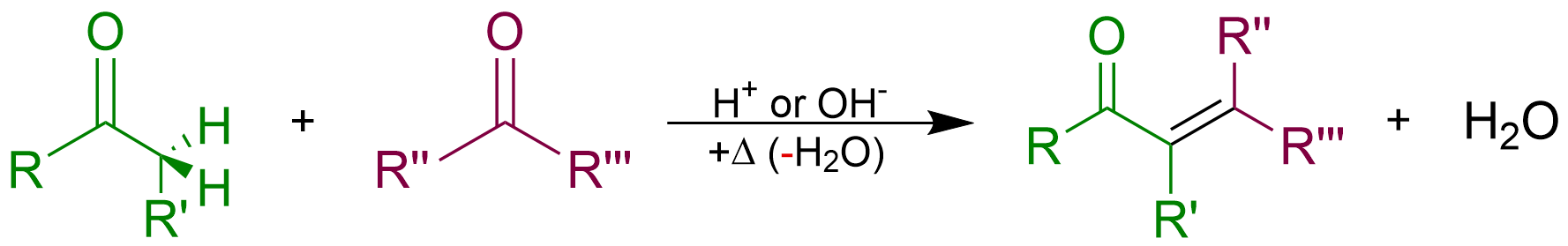|
Ethyl Methylphenylglycidate
Ethyl methylphenylglycidate, commonly known as strawberry aldehyde, is an organic compound used in the flavor industry in artificial fruit flavors, in particular strawberry. Uses Because of its pleasant taste and aroma, ethyl methylphenylglycidate finds use in the fragrance industry, in artificial flavors, and in cosmetics. Its end applications include perfumes, soaps, beauty care products, detergents, pharmaceuticals, baked goods, candies, ice cream, and others. Chemistry Ethyl methylphenylglycidate contains ester and epoxide functional groups, despite its common name, lacks presence of an aldehyde. It is a colourless liquid that is insoluble in water. Ethyl methylphenylglycidate is usually prepared by the condensation of acetophenone and the ethyl ester of monochloroacetic acid in the presence of a base, in a reaction known as the Darzens condensation. Safety Long-term, high-dose studies in rats have demonstrated that ethyl methylphenylglycidate has no significant a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation Reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis. However other molecules can also be lost, such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid and hydrogen sulfide. The addition of the two molecules typically proceeds in a step-wise fashion to the addition product, usually in equilibrium, and with loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). The reaction may otherwise involve the functional groups of the molecule, and is a versatile class of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic conditions or in the presence of a catalyst. This class of reactions is a vital part of life as it is essential to the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids and to the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Many variations of condensation reactions exist. Common examples include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Additives
Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance taste, appearance, or other sensory qualities. Some additives, such as vinegar ( pickling), salt ( salting), smoke (smoking) and sugar (crystallization), have been used for centuries to preserve food. This allows for longer-lasting foods, such as bacon, sweets, and wines. With the advent of ultra-processed foods in the late 20th century, many additives having both natural and artificial origin were introduced. Food additives also include substances that may be introduced to food indirectly (called "indirect additives") in the manufacturing process through packaging, storage or transport. In Europe and internationally, many additives are designated with E numbers, while in the United States, additives in amounts deemed safe for human consumption are designated as GRAS. Identification To regulate these additives and inform consumers each additive is assigned a unique number called an "E number", which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavors
Flavour or flavor is either the sensory perception of taste or smell, or a flavoring in food that produces such perception. Flavour or flavor may also refer to: Science * Flavors (programming language), an early object-oriented extension to Lisp *Flavour (particle physics) In particle physics, flavour or flavor refers to the ''species'' of an elementary particle. The Standard Model counts six flavours of quarks and six flavours of leptons. They are conventionally parameterized with ''flavour quantum numbers'' ..., a quantum number of elementary particles related to their weak interactions *Flavor of Linux, another term for any particular Linux distribution; by extension, "flavor" can be applied to any program or other computer code that exists in more than one current variant at the same time Film and TV * ''Flavors'' (film), romantic comedy concerning Asian-Indian immigrants in America * Flavour Network, is a Canadian TV channel with shows about food. Music Art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoxides
In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether, where the ether forms a three-atom Ring (chemistry), ring: two atoms of carbon and one atom of oxygen. This triangular structure has substantial ring strain, making epoxides highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale for many applications. In general, low molecular weight epoxides are colourless and nonpolar, and often Volatility (chemistry), volatile. Nomenclature A compound containing the epoxide functional group can be called an epoxy, epoxide, oxirane, and ethoxyline. Simple epoxides are often referred to as oxides. Thus, the epoxide of ethylene (C2H4) is ethylene oxide (C2H4O). Many compounds have trivial names; for instance, ethylene oxide is called "oxirane". Some names emphasize the presence of the epoxide functional group, as in the compound ''1,2-epoxyheptane'', which can also be called ''1,2-heptene oxide''. A polymer formed from epoxide precursors is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Esters
Ethyl may refer to: Arts and entertainment *Ethyl Sinclair, a character in the ''Dinosaurs'' television show Science and technology * Ethyl group, an organic chemistry moiety * Ethyl alcohol (or ethanol) * Ethyl Corporation, a fuel additive company ** Tetraethyllead Tetraethyllead (commonly styled tetraethyl lead), abbreviated TEL, is an organolead compound with the formula lead, Pb(ethyl group, C2H5)4. It was widely used as a fuel additive for much of the 20th century, first being mixed with gasoline begi ...-treated gasoline See also * Ethel (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Strawberry Topics
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to strawberries: The strawberry is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus ''Fragaria'' (collectively known as the strawberries). It is cultivated worldwide for its fruit. The fruit (which is not a botanical berry, but an aggregate accessory fruit) is widely appreciated for its characteristic aroma, bright red color, juicy texture, and sweetness. Types of strawberries Cultivars * List of strawberry cultivars * Little Scarlet – according to Wilkin & Sons Limited, it is a '' Fragaria virginiana'' strawberry. It is American by origin but is grown only in Britain. * Marshall strawberry – a cultivated variety of '' Fragaria ananassa'', that is known for "exceptional taste and firmness"Oregon Strawberry Commission and had been described as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generally Recognized As Safe
Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) is a United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) designation that a chemical or substance added to food is considered safe by experts under the conditions of its intended use. An ingredient with a GRAS designation is exempted from the usual Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA) food additive tolerance requirements. The concept of food additives being "generally recognized as safe" was first described in the Food Additives Amendment of 1958, and all additives introduced after this time had to be evaluated by new standards. Some examples of substances recognized as GRAS include ascorbic acid (vitamin C), citric acid, and salt, which are all commonly used in food preservation and flavoring. The FDA list of GRAS notices is updated approximately each month, as of 2021. History On 6 September 1958, the Food Additives Amendment of 1958 was signed into law, with a list of 700 food substances that were exempt from the then-new requirement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C). However, the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Cosmetics Toxicology
''Food and Chemical Toxicology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering aspects of food safety, chemical safety, and other aspects of consumer product safety. It is published by Elsevier and was established in 1963. The editor-in-chief is Bryan Delaney. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Analytical Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, CAB International, Chemical Abstracts Service, Current Contents/Agriculture, Biology & Environmental Sciences, Current Contents/Life Sciences, Elsevier BIOBASE, EMBASE, MEDLINE/PubMed, Science Citation Index, and Scopus. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', it has a 2014 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 2.895, ranking it 30th out of 87 journals in the category "Toxicology" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darzens Condensation
The Darzens reaction (also known as the Darzens condensation or glycidic ester condensation) is the chemical reaction of a ketone or aldehyde with an α-haloester in the presence of a base to form an α,β-epoxy ester, also called a "glycidic ester". This reaction was discovered by the organic chemist Auguste Georges Darzens in 1904. : Reaction mechanism The reaction process begins with deprotonation at the halogenated position. Because of the ester substituents, this carbanion is a resonance-stabilized enolate. This nucleophile next attacks the carbonyl reagent, forming a carbon–carbon bond. These two steps are similar to a base-catalyzed aldol reaction. The oxygen anion in this aldol-like product then SN2 attacks on the formerly-nucleophilic halide-bearing position, displacing the halide to form an epoxide. This reaction sequence is thus a condensation reaction since there is a net loss of HCl when the two reactant molecules join. If the starting halide is an α-halo a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base (chemistry)
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word "base": '' Arrhenius bases'', '' Brønsted bases'', and '' Lewis bases''. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acid An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...s, as originally proposed by Guillaume-François Rouelle, G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century. In 1884, Svante Arrhenius proposed that a base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous solution to form hydroxide ions OH−. These ions can react with Hydron (chemistry), hydrogen ions (H+ according to Arrhenius) from the dissociation of acids to form water in an acid–base reaction. A base was therefore a metal hydroxide such as NaOH or Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2. Such aqueous hydroxide solutions were also described by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |