|
Ericiolacerta
''Ericiolacerta'' is an extinct genus of small therocephalian therapsids from the early Triassic of South Africa and Antarctica. ''Ericiolacerta,'' meaning "hedgehog lizard" (from the Latin ''ericius'', "hedgehon" and ''lacerta'', "lizard"), was named by D.M.S. Watson in 1931. The species ''E. parva'' is known from the holotype specimen which consists of a nearly complete skeleton found in the ''Lystrosaurus'' Assemblage Zone within the Katberg Formation of the Beaufort Group in South Africa, and from a partial jaw found in the Lower Triassic Fremouw Formation in Antarctica. ''Ericiolacerta'' was around in length, with long limbs and relatively small teeth. It probably ate insects and other small invertebrates. The therocephalians – therapsids with mammal-like heads – were abundant in Permian times, but only a few made it into the Triassic. ''Ericiolacerta'' was one of those. It is possible that they gave rise to the cynodonts, the only therapsid group to survive into post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fremouw Formation
The Fremouw Formation is a Triassic-age rock formation in the Transantarctic Mountains of the Ross Depenency of Antarctica. It contains the oldest known fossils of tetrapods from Antarctica, including synapsids, reptiles and amphibians. Fossilized trees have also been found. The formation's beds were deposited along the banks of rivers and on floodplains. During the Triassic, the area would have been a riparian forest at 70–75°S latitude. Stratigraphy The Fremouw Formation is mostly Triassic in age, with the oldest rocks dating back to the latest Permian. Much of the formation is quartzose sandstone that was deposited in stream beds. It overlies the Permian Buckley Formation, which consists of coal and '' Glossopteris'' fossils. The formation is informally divided into lower, middle, and upper units. Most fossils are found in the Lower Fremouw Formation. Here, bones are preserved in fine-grained siltstones and mudstones, coarse-grained channel sandstones, and conglomerate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baurioidea
Baurioidea is a superfamily of therocephalian therapsids. It includes advanced therocephalians such as ''Regisaurus'' and ''Bauria''. The superfamily was named by South African paleontologist Robert Broom in 1911. Bauriamorpha, named by D. M. S. Watson and Alfred Romer in 1956, is a junior synonym of Baurioidea. Many baurioids were once placed in a group called Scaloposauria. Scaloposaurs were characterized by their small size and reduced postorbital bar (a strut of bone behind the eye socket). Scaloposauria is no longer recognized as a valid taxon because it likely represents juvenile forms of many groups of therocephalians. Most scaloposaurs, including ''Scaloposaurus'' and ''Regisaurus'', are now classified in various positions within Bauroidea. Many therocephalians once classified as scaloposaurians are now considered basal baurioids. The classification of these species is uncertain, as there have been no comprehensive phylogenetic analyses of scaloposaurian taxa. The val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 251.9 Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Trias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoological Society Of London
The Zoological Society of London (ZSL) is a charity and organization devoted to the worldwide animal conservation, conservation of animals and their habitat conservation, habitats. It was founded in 1826. Since 1828, it has maintained London Zoo, and since 1931 Whipsnade Zoo. History On 29 November 1822, the birthday of John Ray, "the father of modern zoology", a meeting held in the Linnean Society in Soho Square led by Rev. William Kirby (entomologist), William Kirby, resolved to form a "Zoological Club of the Linnean Society of London". Between 1816 and 1826, discussions between Stamford Raffles, Humphry Davy, Joseph Banks and others led to the idea that London should have an establishment similar to the Jardin des Plantes in Paris. It would house a zoological collection "which should interest and amuse the public." The society was founded in April 1826 by Stamford Raffles, Sir Stamford Raffles, the Henry Petty-Fitzmaurice, 3rd Marquess of Lansdowne, Marquess of Lansdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
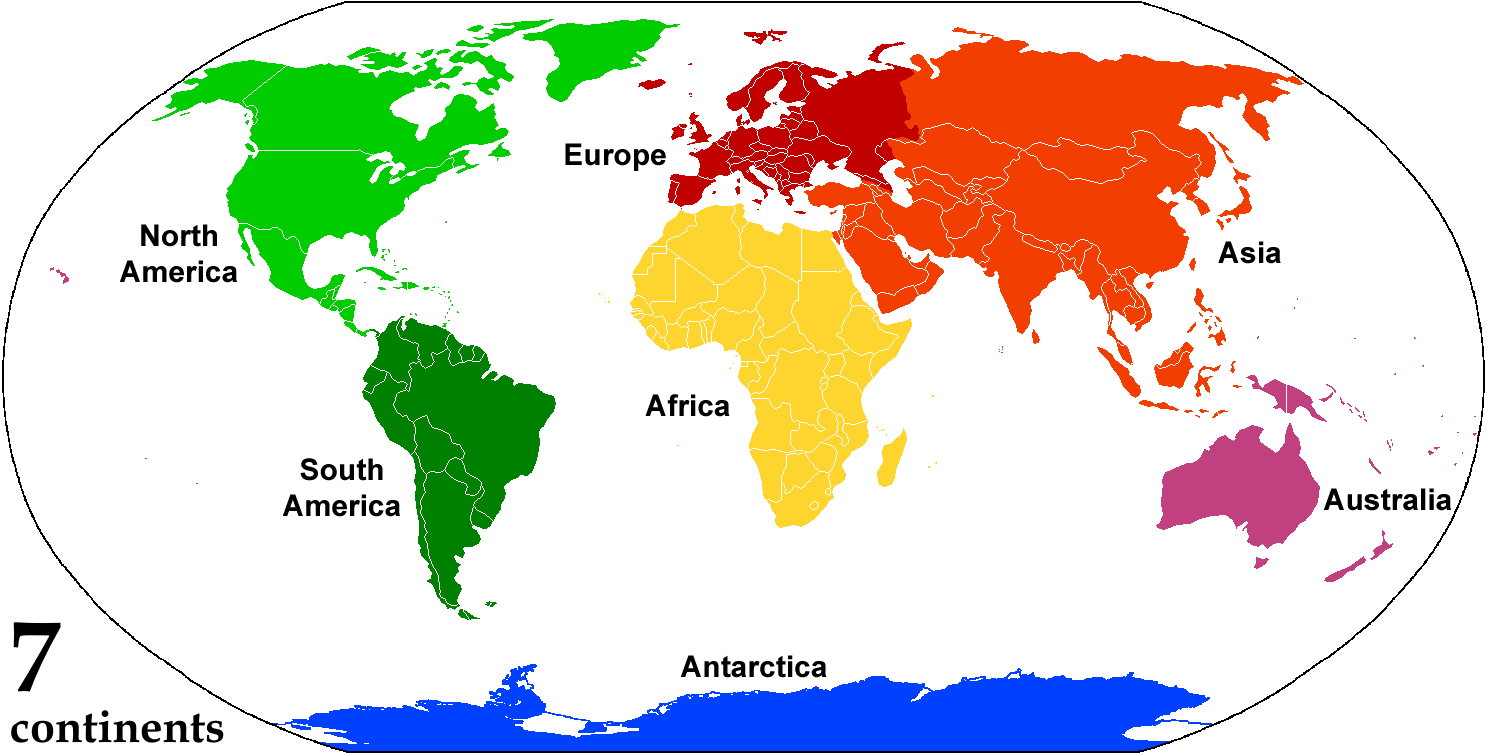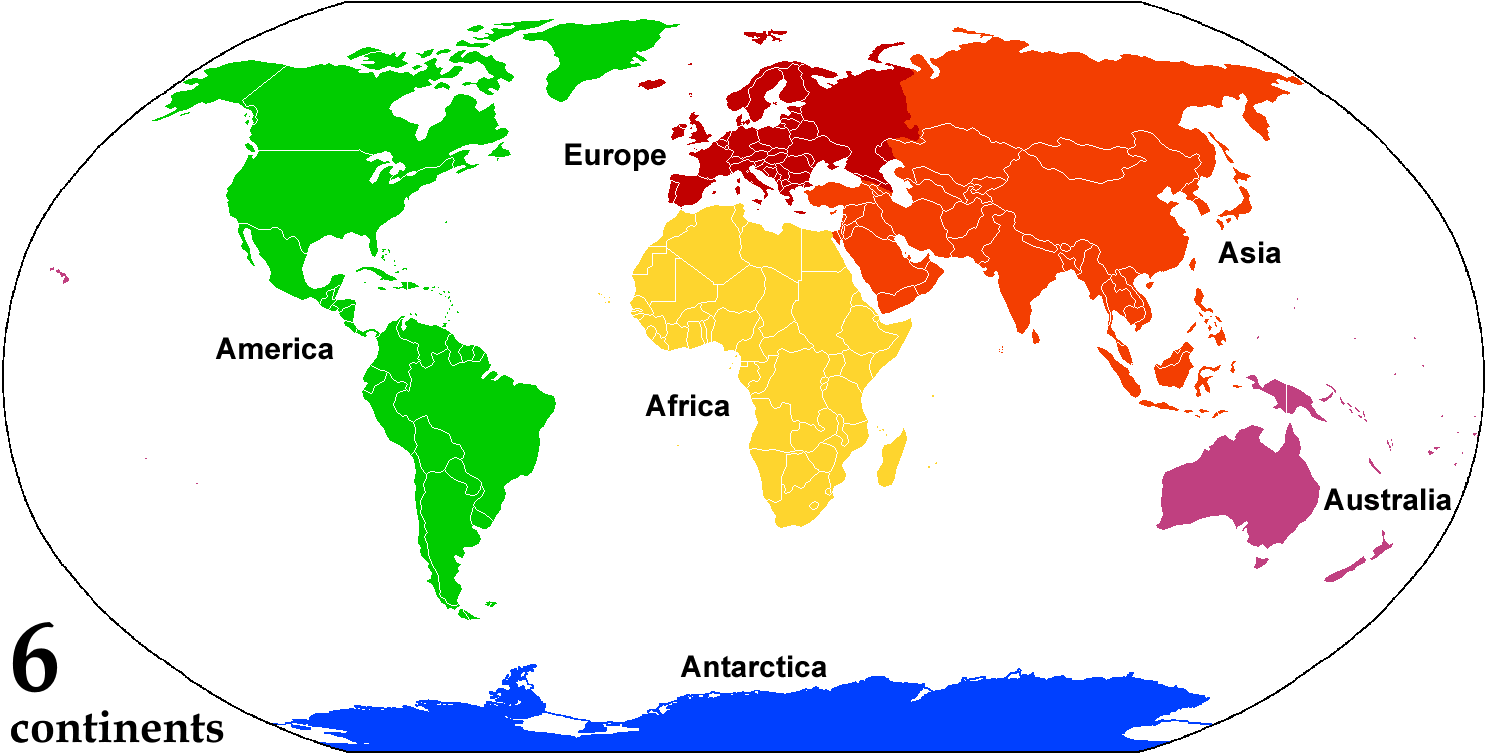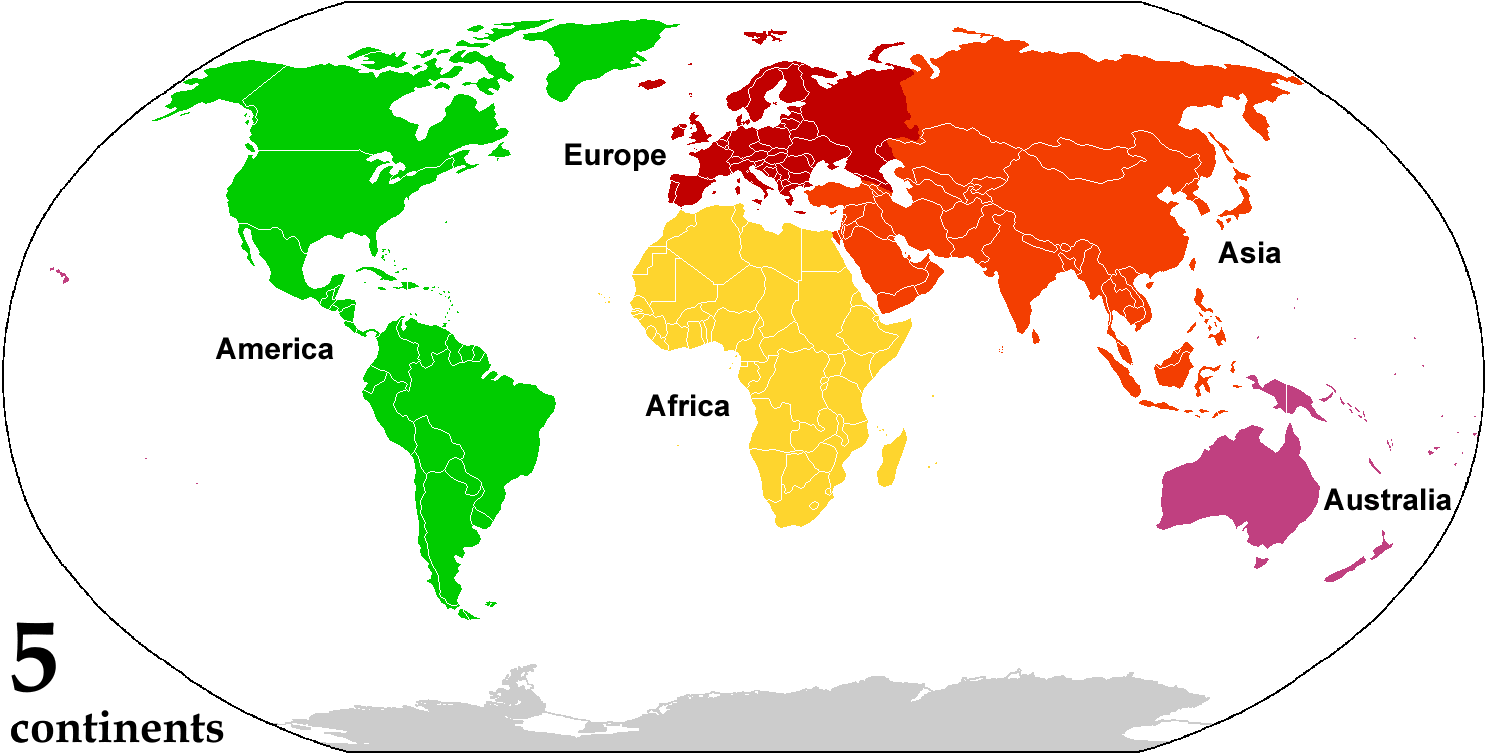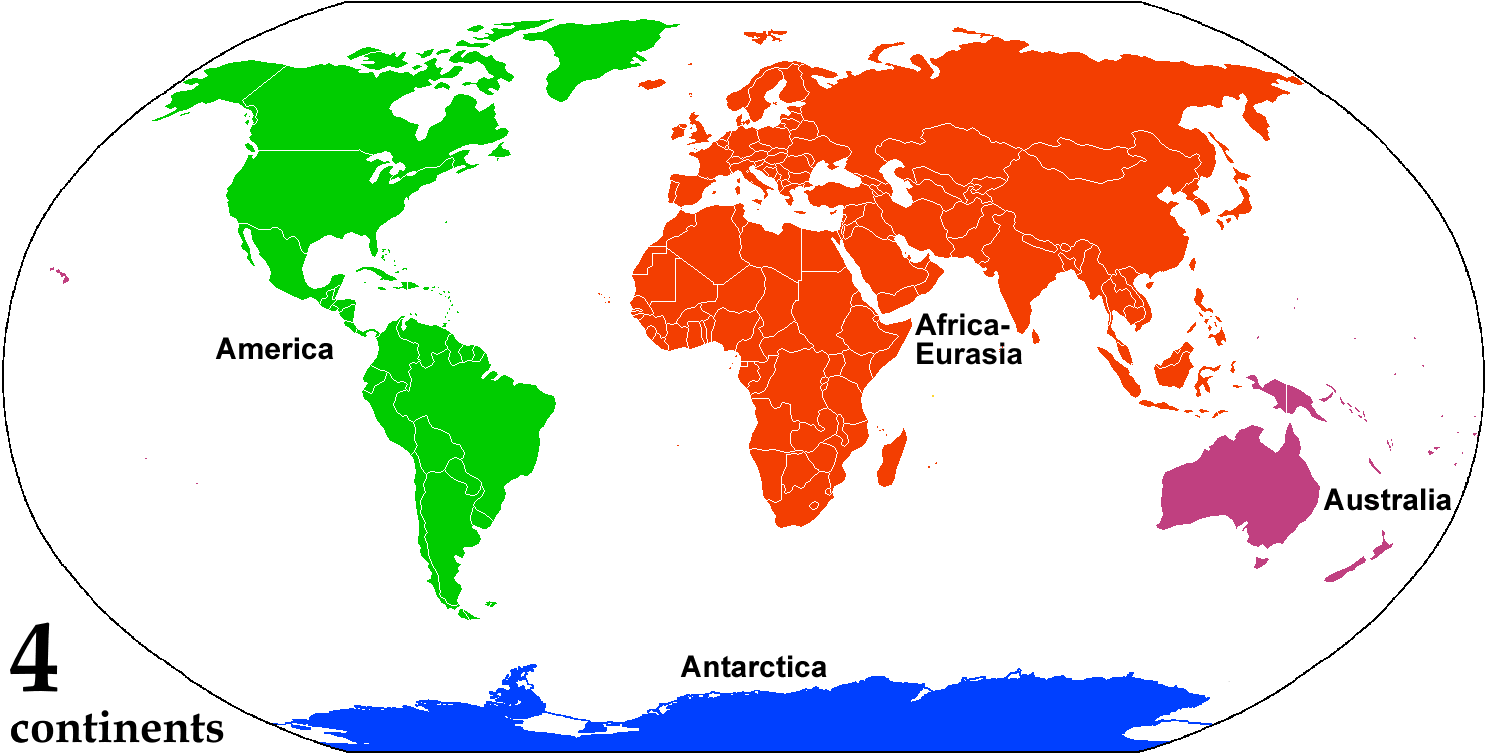
Continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as in the case of Asia or Europe within Eurasia, or a landmass and nearby islands within its continental shelf. Due to these varying definitions, the number of continents varies; up to seven or as few as four geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Most English-speaking world, English-speaking countries recognize seven regions as continents. In order from largest to smallest in area, these seven regions are Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia (continent), Australia (sometimes called Oceania or Australasia). Different variations with fewer continents merge some of these regions; examples of this are merging Asia and Europe into Eurasia, "Most people recognize seven continents—Asia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lystrosaurus
''Lystrosaurus'' (; 'shovel lizard'; proper Ancient Greek is ''lístron'' ‘tool for leveling or smoothing, shovel, spade, hoe’) is an extinct genus of herbivorous dicynodont therapsids from the late Permian and Early Triassic epochs (around 248 million years ago). It lived in what is now Antarctica, India, China, Mongolia, European Russia and South Africa. Four to six species are currently recognized, although from the 1930s to 1970s the number of species was thought to be much higher. They ranged in size from that of a small dog to 8 feet (2.5 meters) long. As a dicynodont, ''Lystrosaurus'' had only two teeth (a pair of tusk-like canines), and is thought to have had a horny beak that was used for biting off pieces of vegetation. ''Lystrosaurus'' was a heavily built, herbivorous animal. The structure of its shoulders and hip joints suggests that ''Lystrosaurus'' moved with a semi-sprawling gait. The forelimbs were even more robust than the hindlimbs, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentition
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiology (that is, the relationship between the shape and form of the tooth in question and its inferred function) of the teeth of an animal. Terminology Animals whose teeth are all of the same type, such as most non-mammalian vertebrates, are said to have '' homodont'' dentition, whereas those whose teeth differ morphologically are said to have '' heterodont'' dentition. The dentition of animals with two successions of teeth (deciduous, permanent) is referred to as '' diphyodont'', while the dentition of animals with only one set of teeth throughout life is ''monophyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are continuously discarded and replaced throughout life is termed '' polyphyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Kitching
James William Kitching (6 February 1922 – 24 December 2003) was a South African vertebrate palaeontologist and regarded as one of the world’s greatest fossil finders. Career His work in the southern hemisphere, including Antarctica, led to the establishment of one of the world's finest fossil collections, housed at the Bernard Price Institute for Palaeontological Research (BPI) in Johannesburg.University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, Bernard Price Institute He contributed greatly to the Karoo palaeontology of southern |
Edwin H
The name Edwin means "wealth-friend". It comes from (wealth, good fortune) and (friend). Thus the Old English form is Ēadwine, a name widely attested in early medieval England. Edwina The name Edwina is a feminine form of the male name Edwin, which derives from Old English and means "rich friend." Edwin was a popular name until the time of the Norman Conquest, then fell out of favour until Victorian era, Victorian times. People ... is the feminine form of the name. Notable people and characters with the name include: Historical figures * Edwin of Northumbria (died 632 or 633), King of Northumbria and Christian saint * Edwin (son of Edward the Elder) (died 933) * Eadwine of Sussex (died 982), Ealdorman of Sussex * Eadwine of Abingdon (died 990), Abbot of Abingdon * Edwin, Earl of Mercia (died 1071), brother-in-law of Harold Godwinson (Harold II) * Edwin Sandys (bishop) (1519–1588), Archbishop of York Modern era * E. W. Abeygunasekera, Sri Lankan Sinhala politi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shackleton Glacier
Shackleton Glacier () is a major Antarctic glacier, over long and from wide, descending from the Antarctic Plateau from the vicinity of Roberts Massif and flowing north through the Queen Maud Mountains to enter the Ross Ice Shelf between Mount Speed and Waldron Spurs. Discovered by the United States Antarctic Service (USAS) (1939–41) and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Sir Ernest Shackleton, British Antarctic explorer. Course The Shackleton Glacier originates in the East Antarctic Ice Sheet and flows northeast between Dismal Buttress to the northwest and Roberts Massif to the southeast. It is joined from the right (east) by Zaneveld Glacier, which also originates in the ice sheet. Further north it is joined from the right by the Logie Glacier, which flows west through the Cumulus Hills. Flowing north, the Shackleton Glacier is joined from the left (west) by the Gallup Glacier and the Baldwin Glacier and from the right (east) by McGregor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transantarctic Mountains
The Transantarctic Mountains (abbreviated TAM) comprise a mountain range of uplifted rock (primarily sedimentary) in Antarctica which extends, with some interruptions, across the continent from Cape Adare in northern Victoria Land to Coats Land. These mountains divide East Antarctica and West Antarctica. They include a number of separately named mountain groups, which are often again subdivided into smaller ranges. The range was first sighted by James Clark Ross in 1841 at what was later named the Ross Ice Shelf in his honour. It was first crossed during the British National Antarctic Expedition of 1901-1904. Geography The mountain range stretches between the Ross Sea and the Weddell Sea, the entire width of Antarctica, hence the name. With a total length of about , the Transantarctic Mountains are one of the longest mountain ranges on Earth. The Antarctandes are even longer, having in common with the Transantarctic Mountains the ranges from Cape Adare to the Queen M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |