|
Erddig
Erddig () is a country house and estate in the community of Marchwiel, approximately south of Wrexham, Wales. It is centred on a country house which dates principally from between 1684 and 1687, when the central block was built by Joshua Edisbury, and the 1720s, when the flanking wings were added by its second owner, John Meller. Erddig was inherited by Simon Yorke in 1733, and remained in the Yorke family until it was given to the National Trust by Philip Scott Yorke in 1973. The Yorke family had an unusual relationship with their servants, and commemorated them in a large and unique collection of portraits and poems. This collection, and the good state of preservation of the servants' quarters and estate workshops, provide an insight into how servants lived between the eighteenth and twentieth centuries. The house is also significant for its collection of seventeenth-century furniture; this includes the state bed, a rare surviving example of a '' lit à la duchesse'' canopy be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erddig Hall - Geograph
Erddig () is a country house and estate in the Community (Wales), community of Marchwiel, approximately south of Wrexham, Wales. It is centred on a country house which dates principally from between 1684 and 1687, when the central block was built by Joshua Edisbury, and the 1720s, when the flanking wings were added by its second owner, John Meller. Erddig was inherited by Simon Yorke in 1733, and remained in the Yorke family until it was given to the National Trust by Philip Scott Yorke in 1973. The Yorke family had an unusual relationship with their servants, and commemorated them in a large and unique collection of portraits and poems. This collection, and the good state of preservation of the servants' quarters and estate workshops, provide an insight into how servants lived between the eighteenth and twentieth centuries. The house is also significant for its collection of seventeenth-century furniture; this includes the state bed, a rare surviving example of a ''Canopy bed#H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marchwiel
Marchwiel (; standardised: ) is a village and community in Wrexham County Borough, Wales. It is about 2 miles south-east of Wrexham city on the A525 road towards Bangor-on-Dee. The community has an area of 1,488 hectares and a population of 1,418 ( 2001 census), the population falling to 1,379 at the 2011 Census. There are several large country houses in the area including Marchwiel Hall, Bryn-y-grog, Old Sontley and Erddig Hall, now a National Trust property and a popular tourist attraction. The churchyard is the resting place of the penultimate owner of Erddig, Simon Yorke (1903-1966). The 19th century, Marchwiel Hall was acquired by Sir Alfred McAlpine, founder of Alfred McAlpine and son of 'Concrete' Bob McAlpine. In the Middle Ages there was a church at Marchwiel dedicated to Saint Deiniol. It was recorded in early times as ''Plwyf y Marchwiail'', "the parish of the saplings";''Archaeologia Cambrensis'', 1917, 308 this is sometimes taken to refer to the materials u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Æthelbald Of Mercia
Æthelbald (also spelled Ethelbald or Aethelbald; died 757) was the King of Mercia, in what is now the English Midlands from 716 until he was killed in 757. Æthelbald was the son of Alweo and thus a grandson of King Eowa. Æthelbald came to the throne after the death of his cousin, King Ceolred, who had driven him into exile. During his long reign, Mercia became the dominant kingdom of the Anglo-Saxons, and recovered the position of pre-eminence it had enjoyed during the strong reigns of Mercian kings Penda and Wulfhere between about 628 and 675. When Æthelbald came to the throne, both Wessex and Kingdom of Kent, Kent were ruled by stronger kings, but within fifteen years the contemporary chronicler Bede describes Æthelbald as ruling all England south of the Humber estuary. The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' does not list Æthelbald as a bretwalda, or "Ruler of Britain", though this may be due to the West Saxon origin of the ''Chronicle''. Saint Boniface, St. Boniface wrote to Æ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master Of The Rolls
The Keeper or Master of the Rolls and Records of the Chancery of England, known as the Master of the Rolls, is the President of the Court of Appeal (England and Wales)#Civil Division, Civil Division of the Court of Appeal of England and Wales and Head of Civil Justice. As a judge, the Master of the Rolls is second in seniority in England and Wales only to the Lord Chief Justice. The position dates from at least 1286, although it is believed that the office probably existed earlier than that. The Master of the Rolls was initially a clerk responsible for keeping the "Rolls" or records of the Court of Chancery, and was known as the Keeper of the Rolls of Chancery. The Keeper was the most senior of the dozen Chancery clerks, and as such occasionally acted as keeper of the Great Seal of the Realm. The post evolved into a judicial one as the Court of Chancery did; the first reference to judicial duties dates from 1520. With the Judicature Act 1873, which merged the Court of Chancery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Sheriff Of Denbighshire
The first High Sheriff of Denbighshire was John Salusbury (died 1540s), John Salusbury, snr, appointed in 1540. The shrievalty of Denbighshire, together with that of Flintshire, continued until 1974 when it was abolished after the county and shrievalty of Clwyd was created. The role High Sheriff in each county is the oldest secular office under the Crown. The High Sheriff changed every March. Formerly the High Sheriff was the principal law enforcement officer in the county but over the centuries most of the responsibilities associated with the post have been transferred elsewhere or are now defunct, so that its functions are now largely ceremonial. List of High Sheriffs 16th century 17th century 18th century 19th century 20th century References {{High Shrievalties High sheriffs of Denbighshire, Denbighshire High shrievalties in Wales, Denbighshire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations. Due to the similarity, the term '' scarp'' may mistakenly be incorrectly used interchangeably with ''escarpment.'' ''Escarpment'' referring to the margin between two landforms, and ''scarp'' referring to a cliff or a steep slope. In this usage an escarpment is a ridge which has a gentle slope on one side and a steep scarp on the other side. More loosely, the term ''scarp'' also describes a zone between a coastal lowland and a continental plateau which shows a marked, abrupt change in elevation caused by coastal erosion at the base of the plateau. Formation and description Scarps are generally formed by one of two processes: either by differential erosion of sedimentary rocks, or by movement of the Earth's crust at a geologic fault. The first process is the more common type: the escarpment is a transition from one seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denbigh
Denbigh ( ; ) is a market town and a community (Wales), community in Denbighshire, Wales. It was the original county town of the Denbighshire (historic), historic county of Denbighshire created in 1536. Denbigh's Welsh name () translates to "Little Fortress"; a reference to Denbigh Castle and town walls, its historic castle. Denbigh lies near the Clwydian Hills. History Denbigh anciently formed part of the cantref of Rhufoniog. For much of its history, Rhufoniog was subordinate to the Kingdom of Gwynedd, but it also spent periods under English control during the 12th and 13th centuries. By the 13th century, Denbigh was the main town of Rhufoniog. In 1284, following the Conquest of Wales by Edward I, Rhufoniog was made part of a new marcher lordship called Lordship of Denbigh, Denbigh or Denbighland, which Edward initially granted to Henry de Lacy, Earl of Lincoln. As part of his campaign to take and retain control of the area, Edward I decided to fortify Denbigh, ordering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruthin
Ruthin ( ; ) is a market town and community in Denbighshire, Wales, in the south of the Vale of Clwyd. The town, castle and St Peter's Square lie on a hill, skirted by villages such as Pwllglas and Rhewl. The name comes from the Welsh ''rhudd'' (red) and ''din'' (fort), after the colour of sandstone bedrock, from which the castle was built in 1277–1284. The Old Mill, Ruthin, is nearby. Maen Huail, a registered ancient monument associated with King Arthur and with Hueil mab Caw, the brother of the historian Gildas, stands in St Peter's Square. History There is evidence of Celtic and later Roman settlements in the area. However, little is known of the history of the town before the construction of Ruthin Castle was started in 1277 by Dafydd, the brother of prince Llywelyn ap Gruffudd. However, he forfeited the castle when he rebelled against King Edward I with his brother; Edward's queen, Eleanor, was in residence in 1281. The original name was ''Castell Coch yng Ngwern- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
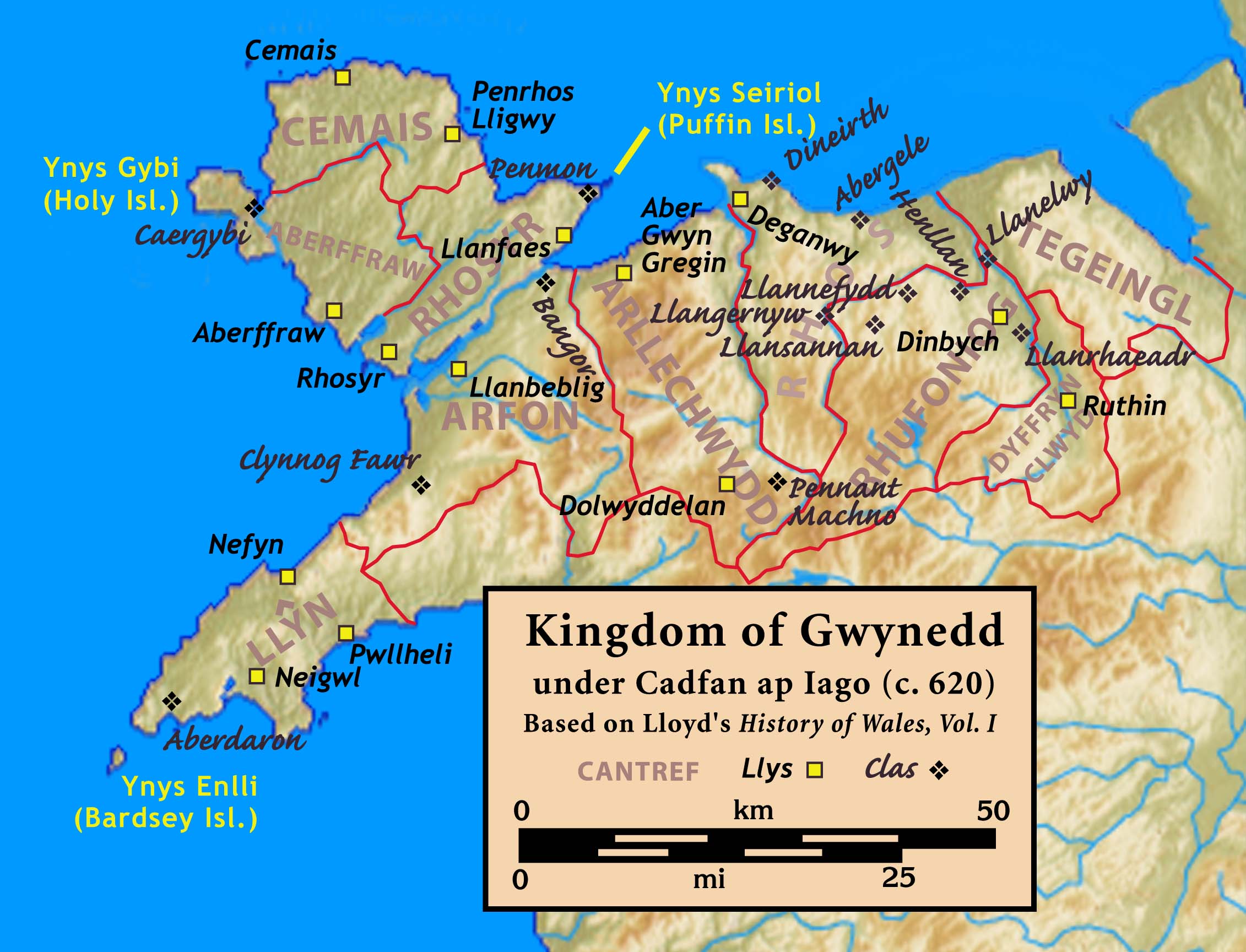
Kingdom Of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Wales in the Early Middle Ages, Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire Succession of states, successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. Based in northwest Wales, the list of rulers of Gwynedd, rulers of Gwynedd repeatedly rose to dominance and were acclaimed as "King of the Britons" before losing their power in civil wars or invasions. The kingdom of Gruffydd ap Llywelynthe King of Wales from 1055 to 1063was shattered by a Timeline of conflict in Anglo-Saxon Britain, Saxon invasion in 1063 just prior to the Norman invasion of Wales, but the House of Aberffraw restored by Gruffudd ap Cynan slowly recovered and Llywelyn the Great of Gwynedd was able to proclaim the Principality of Wales at the Aberdyfi gathering of Welsh princes in 1216. In 1277, the Treaty of Aberconwy between Edward I of England and Llywelyn's grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffudd granted pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of England
The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from the late 9th century, when it was unified from various Heptarchy, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain, which would later become the United Kingdom. The Kingdom of England was among the most powerful states in Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern period, early modern periods. Beginning in the year 886 Alfred the Great reoccupied London from the Danish Vikings and after this event he declared himself King of the Anglo-Saxons, until his death in 899. During the course of the early tenth century, the various Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms were united by Alfred's descendants Edward the Elder (reigned 899–924) and Æthelstan (reigned 924–939) to form the Kingdom of the English. In 927, Æthelstan conquered the last remaining Viking kingdom, Scandinavian York, York, making him the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, French people, French, Flemish people, Flemish, and Bretons, Breton troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conqueror. William's claim to the English throne derived from his familial relationship with the childless Anglo-Saxon king Edward the Confessor, who may have encouraged William's hopes for the throne. Edward died in January 1066 and was succeeded by his brother-in-law Harold Godwinson. The Norwegian king Harald Hardrada invaded northern England in September 1066 and was victorious at the Battle of Fulford on 20 September, but Godwinson's army defeated and killed Hardrada at the Battle of Stamford Bridge on 25 September. Three days later on 28 September, William's invasion force of thousands of men and hundreds of ships landed at Pevensey in Sussex in southern England. Harold marched south to oppose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Clywedog
The River Clywedog is a river in Wrexham County Borough, Wales. Its uses have been watering crops, powering industrial machinery but is now used as walking trails or geography trips. The river originates to the west of Wrexham, and joins the River Dee some four miles south east of the city. Course of the river The river Clywedog rises in the hills west of the village of Minera. After flowing through Minera it turns south-east, past Coedpoeth, Bersham and Rhostyllen and through the Erddig Country Park, then east, passing slightly to the south of Wrexham. There is a path along the entire river bank from Minera to Wrexham. After passing the Wrexham industrial estate, the river joins the River Dee near the English/Welsh border. History During the 18th and early 19th centuries there were 17 watermills along the river: fulling mills for preparing cloth, mills for grinding corn and malt, and paper mills. Large waterwheels powered the bellows blasting air into the iron furnaces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |