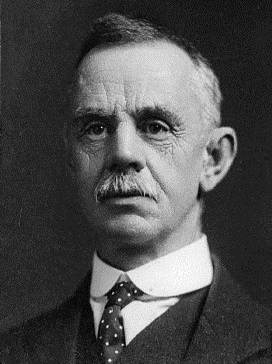|
Ernest Lee
Ernest Page Lee (27 August 1862 – 19 February 1932) was a New Zealand lawyer and politician of the Reform Party. Early life Born in 1862 in Teignmouth, England, he received his education at Cheltenham and London. Aged 18, he started learning the legal trade in a firm of solicitors in the West of England. He was submitted to the Supreme Court of Judicature in 1885. A year later, he emigrated to New Zealand. He settled in Oamaru, and was at first a clerk in a legal firm owned by Thomas William Hislop and Arthur Gethin Creagh. He founded the firm of Lee, Grave and Grave. In 1895 married Miss de Lambert. His sister, Leah Lee, was married to the French poet Jules Laforgue. Political career Lee was elected onto the Oamaru Borough council. In the , he defeated the incumbent in the Oamaru electorate, Thomas Young Duncan. He represented the electorate until 1922, when he was defeated in the 1922 election. The 1922 Oamaru election result was invalidated due to irregularitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1925 New Zealand General Election
The 1925 New Zealand general election was held 4 November (the Māori people, Māori vote had taken place the previous day) to elect a total of 80 MPs to the 22nd New Zealand Parliament, 22nd session of the New Zealand Parliament. The result was a landslide victory for the Reform Party (New Zealand), Reform Party. A total number of 678,877 (90.02%) voters turned out to vote. In one seat (Bay of Plenty (New Zealand electorate), Bay of Plenty) there was only one candidate. In 1922, registration as an elector was made compulsory for all those eligible (except Māori). Results Gordon Coates continued as Prime Minister of New Zealand, Prime Minister, with his Reform Party (New Zealand), Reform Party winning an outright majority of 30. Leonard Isitt (minister), Leonard Isitt and George Witty were both appointed to the New Zealand Legislative Council, Legislative Council by Gordon Coates on 28 October 1925; shortly before the election on 4 November. Both were New Zealand Liberal Part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minister Of Police (New Zealand) ...
The Minister of Police is the minister in the New Zealand Government with responsibility for the New Zealand Police. The current officeholder is Mark Mitchell. History Initially, responsibility for the police force had rested with the Minister of Defence but was instead allocated to the Minister of Justice in 1896. The minister responsible for police was, for the most part, the holder of either aforementioned office until it was later split into a separate full ministerial portfolio in 1969. List of Police Ministers The following ministers have held the office of Minister of Police. ;Key Notes References * External linksNew Zealand Police {{DEFAULTSORT:Minister Of Police (New Zealand) Police The police are Law enforcement organization, a constituted body of Law enforcement officer, people empowered by a State (polity), state with the aim of Law enforcement, enforcing the law and protecting the Public order policing, public order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
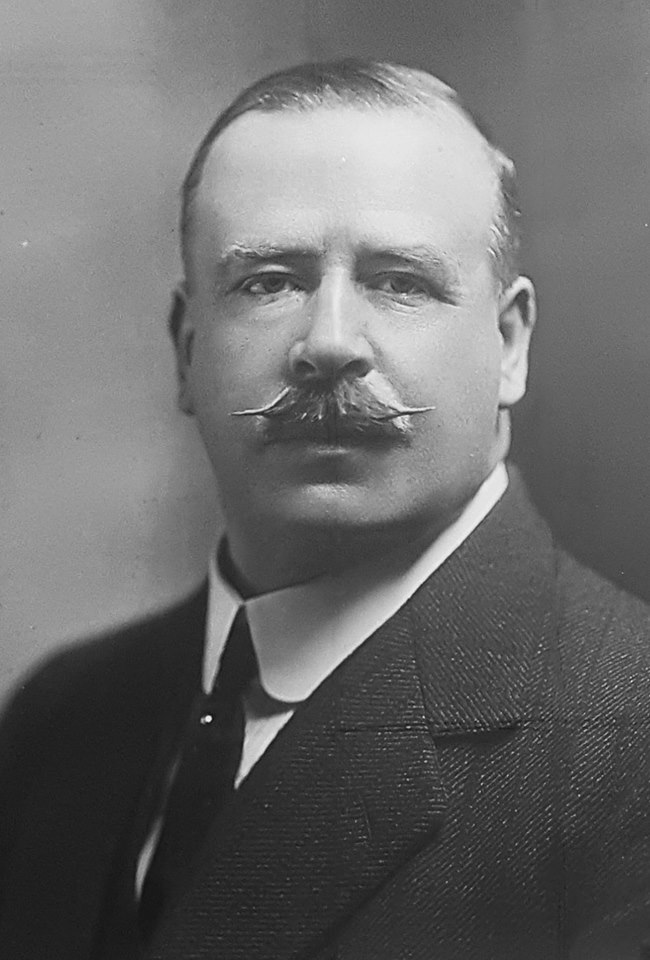
William Massey
William Ferguson Massey (26 March 1856 – 10 May 1925) was a politician who served as the 19th prime minister of New Zealand from May 1912 to May 1925. He was the founding leader of the Reform Party, New Zealand's second organised political party, from 1909 until his death. Massey was born in County Londonderry in Ireland. After migrating to New Zealand in 1870, Massey farmed near Auckland (earning his later nickname, ''Farmer Bill'') and assumed leadership in farmers' organisations. He entered parliament in 1894 as a conservative, and from 1894 to 1912 was a leader of the conservative opposition to the Liberal ministries of Richard Seddon and Joseph Ward. Massey became the first Reform Party Prime Minister after he led a successful motion of no confidence against the Liberal government. Throughout his political career Massey was known for the particular support he showed for agrarian interests, as well as his opposition to organised labour. He pledged New Zealand's suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Bell (New Zealand Politician)
Sir Francis Henry Dillon Bell (31 March 1851 – 13 March 1936) was a New Zealand lawyer and politician who served as the 20th prime minister of New Zealand from 14 to 30 May 1925. He was the first New Zealand-born prime minister, holding office in a caretaker capacity following the death of William Massey. The second Jewish person to become prime minister, Bell was born in Nelson. His father, Sir Dillon Bell, was also a politician. Bell attended Auckland Grammar School and Otago Boys' High School before going on to St John's College, Cambridge. He returned to New Zealand to practise law, settling in Wellington and eventually becoming president of the New Zealand Law Society. Bell served as Mayor of Wellington from 1891 to 1893 and from 1896 to 1897. He was elected to the House of Representatives in 1893, after two previous defeats, but served only a single term before retiring in 1896 to return to the legal profession. In 1912, Bell was appointed to the Legislative Council as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordon Coates
Joseph Gordon Coates (3 February 1878 – 27 May 1943) served as the 21st prime minister of New Zealand from 1925 to 1928. He was the third successive Reform prime minister since 1912. Born in rural Northland, Coates grew up on a farm, which he took charge of at a young age due to his father's mental illness, before becoming a member of Parliament in 1911. He maintained a focus on farming issues and stood as an independent candidate. After distinguished service during World War I, he was appointed as Minister of Justice and Postmaster-General in the Reform government of William Massey (1919); he served as Minister of Public Works (1920–26) and Native Affairs (1921–28) and became prime minister in 1925 on Massey's death. Defeated in the elections of 1928, Coates returned to government in 1931 as the key figure in the coalition government of George Forbes. Serving as Minister of Public Works (1931–33) and of Finance (1933–35), he instituted rigorous policies to combat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Internal Affairs (New Zealand)
The Department of Internal Affairs (DIA; ) is the public service department of New Zealand charged with issuing passports; administering applications for citizenship and lottery grants; enforcing censorship and gambling laws; registering births, deaths, marriages and civil unions; supplying support services to ministers; and advising the government on a range of relevant policies and issues. Other services provided by the department include a translation service, publication of the ''New Zealand Gazette'' (the official government newspaper), a flag hire service, management of VIP visits to New Zealand, running the Lake Taupō harbourmaster's office (under a special agreement with the local iwi) and the administration of offshore islands. History 19th century The Department of Internal Affairs traces its roots back to the Colonial Secretary's Office, which from the time New Zealand became a British colony, in 1840, was responsible for almost all central government duties. The d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queenstown, New Zealand
Queenstown () is a resort town in Otago in the south-west of New Zealand's South Island. It is the seat and largest town in the Queenstown-Lakes District. The town located on the northwestern edge of Lake Wakatipu, a long, thin, Z-shaped lake formed by glacial processes, and has views of nearby mountains such as The Remarkables, Cecil Peak, Walter Peak (New Zealand), Walter Peak and just above the town, Ben Lomond (Otago), Ben Lomond and Queenstown Hill. Queenstown is known for its tourism businesses, especially adventure and ski tourism. Toponymy ''Tāhuna'', the Māori-language, ''te reo'' name for Queenstown, means 'shallow bay'. There are various Apocrypha (fiction), apocryphal accounts of how Queenstown gained its name, of which the following appears to be the most likely: There was then a public meeting to name the ''township on the lake'' in January 1863 (probably the weekend of the 3rd and 4th) in which the town was officially given the name of ''Queenstown'' in re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Wakatipu
Lake Wakatipu () is an inland lake (finger lake) in the South Island of New Zealand. It is in the southwest corner of the Otago region, near its boundary with Southland, New Zealand, Southland. ''Lake Wakatipu'' comes from the original Māori language, Māori name . With a length of , it is New Zealand's longest lake, and, at , its List of lakes in New Zealand#Largest lakes, third largest. The lake is also very deep, its floor being below sea level (−110 metres), with a maximum depth of . It is at an altitude of , towards the southern end of the Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana. The general topography is a reversed "N" shape or "dog leg". The Dart River / Te Awa Whakatipu flows into the northern end, the lake then runs south for 30 kilometres before turning abruptly to the east. further along, it turns sharply to the south, reaching its southern end further south, near Kingston, New Zealand, Kingston. At the north end of the lake is the settlement of Glenorchy, New Ze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Alps (New Zealand)
The Southern Alps (; officially Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana) are a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side. The name "Southern Alps" generally refers to the entire range, although separate names are given to many of the smaller ranges that form part of it. The range includes the South Island's Main Divide, which separates the water catchments of the more heavily populated eastern side of the island from those on the west coast. Politically, the Main Divide forms the boundary between the Marlborough, Canterbury and Otago regions to the southeast and the Tasman and West Coast regions to the northwest. Names The Māori name of the range is , meaning "the Mirage of the Ocean". The English explorer James Cook bestowed the name ''Southern Alps'' on 23 March 1770, admiring their "prodigious height". p. 384. They had previously been noted by Abel Tasman in 1642, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reform Government Of New Zealand
The Reform Government of New Zealand was the government of New Zealand from 1912 to 1928, led by the conservative Reform Party. It is probably best remembered for its anti-trade union stance in the Waihi miners' strike of 1912 and a dockworkers' strike the following year. It governed during World War I, during which a temporary coalition was formed with the Liberal Party. Significant policies Industrial * Sided with employers in the 1912 Waihi miners' strike and the waterfront workers' strike of 1913. In the latter strike, civilians enrolled as ' special constables' became known as 'Massey's Cossacks'. * The Board of Trade Act (1919) gave government the power to regulate industries "in the interests of economic welfare".Poverty and Progress in New Zealand: A Re-assessment by William Ball Sutch Public service * The Public Service Act (1912) put a commissioner at the head of the public service and replaced political patronage over appointments and inconsistency between departm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minister Of Industries And Commerce
The Minister of Industries and Commerce in New Zealand New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ... is a former cabinet position (existing from 1894 to 1972) appointed by the Prime Minister to be in charge of matters of industrial and commercial growth and trade. In 1972 it was replaced with the new office of Minister of Trade and Industry. List of ministers The following ministers have held the office of Minister of Industries and Commerce. ;Key Notes References * {{NZ ministerial portfolios Industries and Commerce Political office-holders in New Zealand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |