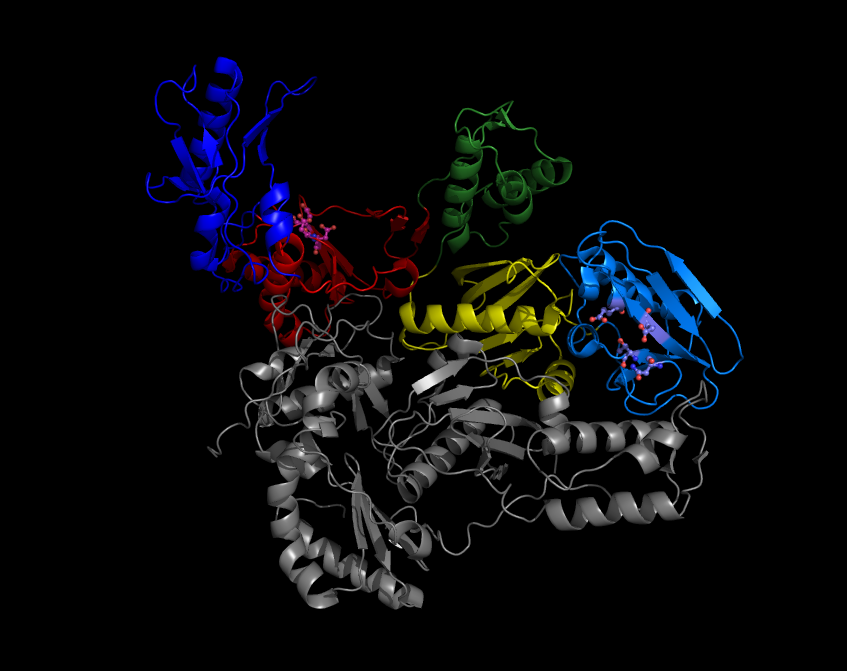
Reverse Transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to convert RNA genome to DNA, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobile genetic elements to proliferate within the host genome, and by eukaryotic cells to extend the telomeres at the ends of their linear chromosomes. The process does not violate the flows of genetic information as described by the classical central dogma, but rather expands it to include transfers of information from RNA to DNA. Retroviral RT has three sequential biochemical activities: RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity, ribonuclease H (RNase H), and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity. Collectively, these activities enable the enzyme to convert single-stranded RNA into double-stranded cDNA. In retroviruses and retrotransposons, this cDNA can then integrate into the host genome, from which new RNA copies can be made via host-cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conformational Isomerism
In chemistry, rotamers are chemical species that differ from one another primarily due to rotations about one or more single bonds. Various arrangements of atoms in a molecule that differ by rotation about single bonds can also be referred to as conformations. Conformers/rotamers differ little in their energies, so they are almost never separable in a practical sense. Rotations about single bonds are subject to small energy barriers. When the time scale for interconversion is long enough for isolation of individual rotamers (usually arbitrarily defined as a half-life of interconversion of 1000 seconds or longer), the species are termed atropisomers (''see:'' atropisomerism). The Ring flip, ring-flip of substituted cyclohexanes constitutes a common form of conformers. The study of the energetics of bond rotation is referred to as conformational analysis. In some cases, conformational analysis can be used to predict and explain product selectivity, mechanisms, and rates of reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Molecule
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even hydrogen cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efavirenz
Efavirenz (EFV), sold under the brand names Sustiva among others, is an antiretroviral medication used to treat and prevent HIV/AIDS. It is generally recommended for use with other antiretrovirals. It may be used for prevention after a needlestick injury or other potential exposure. It is sold both by itself and in combination as efavirenz/emtricitabine/tenofovir. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include rash, nausea, headache, feeling tired, and trouble sleeping. Some of the rashes may be serious such as Stevens–Johnson syndrome. Other serious side effects include Depression (mood), depression, suicidal ideations, thoughts of suicide, liver problems, and seizures. It is not safe for use during pregnancy. It is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) and works by blocking the function of reverse transcriptase. Efavirenz was approved for medical use in the United States in 1998, and in the European Union in 1999. It is on the WHO Model List of Essent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |