|
Esophageal Motility Study
An esophageal motility study (EMS) or esophageal manometry is a test to assess motor function of the upper esophageal sphincter (UES), esophageal body and lower esophageal sphincter (LES). Indications An EMS is typically done to evaluate suspected disorders of motility or peristalsis of the esophagus. These include achalasia, diffuse esophageal spasm, nutcracker esophagus and hypertensive lower esophageal sphincter. These disorders typically present with dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, usually to both solids and liquids even initially. Other patients with spasm disorders may have the test done to diagnose chest pain thought not to be of cardiac cause. The test is not useful for anatomical disorders of the esophagus (that is, disorders that distort the anatomy of the esophagus), such as peptic strictures and esophageal cancer. Procedure A technician places a catheter into the nose and then guides it into the stomach. Once placed in the stomach lining, the catheter is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutcracker Esophagus
Nutcracker esophagus, jackhammer esophagus, or hypercontractile peristalsis, is a disorder of the movement of the esophagus characterized by Peristalsis, contractions in the smooth muscle of the esophagus in a normal sequence but at an excessive amplitude or duration. Nutcracker esophagus is one of several Esophageal motility disorder, motility disorders of the esophagus, including achalasia and esophageal spasm, diffuse esophageal spasm. It causes difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) with both solid and liquid foods, and can cause significant chest pain; it may also be asymptomatic. Nutcracker esophagus can affect people of any age but is more common in the sixth and seventh decades of life. The diagnosis is made by an esophageal motility study (esophageal manometry), which evaluates the pressure of the esophagus at various points along its length. The term "nutcracker esophagus" comes from the finding of increased pressures during peristalsis, with a diagnosis made when press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer (American English) or oesophageal cancer (British English) is cancer arising from the esophagus—the food pipe that runs between the throat and the stomach. Symptoms often include dysphagia, difficulty in swallowing and weight loss. Other symptoms may include odynophagia, pain when swallowing, a hoarseness, hoarse voice, Lymphadenopathy, enlarged lymph nodes ("glands") around the clavicle, collarbone, a dry cough, and possibly hemoptysis, coughing up or hematemesis, vomiting blood. The two main Histopathology, sub-types of the disease are esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma (often abbreviated to ESCC), which is more common in the developing world, and esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), which is more common in the developed world. A number of less common types also occur. Squamous-cell carcinoma arises from the squamous epithelium, epithelial cells that line the esophagus. Adenocarcinoma arises from glandular cells present in the lower third of the esophagus, ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Tests
A medical test is a medical procedure performed to screening (medicine), detect, medical diagnosis, diagnose, or monitoring (medicine), monitor diseases, disease processes, susceptibility, or to determine a course of treatment. Medical tests such as, physical and visual exams, diagnostic imaging, genetic testing, chemical and cellular analysis, relating to clinical chemistry and molecular diagnostics, are typically performed in a Medical laboratory, medical setting. Types of tests By purpose Medical tests can be classified by their purposes, including diagnosis, screening or monitoring. Diagnostic A diagnostic test is a procedure performed to confirm or determine the presence of disease in an individual suspected of having a disease, usually following the report of symptoms, or based on other medical test results. This includes posthumous diagnosis. Examples of such tests are: * Using nuclear medicine to examine a patient suspected of having a lymphoma. * Measuring the blood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anorectal Manometry
Anorectal manometry (ARM) is a medical test used to measure pressures in the anus and rectum and to assess their function. The test is performed by inserting a catheter, that contains a probe embedded with pressure sensors, through the anus and into the rectum. Patients may be asked to perform certain maneuvers, such as coughing or attempting to defecate, to assess for pressure changes. Anorectal manometry is a safe and low risk procedure. From 2014 to 2018, the international anorectal physiology working group (IAPWG) meet several times to develop consensus on indications for anorectal manometry. Their assessment concluded that anorectal manometry was indicated when used in assessment of fecal incontinence, constipation, evacuation disorders (including Hirschsprung's disease), functional anorectal pain and in the assessment of anorectal function preoperatively or after a traumatic obstetric injury. In addition to the indications outlined by the IAPWG, anorectal manometry has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Lumen Imaging Probe
Functional Lumen Imaging Probe (FLIP) is a test used to evaluate the function of the esophagus, by measuring the dimensions of the esophageal lumen using impedance planimetry. Typically performed with sedation during upper endoscopy, FLIP is used to evaluate for esophageal motility disorders, such as achalasia, diffuse esophageal spasm, etc. Procedure FLIP is most often performed immediately following upper endoscopy (EGD). EGD helps to rule out a mechanical obstruction as a cause for symptoms, and also provides an estimation on the distance from the incisors to the EGJ. FLIP uses impedance planimetry to measure the cross sectional area of the esophageal lumen. The FLIP device consists of a balloon that encases a catheter with multiple pairs of impedance electrodes. Two catheter configurations are available, which are 8 cm and 16 cm in length. The 8 cm catheter includes 16 sensors spaced 0.5 cm apart, and is used to evaluate esophagogastric junction (EGJ) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutcracker Esophagus
Nutcracker esophagus, jackhammer esophagus, or hypercontractile peristalsis, is a disorder of the movement of the esophagus characterized by Peristalsis, contractions in the smooth muscle of the esophagus in a normal sequence but at an excessive amplitude or duration. Nutcracker esophagus is one of several Esophageal motility disorder, motility disorders of the esophagus, including achalasia and esophageal spasm, diffuse esophageal spasm. It causes difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) with both solid and liquid foods, and can cause significant chest pain; it may also be asymptomatic. Nutcracker esophagus can affect people of any age but is more common in the sixth and seventh decades of life. The diagnosis is made by an esophageal motility study (esophageal manometry), which evaluates the pressure of the esophagus at various points along its length. The term "nutcracker esophagus" comes from the finding of increased pressures during peristalsis, with a diagnosis made when press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophageal Motility Disorder
An esophageal motility disorder (EMD) is any medical disorder resulting from dysfunction of the coordinated movement of esophagus, which causes dysphagia (i.e. difficulty in swallowing, regurgitation of food). Primary motility disorders are: * Achalasia * Diffuse esophageal spasm * Nutcracker esophagus * Hypertensive lower esophageal sphincter An esophageal motility disorder can also be secondary to other diseases. For example, it may be a result of CREST syndrome, referring to the five main features: calcinosis, Raynaud syndrome, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly and telangiectasia.Winterbauer RH (1964). "Multiple telangiectasia, Raynaud's phenomenon, sclerodactyly, and subcutaneous calcinosis: a syndrome mimicking hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia". Bulletin of the Johns Hopkins Hospital 114: 31–83. . Symptoms The most common symptom of esophageal motility disorders is dysphagia. Compared to causes of mechanical obstruction, which usually coincide with diffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Resolution Manometry
High-resolution manometry (HRM) is a gastrointestinal motility diagnostic system that measures intraluminal pressure activity in the gastrointestinal tract using a series of closely spaced pressure sensors. For a manometry system to be classified as "high-resolution" as opposed to "conventional", the pressure sensors need to be spaced at most 1 cm apart. Two dominant pressure transduction technologies are used: solid state pressure sensors and water perfused pressure sensors. Each pressure transduction technology has its own inherent advantages and disadvantages. HRM systems also require advanced computer hardware and software to store and analyze the manometry data. See also * Functional Lumen Imaging Probe *Anorectal manometry Anorectal manometry (ARM) is a medical test used to measure pressures in the anus and rectum and to assess their function. The test is performed by inserting a catheter, that contains a probe embedded with pressure sensors, through the anus and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-rays
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 Nanometre, nanometers to 10 Picometre, picometers, corresponding to frequency, frequencies in the range of 30 Hertz, petahertz to 30 Hertz, exahertz ( to ) and photon energies in the range of 100 electronvolt, eV to 100 keV, respectively. X-rays were discovered in 1895 in science, 1895 by the German scientist Wilhelm Röntgen, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . X-rays can penetrate many solid substances such as construction materials and living tissue, so X-ray radiography is widely used in medical diagnostics (e.g., checking for Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy (), informally referred to as "fluoro", is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a surgeon to see the internal anatomy, structure and physiology, function of a patient, so that the pumping action of the heart or the motion of swallowing, for example, can be watched. This is useful for both medical diagnosis, diagnosis and therapy and occurs in general radiology, interventional radiology, and image-guided surgery. In its simplest form, a fluoroscope consists of an X-ray generator, X-ray source and a fluorescence, fluorescent screen, between which a patient is placed. However, since the 1950s most fluoroscopes have included X-ray image intensifiers and cameras as well, to improve the image's visibility and make it available on a remote display screen. For many decades, fluoroscopy tended to produce live pictures that were not recorded, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
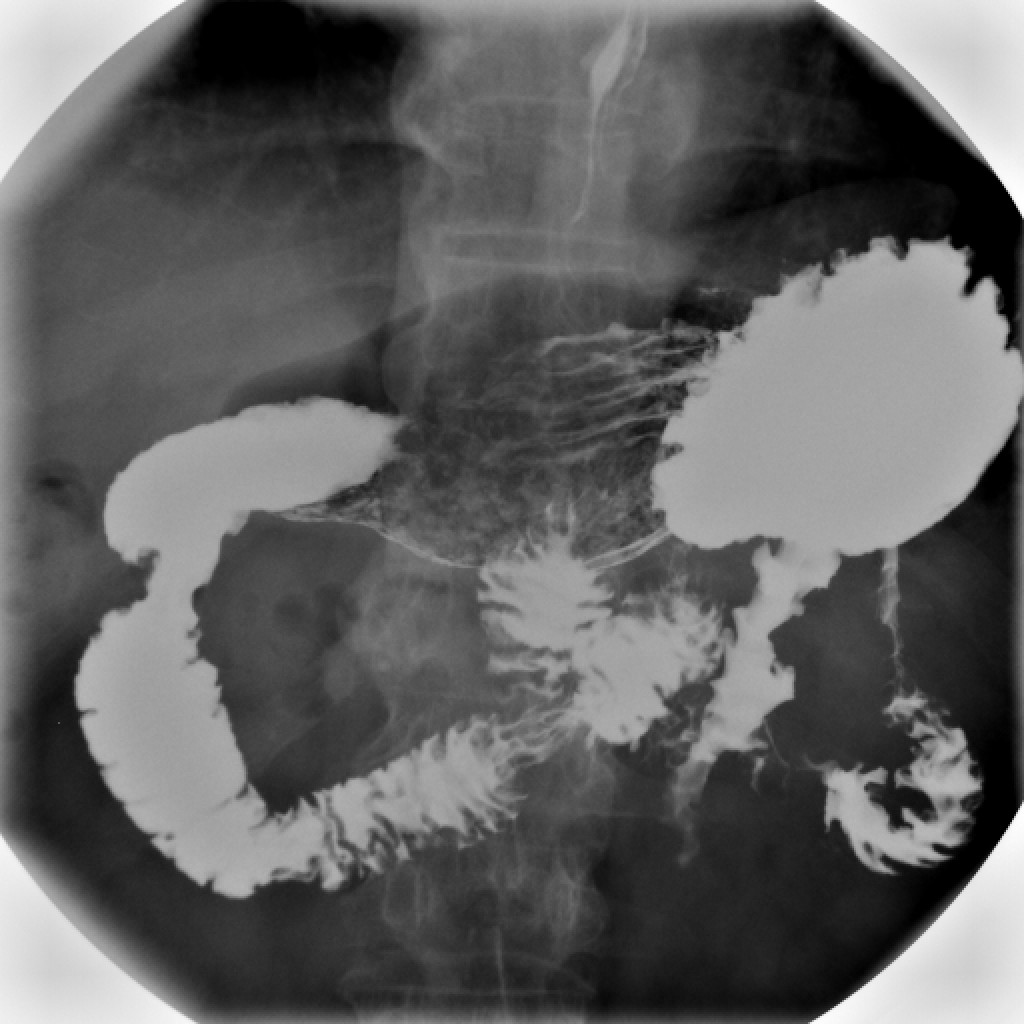
Upper Gastrointestinal Series
An upper gastrointestinal series, also called a barium swallow, barium study, or barium meal, is a series of radiographs used to examine the gastrointestinal tract for abnormalities. A contrast medium, usually a radiocontrast agent such as barium sulfate mixed with water, is ingested or instilled into the gastrointestinal tract, and X-rays are used to create radiographs of the regions of interest. The barium enhances the visibility of the relevant parts of the gastrointestinal tract by coating the inside wall of the tract and appearing white on the film. This in combination with other plain radiographs allows for the imaging of parts of the upper gastrointestinal tract such as the pharynx, larynx, esophagus, stomach, and small intestine such that the inside wall lining, size, shape, contour, and patency are visible to the examiner. With fluoroscopy, it is also possible to visualize the functional movement of examined organs such as swallowing, peristalsis, or sphincter closure. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedation
Sedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure. Examples of drugs which can be used for sedation include isoflurane, diethyl ether, propofol, etomidate, ketamine, pentobarbital, lorazepam and midazolam. Medical uses Sedation is typically used in minor surgical procedures such as endoscopy, vasectomy, or dentistry and for reconstructive surgery, some cosmetic surgeries, removal of wisdom teeth, or for high-anxiety patients. Sedation methods in dentistry include inhalation sedation (using nitrous oxide), oral sedation, and intravenous (IV) sedation. Inhalation sedation is also sometimes referred to as "relative analgesia". Sedation is also used extensively in the intensive care unit so that patients who are being mechanical ventilation, ventilated tolerate having an endotracheal tube in their vertebrate trachea, trachea. It can also be used during a long term brain EEG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |