|
Eric Scerri
Eric R. Scerri (born August 30, 1953) is an American chemist, writer and philosopher of science of Maltese origin. He is a lecturer at the University of California, Los Angeles; and the founder and editor-in-chief of '' Foundations of Chemistry'', an international peer reviewed journal covering the history and philosophy of chemistry, and chemical education.Rocke A 2012,A place at the periodic table' '' The Times Higher Education Supplement'', 15 AugustUCLA Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry 2013, 'Scerri, Eric R.', University of California. For current biographical information see the home page oEric Scerri/ref> He is an authority on the history and philosophy of the periodic table and is the author and editor of several books in this and related fields.Sella A 2013,An elementary history lesson' ''New Scientist'', 13 August Scerri was a participant in the 2014 PBS documentary film, '' The Mystery of Matter''. Scerri attended Walpole Grammar School in Ealing. He recei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California, Los Angeles
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Its academic roots were established in 1881 as a normal school then known as the southern branch of the California State Normal School which later evolved into San Jose State University, San José State University. The branch was transferred to the University of California to become the Southern Branch of the University of California in 1919, making it the second-oldest of the ten-campus University of California system after the University of California, Berkeley. UCLA offers 337 undergraduate and graduate degree programs in a range of disciplines, enrolling about 31,600 undergraduate and 14,300 graduate and professional students annually. It received 174,914 undergraduate applications for Fall 2022, including transfers, the most of any Higher education in the United States, university in the United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Mystery Of Matter (film)
''The Mystery of Matter: Search for the Elements'' is a 2014 American documentary miniseries, which premiered nationwide on August 19, 2015. The PBS documentary, in three-episodes of one hour each, was directed by Stephen Lyons and Muffie Meyer. The series, which took ten years to make, describes the search for the basic chemical elements that form matter by focusing on the lives and times of seven scientific visionaries. Hosted by actor Michael Emerson, the series depicts the creative process of the scientists, with actors describing the process of discovery in the scientists' own words and reenacting their major discoveries using replicas of their original laboratory equipment. Episodes Participants The documentary is narrated by Michael Emerson and includes the following participants (alphabetized by last name): * Matthew Amendt (actor) * Michael Aronov (actor) * Hugo Becker (actor) * Ava Deluca-Verley (actress) * Michael Emerson (narrator) * Russell Egdell (chemist) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concordia University
Concordia University () is a Public university, public English-language research university located in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Founded in 1974 following the merger of Loyola College (Montreal), Loyola College and Sir George Williams University, Concordia is one of the three universities in Quebec where English is the primary language of instruction (the others being McGill University, McGill and Bishop's University, Bishop's). As of the 2022–23 academic year, there were 49,898 students enrolled in credit and non-credit courses at Concordia, making the university among the largest in Canada by enrollment. The university has two campuses, set approximately apart: Sir George Williams Campus is the main campus, located in the Quartier Concordia neighbourhood of Downtown Montreal in the borough of Ville-Marie, Montreal, Ville Marie; and Loyola Campus in the residential district of Notre-Dame-de-Grâce. With four faculties, a school of graduate studies and numerous colleges, centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Chemistry
''Nature Chemistry'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Nature Portfolio. It was established in April 2009. The editor-in-chief is Stuart Cantrill. The journal covers all aspects of chemistry. Publishing formats include primary research articles, reviews, news, views, highlights of notable research from other journals, commentaries, book reviews, correspondence. Other formats are analysis of issues such as education, funding, policy, intellectual property, and the impact chemistry has on society. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: * Chemical Abstracts Service * Science Citation Index * Current Contents/Physical, Chemical & Earth Sciences * BIOSIS Previews According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2024 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Kuhn
Thomas Samuel Kuhn (; July 18, 1922 – June 17, 1996) was an American History and philosophy of science, historian and philosopher of science whose 1962 book ''The Structure of Scientific Revolutions'' was influential in both academic and popular circles, introducing the term ''paradigm shift'', which has since become an English-language idiom. Kuhn made several claims concerning the progress of science, scientific knowledge: that scientific fields undergo periodic "paradigm shifts" rather than solely progressing in a linear and continuous way, and that these paradigm shifts open up new approaches to understanding what scientists would never have considered valid before; and that the notion of scientific truth, at any given moment, cannot be established solely by Objectivity (philosophy), objective criteria but is defined by a consensus of a scientific community. Competing paradigms are frequently Commensurability (philosophy of science), incommensurable; that is, there is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonius Van Den Broek
Antonius Johannes van den Broek (4 May 1870 – 25 October 1926) was a Dutch mathematical economist and amateur physicist, notable for being the first who realized that the position of an element in the periodic table (now called atomic number) corresponds to the charge of its atomic nucleus. This hypothesis was published in 1911 and inspired the experimental work of Henry Moseley, who found good experimental evidence for it by 1913. Life Van den Broek was the son of a civil law notary and trained to be a lawyer himself. He studied at Leiden University and at the Sorbonne in Paris, obtaining a degree in 1895 in Leiden. From 1895 to 1900 he held a lawyers office in The Hague until 1900, after which he studied mathematical economy in Vienna and Berlin. However, from 1903 on, his main interest was physics. Much of the time between 1903 and 1911 he lived in France and Germany. Most of his papers he wrote between 1913 and 1916 while living in Gorssel. He married Elisabeth Margaretha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John William Nicholson
John William Nicholson, FRS (1 November 1881 – 3 October 1955) was an English mathematician and physicist. Nicholson is noted as the first to create an atomic model that quantized angular momentum as h/2π. Nicholson was also the first to create a nuclear and quantum theory that explains spectral line radiation as electrons descend toward the nucleus, identifying hitherto unknown solar and nebular spectral lines. Niels Bohr quoted him in his 1913 paper of the Bohr model of the atom. Education Nicholson studied at the University of Manchester, residing in Hulme Hall, where he earned a B.Sc. and later an M.Sc. Among his peers was Arthur Stanley Eddington, who became a lifelong friend. They both continued to Trinity College, Cambridge, where Nicholson passed the Mathematical Tripos in 1904 as Twelfth Wrangler. He was awarded the Isaac Newton Studentship in 1906, was a Smith's Prizeman in 1907, and won the Adams Prize in 1913 and 1917. Career Nicholson began his academic career ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evgeny Lifshitz
Evgeny Mikhailovich Lifshitz (; ; 21 February 1915 – 29 October 1985) was a leading Soviet physicist and brother of the physicist Ilya Lifshitz. Work Born into a Ukrainian Jewish family in Kharkov, Kharkov Governorate, Russian Empire (now Kharkiv, Ukraine). Lifshitz is well known in the field of general relativity for coauthoring the BKL conjecture concerning the nature of a ''generic curvature singularity''. , this is widely regarded as one of the most important open problems in the subject of classical gravitation. With Lev Landau, Lifshitz co-authored '' Course of Theoretical Physics'', an ambitious series of physics textbooks, in which the two aimed to provide a graduate-level introduction to the entire field of physics. These books are still considered invaluable and continue to be widely used. Lifshitz was the second of only 43 people ever to pass Landau's "Theoretical Minimum" examination. He made many invaluable contributions, in particular to quantum electrodynami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lev Landau
Lev Davidovich Landau (; 22 January 1908 – 1 April 1968) was a Soviet physicist who made fundamental contributions to many areas of theoretical physics. He was considered as one of the last scientists who were universally well-versed and made seminal contributions to all branches of physics. He is credited with laying the foundations of twentieth century condensed matter physics, and is also considered arguably the greatest Soviet theoretical physicist. His accomplishments include the independent co-discovery of the density matrix method in quantum mechanics (alongside John von Neumann), the quantum mechanical theory of diamagnetism, the theory of superfluidity, the theory of second-order phase transitions, invention of order parameter technique, the Ginzburg–Landau theory of superconductivity, the theory of Fermi liquids, the explanation of Landau damping in plasma physics, the Landau pole in quantum electrodynamics, the two-component theory of neutrinos, and Landau's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
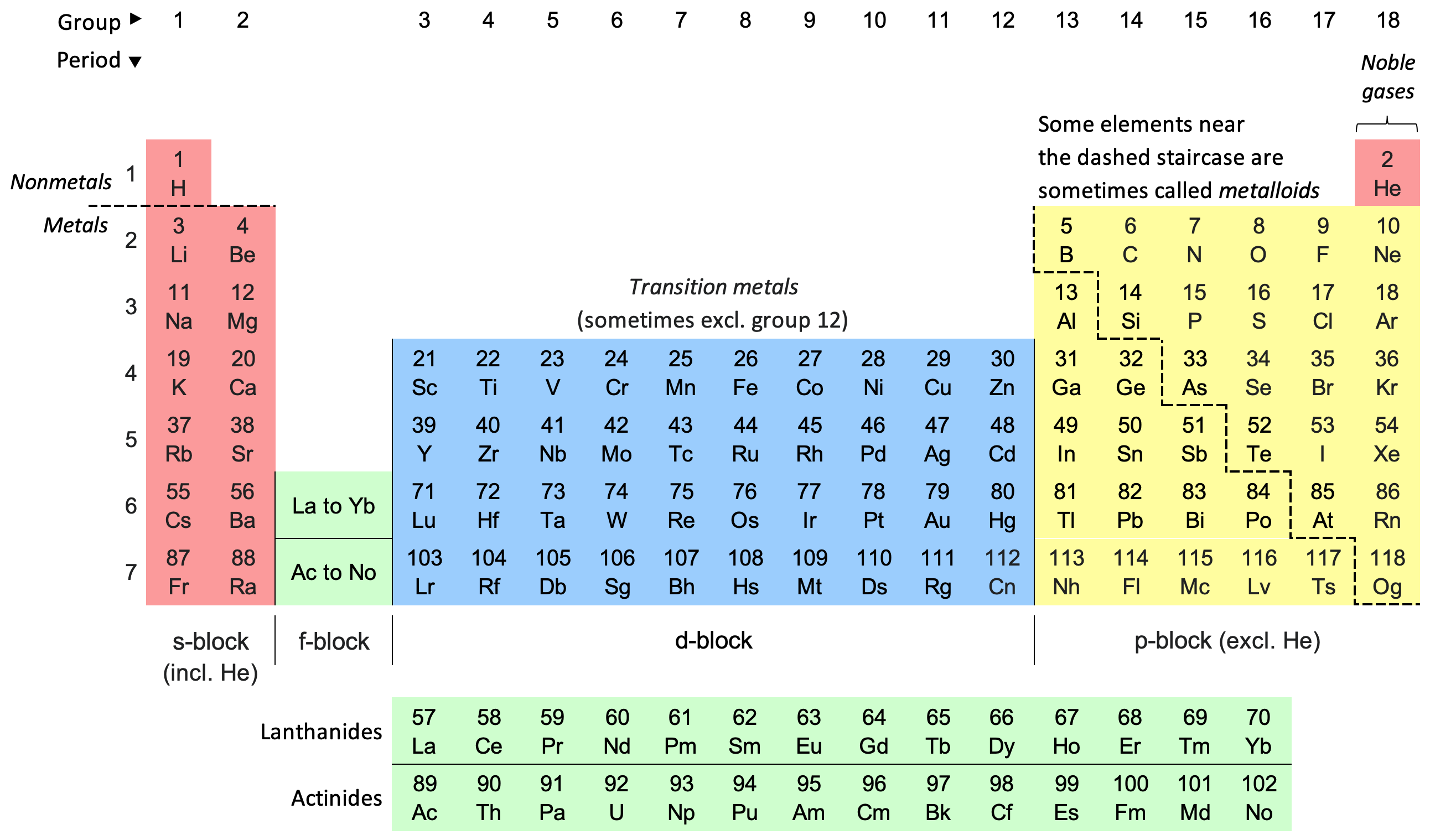
Periodic Table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other sciences. It is a depiction of the periodic law, which states that when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers an approximate recurrence of their properties is evident. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. Elements in the same group tend to show similar chemical characteristics. Vertical, horizontal and diagonal trends characterize the periodic table. Metallic character increases going down a group and from right to left across a period. Nonmetallic character increases going from the bottom left of the periodic table to the top right. The first periodic table to become generally accepted was that of the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869; he formulated the periodic law as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group 3 Element
Group 3 is the first group of transition metals in the periodic table. This group is closely related to the rare-earth elements. It contains the four elements scandium (Sc), yttrium (Y), lutetium (Lu), and lawrencium (Lr). The group is also called the scandium group or scandium family after its lightest member. The chemistry of the group 3 elements is typical for early transition metals: they all essentially have only the group oxidation state of +3 as a major one, and like the preceding main-group metals are quite electropositive and have a less rich coordination chemistry. Due to the effects of the lanthanide contraction, yttrium and lutetium are very similar in properties. Yttrium and lutetium have essentially the chemistry of the heavy lanthanides, but scandium shows several differences due to its small size. This is a similar pattern to those of the early transition metal groups, where the lightest element is distinct from the very similar next two. All the group 3 elemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. IUPAC's executive director heads this administrative office, currently Greta Heydenrych. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national List of chemistry societies, chemistry societies, national Academy of Sciences, academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |