|
Erg Admer
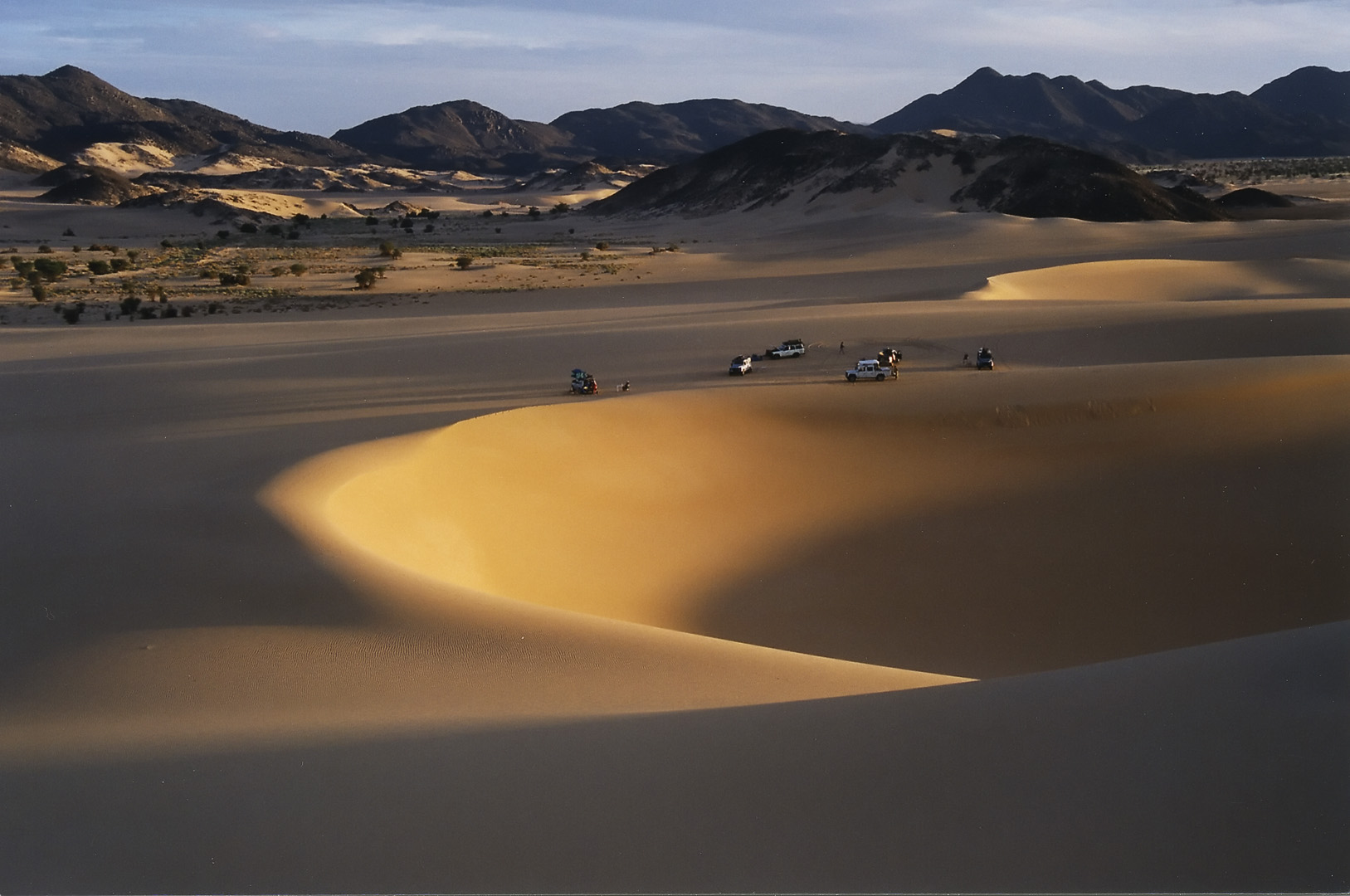
The Erg Admer is a large erg or field of sand dunes in the Sahara Desert. Situated in the Illizi Province west of the oasis town of Djanet in south-eastern Algeria, the erg covers an area some 20 km wide by some 100 km large north to south. It originates in the centre of Tassili n'Ajjer, towards ''Essendilène'' and extends southwards to reach Ténéré at the Niger border. Assemblages of lithic industry have been discovered, such as Acheulean and Aterian hand axes. To the east of ''Erg Admer'' there is the Tighaghart with La vache qui pleure rock gravings.Joseph Ki-Zerbo Joseph Ki-Zerbo (June 21, 1922 – December 4, 2006, Burkina Faso) was a Burkinabé historian, politician and writer. He is recognized as one of Africa's foremost thinkers. From 1972 to 1978 he was professor of African History at the University o ..., ''General History of Africa I. Methodology and African History'', éditions Abridged, 1990, , . References {{coord, 24, 13, N, 9, 14, E, type:landma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erg (landform)
An erg (also sand sea or dune sea, or sand sheet if it lacks dunes) is a broad, flat area of desert covered with wind-swept sand with little or no vegetative cover. The word is derived from the Arabic word ''ʿarq'' (), meaning "dune field". Strictly speaking, an erg is defined as a desert area that contains more than of aeolian or wind-blown sand and where sand covers more than 20% of the surface. Smaller areas are known as "dune fields". The largest hot desert in the world, the Sahara, covers and contains several ergs, such as the Chech Erg and the Issaouane Erg in Algeria. Approximately 85% of all the Earth's mobile sand is found in ergs that are greater than . Ergs are also found on other celestial bodies, such as Venus, Mars, and Saturn's moon Titan. Description Ergs are concentrated in two broad belts between 20° to 40°N and 20° to 40°S latitudes, which include regions crossed by the dry, subsiding air of the trade winds. Active ergs are limited to regions that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assemblage (archaeology)
This page is a glossary of archaeology, the study of the human past from material remains. A B C D E F G H I K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z See also * Outline of archaeology * Table of years in archaeology * Glossary of history References Bibliography * * * * * * * External links About.com Archaeology Glossary {{Glossaries of science and engineering Archaeology Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Algeria
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sahara
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg , photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972 , map = , map_image = , location = , country = , country1 = , country2 = , country3 = , country4 = , country5 = , country6 = , country7 = , country8 = , country9 = , country10 = ( disputed) , region = , state = , district = , city = , relief = , label = , label_position = , coordinates = , coordinates_ref = , elevation = , elevation_m = , elevation_ft = , elevation_ref = , length = , length_mi = , length_km = 4,800 , length_orientation = , length_note = , width = , width_mi = , widt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Ki-Zerbo
Joseph Ki-Zerbo (June 21, 1922 – December 4, 2006, Burkina Faso) was a Burkinabé historian, politician and writer. He is recognized as one of Africa's foremost thinkers. From 1972 to 1978 he was professor of African History at the University of Ouagadougou. In 1983, he was forced into exile, only being able to return in 1992. Ki-Zerbo founded the Party for Democracy and Progress / Socialist Party. He was its chairman until 2005, and represented it in the Burkina Faso parliament until his death in 2006. A socialist and an advocate of African independence and unity, Ki-Zerbo was also a vocal opponent of Thomas Sankara's revolutionary government. Early life Ki-Zerbo was born in Toma, Burkina Faso, Toma in the province of Nayala Province, Nayala, in what was, at that time, the French colony of French Upper Volta, Upper Volta. He was the son of Alfred Diban Ki Zerbo and Thérèse Folo Ki.Holenstein, R. (2006, December 11). Joseph Ki-Zerbo: A quand l’Afrique. Le Faso.net (2006). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
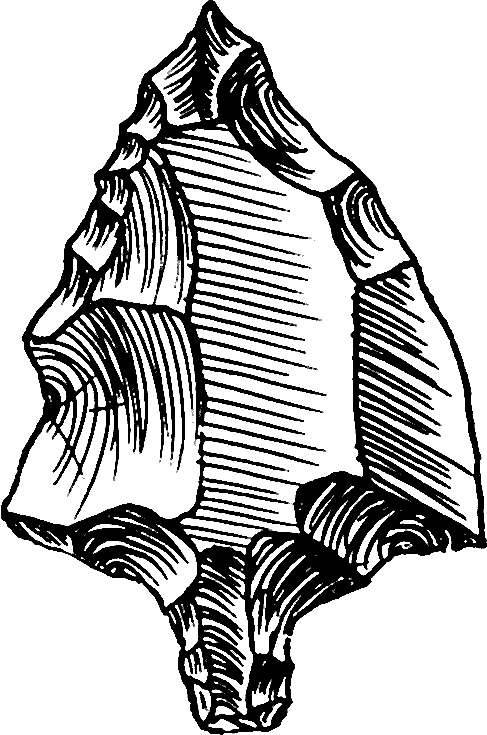
Hand Axe
A hand axe (or handaxe or Acheulean hand axe) is a prehistoric stone tool with two faces that is the longest-used tool in human history, yet there is no academic consensus on what they were used for. It is made from stone, usually flint or chert that has been "reduced" and shaped from a larger piece by knapping, or hitting against another stone. They are characteristic of the lower Acheulean and middle Palaeolithic ( Mousterian) periods, roughly 1.6 million years ago to about 100,000 years ago, and used by ''Homo erectus'' and other early humans, but rarely by ''Homo sapiens''. Their technical name (biface) comes from the fact that the archetypical model is a generally bifacial (with two wide sides or faces) and almond-shaped (amygdaloidal) lithic flake. Hand axes tend to be symmetrical along their longitudinal axis and formed by pressure or percussion. The most common hand axes have a pointed end and rounded base, which gives them their characteristic almond shape, and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aterian
The Aterian is a Middle Stone Age (or Middle Palaeolithic) stone tool industry centered in North Africa, from Mauritania to Egypt, but also possibly found in Oman and the Thar Desert. The earliest Aterian dates to c. 150,000 years ago, at the site of Ifri n'Ammar in Morocco. However, most of the early dates cluster around the beginning of the Last Interglacial, around 150,000 to 130,000 years ago, when the environment of North Africa began to ameliorate. The Aterian disappeared around 20,000 years ago. The Aterian is primarily distinguished through the presence of tanged or pedunculated tools, and is named after the type site of Bir el Ater, south of Tébessa. Bifacially-worked, leaf-shaped tools are also a common artefact type in Aterian assemblages, and so are racloirs and Levallois flakes and cores. Items of personal adornment (pierced and ochred Nassarius shell beads) are known from at least one Aterian site, with an age of 82,000 years. The Aterian is one of the olde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acheulean
Acheulean (; also Acheulian and Mode II), from the French ''acheuléen'' after the type site of Saint-Acheul, is an archaeological industry of stone tool manufacture characterized by the distinctive oval and pear-shaped " hand axes" associated with ''Homo erectus'' and derived species such as '' Homo heidelbergensis''. Acheulean tools were produced during the Lower Palaeolithic era across Africa and much of West Asia, South Asia, East Asia and Europe, and are typically found with ''Homo erectus'' remains. It is thought that Acheulean technologies first developed about 1.76 million years ago, derived from the more primitive Oldowan technology associated with ''Homo habilis''. The Acheulean includes at least the early part of the Middle Paleolithic. Its end is not well defined, depending on whether Sangoan (also known as "Epi-Acheulean") is included, it may be taken to last until as late as 130,000 years ago. In Europe and Western Asia, early Neanderthals adopted Acheul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industry (archaeology)
:''Not to be confused with industrial archaeology, the archaeology of (modern) industrial sites.'' In the archaeology of the Stone Age, an industry or technocomplex is a typological classification of stone tools. An industry consists of a number of lithic assemblages, typically including a range of different types of tools, that are grouped together on the basis of shared technological or morphological characteristics. For example, the Acheulean industry includes hand-axes, cleavers, scrapers and other tools with different forms, but which were all manufactured by the symmetrical reduction of a bifacial core producing large flakes. Industries are usually named after a type site where these characteristics were first observed (e.g. the Mousterian industry is named after the site of Le Moustier). By contrast, Neolithic axeheads from the Langdale axe industry were recognised as a type well before the centre at Great Langdale was identified by finds of debitage and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niger
) , official_languages = , languages_type = National languagesRépublique du Niger, "Loi n° 2001-037 du 31 décembre 2001 fixant les modalités de promotion et de développement des langues nationales." L'aménagement linguistique dans le monde (accessed 21 September 2016) , languages = , religion_ref = , religion_year = 2012 , religion = , demonym = Nigerien , capital = Niamey , coordinates = , largest_city = Niamey , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Semi-presidential s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Vache Qui Pleure (rock Gravings)
About 25 km from the oasis of Djanet in southeast Algeria, on the eastern border of erg Admer towards Tassili n'Ajjer in the ''Tigharghart'' region, stands a large sand monolith. On one side of the rocks of the monolith are the rock engravings of La vache qui pleure (the crying cow), dated more than 7000 years ago. The rock engravings of ''La vache qui pleure'' are a masterpiece of Neolithic sculpture. Carried out in bas-relief, the engravings are of extraordinary workmanship and harmony, made of deep grooves carved into the rock. Leaning towards a small depression at the foot of the rock, the engravings represent a small herd of bovidae. The cows seem to be waiting for the water to arrive to drink from it. The tear shed by one of these cows has given rise to many interpretations and legends. File:" La Vache Qui Pleure" Parc National du Tassili . Algérie..jpg, Monolith containing the rock engravings of La vache qui pleure File:La vache qui pleure.jpg, Rock engravings of La vache q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ténéré
The Ténéré (Tuareg: Tenere, literally: "desert") is a desert region in the south central Sahara. It comprises a vast plain of sand stretching from northeastern Niger into western Chad, occupying an area of over . The Ténéré's boundaries are said to be the Aïr Mountains in the west, the Hoggar Mountains in the north, the Djado Plateau in the northeast, the Tibesti Mountains in the east, and the basin of Lake Chad in the south. The central part of the desert, the Erg du Bilma, is centred at approximately . It is the locus of the Neolithic Tenerian culture. Name The name ''Ténéré'' comes from the Tuareg language, meaning "desert", in much the same way that the Arabic word for "desert", ''Sahara'', came to be applied to the region as a whole. Climate The Ténéré has a hot desert climate (Köppen climate classification ''BWh''), typical of the large Sahara Desert. The climate is hyper-arid, extremely hot, sunny and dry year-round and there is virtually no plant life. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)