|
Eriodictyon Traskiae
''Eriodictyon traskiae'' is a species of flowering plant in the waterleaf family known by the common names Pacific yerba santa and Trask's yerba santa. Description ''Eriodictyon traskiae'' approaches a maximum height of two meters. Its twigs and foliage are covered in a dense coat of white woolly hairs, giving the bush a gray-green look. The leaves are oval and anywhere from 3 to 14 centimeters long and 1 to 7 wide. They are woolly and crinkled and the edges roll under, and they may have small teeth. The bush flowers in dense fuzzy bunches of white to brownish-purple glandular blossoms, each under a centimeter wide. The fruit is a tiny capsule up to three millimeters wide containing two to four minute seeds. Distribution This shrub is endemic to California, where it grows on the chaparral slopes of the central Coast Ranges The Pacific Coast Ranges (officially gazetted as the Pacific Mountain System in the United States) are the series of mountain ranges that stretch along t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alice Eastwood
__NOTOC__ Alice Eastwood (January 19, 1859 – October 30, 1953) was a Canadian American botanist. She is credited with building the botanical collection at the California Academy of Sciences, in San Francisco. She published over 310 scientific articles and authored 395 land plant species names, the fourth-highest number of such names authored by any female scientist. There are seventeen currently recognized species named for her, as well as the genera '' Eastwoodia'' and '' Aliciella''. Biography Alice Eastwood was born on January 19, 1859, in Toronto, Canada, to Colin Skinner Eastwood and Eliza Jane Gowdey Eastwood. When she was six her mother died. The children were cared for by various relatives, and for a time, Alice and her sister were placed at the Oshawa Convent in Toronto. The family reunited with their father and moved to Denver, Colorado, in 1873. In 1879, she graduated as valedictorian from East Denver High School. For the next ten years, Eastwood would teach at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrub
A shrub (often also called a bush) is a small-to-medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees by their multiple stems and shorter height, less than tall. Small shrubs, less than 2 m (6.6 ft) tall are sometimes termed as subshrubs. Many botanical groups have species that are shrubs, and others that are trees and herbaceous plants instead. Some definitions state that a shrub is less than and a tree is over 6 m. Others use as the cut-off point for classification. Many species of tree may not reach this mature height because of hostile less than ideal growing conditions, and resemble a shrub-sized plant. However, such species have the potential to grow taller under the ideal growing conditions for that plant. In terms of longevity, most shrubs fit in a class between perennials and trees; some may only last about fiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example ''Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. ''Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the most populated subnational entity in North America and the 34th most populous in the world. The Greater Los Angeles area and the San Francisco Bay Area are the nation's second and fifth most populous urban regions respectively, with the former having more than 18.7million residents and the latter having over 9.6million. Sacramento is the state's capital, while Los Angeles is the most populous city in the state and the second most populous city in the country. San Francisco is the second most densely populated major city in the country. Los Angeles County is the country's most populous, while San Bernardino County is the largest county by area in the country. California borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
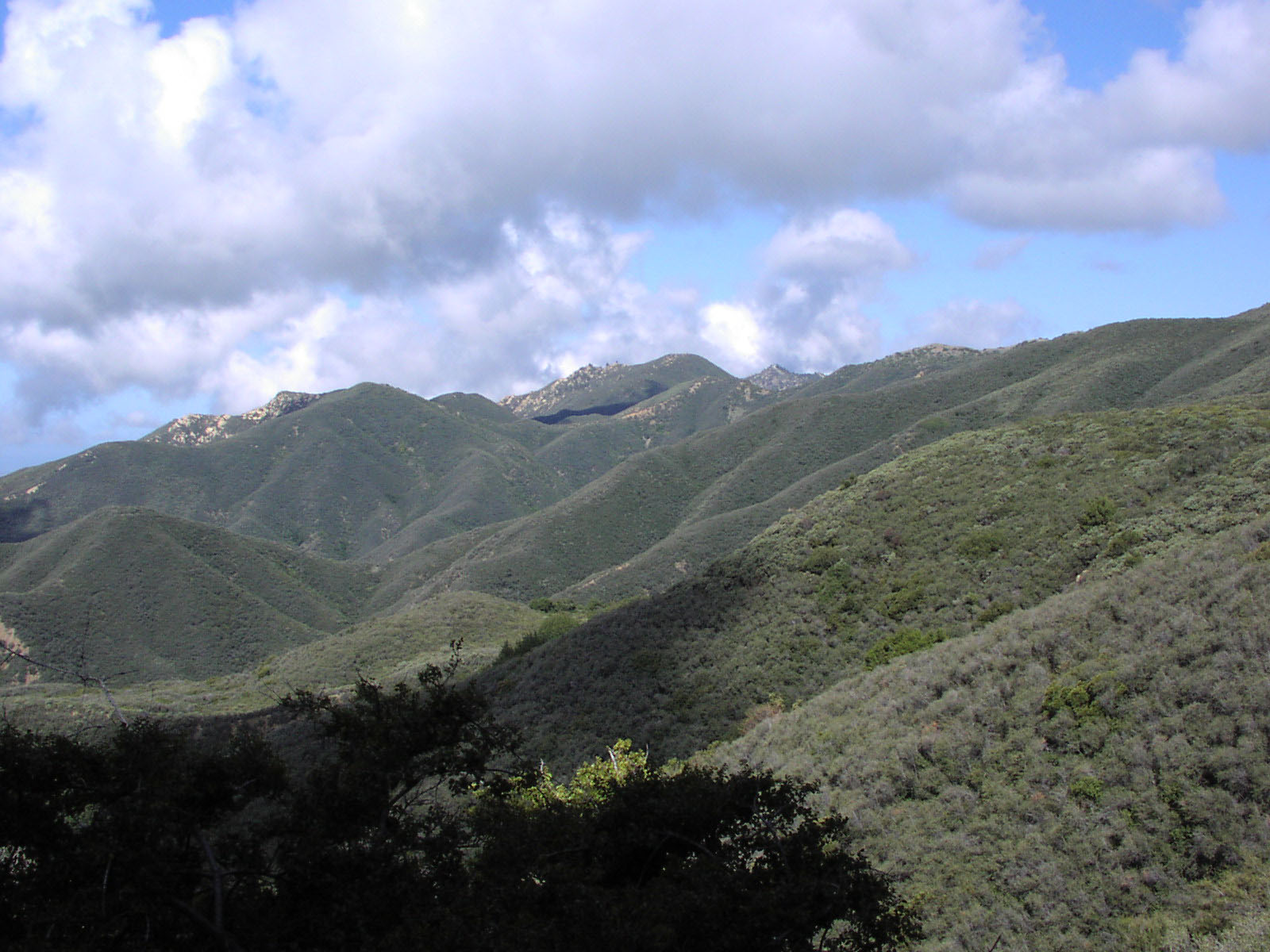
Chaparral
Chaparral ( ) is a shrubland plant community and geographical feature found primarily in the U.S. state of California, in southern Oregon, and in the northern portion of the Baja California Peninsula in Mexico. It is shaped by a Mediterranean climate (mild wet winters and hot dry summers) and infrequent, high-intensity crown fires. Chaparral features summer-drought-tolerant plants with hard sclerophyllous evergreen leaves, as contrasted with the associated soft-leaved, drought-deciduous, scrub community of coastal sage scrub, found often on drier, southern facing slopes within the chaparral biome. Three other closely related chaparral shrubland systems occur in central Arizona, western Texas, and along the eastern side of central Mexico's mountain chains (mexical), all having summer rains in contrast to the Mediterranean climate of other chaparral formations. Chaparral comprises 9% of California's wildland vegetation and contains 20% of its plant species. The name comes fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
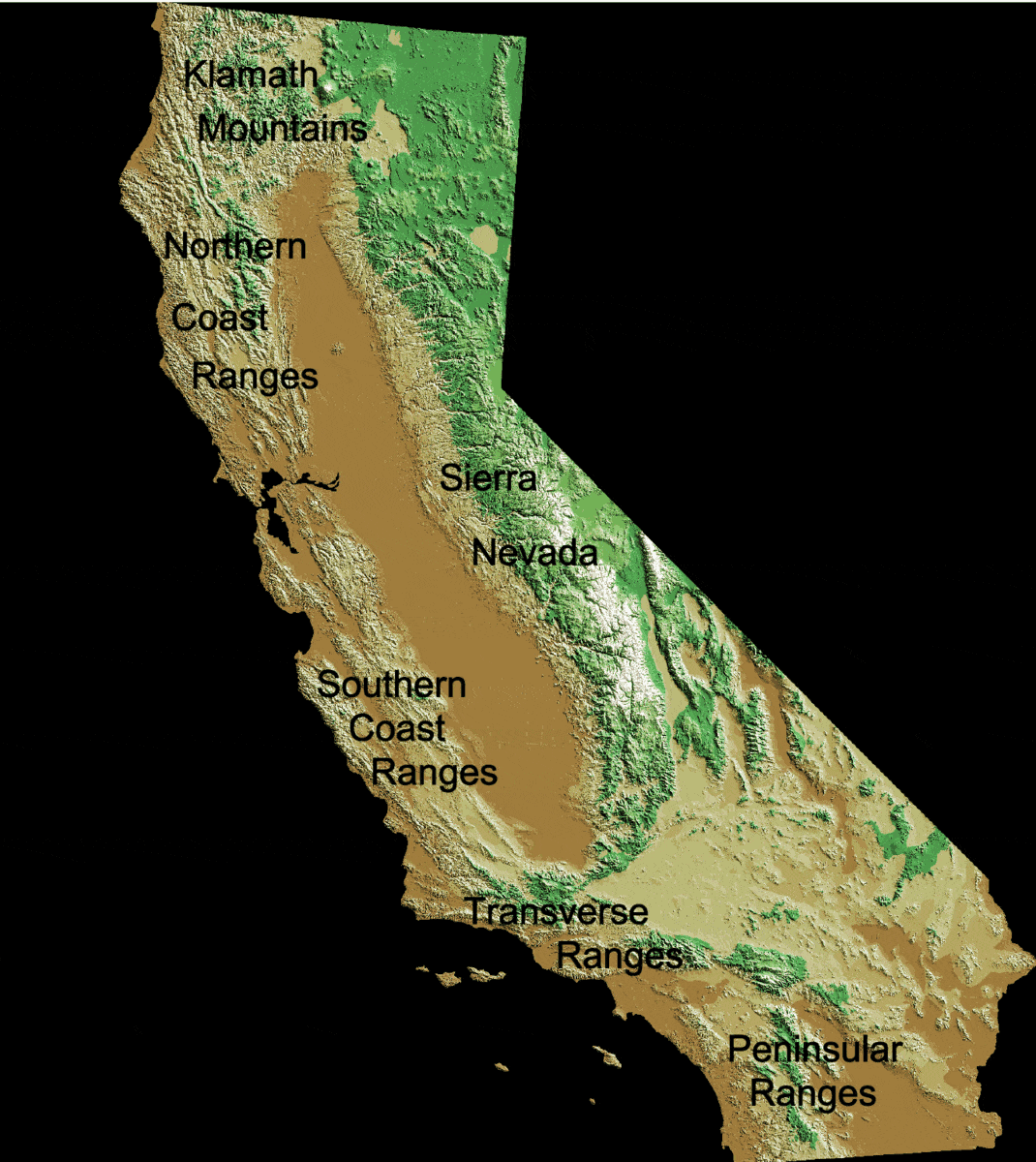
California Coast Ranges
The Coast Ranges of California span from Del Norte or Humboldt County, California, south to Santa Barbara County. The other three coastal California mountain ranges are the Transverse Ranges, Peninsular Ranges and the Klamath Mountains. Physiographically, they are a section of the larger Pacific Border province, which in turn is part of the larger Pacific Mountain System physiographic division. UNESCO has included the " California Coast Ranges Biosphere Reserve" in its Man and the Biosphere Programme of World Network of Biosphere Reserves since 1983. * Physiography The northern end of the California Coast Ranges overlap the southern end of the Klamath Mountains for approximately 80 miles on the west. They extend southward for more than 600 miles to where the coastline turns eastward along the Santa Barbara Channel, around the area of Point Conception. Here the southern end meets the Los Angeles Transverse Ranges, or ''Sierras de los Angeles''. The rocks themselves that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern California
Southern California (commonly shortened to SoCal) is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. It includes the Los Angeles metropolitan area, the second most populous urban agglomeration in the United States. The region generally contains ten of California's 58 counties: Imperial, Kern, Los Angeles, Orange, Riverside, San Bernardino, San Diego, Santa Barbara, San Luis Obispo and Ventura counties. The Colorado Desert and the Colorado River are located on Southern California's eastern border with Arizona, and San Bernardino County shares a border with Nevada to the northeast. Southern California's southern border with Baja California is part of the Mexico–United States border. Constituent metropolitan areas Southern California includes the heavily built-up urban area which stretches along the Pacific coast from Ventura through Greater Los Angeles down to Greater San Diego (the contiguous urban area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Ranges
The Transverse Ranges are a group of mountain ranges of southern California, in the Pacific Coast Ranges physiographic region in North America. The Transverse Ranges begin at the southern end of the California Coast Ranges and lie within Santa Barbara, Ventura, Los Angeles, San Bernardino, Riverside and Kern counties. The Peninsular Ranges lie to the south. The name Transverse Ranges is due to their east–west orientation, making them transverse to the general northwest–southeast orientation of most of California's coastal mountains.Dibblee Jr, T.W., 1982. Regional geology of the Transverse Ranges Province of southern California. ''Geology and mineral wealth of the California Transverse Ranges'', ''10'', pp.7-26. The ranges extend from west of Point Conception eastward approximately 500 kilometers into the Mojave and Colorado Desert. The geology and topography of the ranges express three distinct segments that have contrasting elevations, rock types, and vegetation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eriodictyon
''Eriodictyon'' is a genus of plants known by the common name yerba santa within the Hydrophylloideae subfamily of the borage family, Boraginaceae. They are distributed throughout the southwestern United States and Mexico. Description Most species grow as either perennial herbs or shrubs. They grow in a prostrate to ascending or erect stance. The stems are characterized by shredding barking. The leaves are cauline and alternate. The inflorescence is generally open and terminal. The corolla is funnel to urn shaped, and white, lavender or purple, and generally hairy on the abaxial surface. The sexual organs of the plant, including the stamens, filaments, and ovaries, are also generally hairy.. Accessed 14 December 2021 The fruits are 1 to 3 mm wide. The fruits are schizocarpic, and not all mericarpids are fertile. The seeds are striated, and colored a dark brown or black. Taxonomy Etymology It includes California yerba santa (''Eriodictyon californica''), along with other s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Flora Of California
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example ''Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. ''Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History Of The California Chaparral And Woodlands
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena. The word ''nature'' is borrowed from the Old French ''nature'' and is derived from the Latin word ''natura'', or "essential qualities, innate disposition", and in ancient times, literally meant " birth". In ancient philosophy, ''natura'' is mostly used as the Latin translation of the Greek word '' physis'' (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics of plants, animals, and other features of the world to develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)