|
Erastin
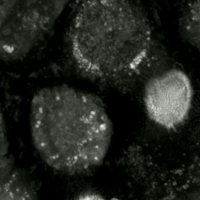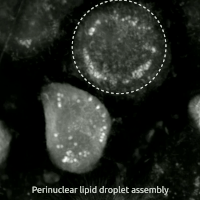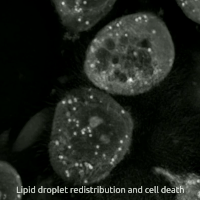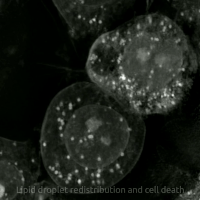
Erastin is a small molecule capable of initiating ferroptotic cell death. Erastin binds and activates voltage-dependent anion channels (VDAC) by reversing tubulin's inhibition on VDAC2 and VDAC3, and functionally inhibits the cystine-glutamate antiporter enzyme SLC7A11 Cells treated with erastin are deprived of cysteine and are unable to synthesize the antioxidant glutathione. Depletion of glutathione eventually leads to excessive lipid peroxidation and cell death Cell death is the event of a biological cell ceasing to carry out its functions. This may be the result of the natural process of old cells dying and being replaced by new ones, as in programmed cell death, or may result from factors such as di .... Erastin was first described in 2003. Its name is short for "eradicator of RAS and ST-expressing cells". References Experimental drugs 4-Chlorophenyl compounds Piperazines Phenol ethers {{pharma-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferroptosis
Ferroptosis (also known as oxytosis) is a type of programmed cell death dependent on iron and characterized by the accumulation of lipid peroxides. Ferroptosis is biochemically, genetically, and morphologically distinct from other forms of regulated cell death such as apoptosis and necroptosis. Oxytosis/ferroptosis can be initiated by the failure of the glutathione-dependent antioxidant defenses, resulting in unchecked lipid peroxidation and eventual cell death. Lipophilic antioxidants and iron chelators can prevent ferroptotic cell death. Researchers have identified roles in which oxytosis/ferroptosis can contribute to the medical field, such as the development of cancer therapies. Ferroptosis activation plays a regulatory role on growth of tumor cells in the human body. However, the positive effects of oxytosis/ferroptosis could be potentially neutralized by its disruption of metabolic pathways and disruption of homeostasis in the human body. Since oxytosis/ferroptosis is a form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLC7A11
Cystine/glutamate transporter is an antiporter that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC7A11'' gene. The ''SLC7A11'' gene encodes a sodium-independent cystine-Glutamate (neurotransmitter), glutamate antiporter that is chloride dependent, also known as xCT. Along with a heavy chain subunit from ''SLC3A2'', the SLC7A11 light chain comprises system Xc-, which is the functional cystine-glutamate antiporter. While the SLC3A2 heavy chain is a chaperone for many other light chains that participate in amino acid transport, the SLC7A11 light chain is specific for system Xc-, and the terms xCT/SLC7A11 and system Xc- are used interchangeably in much of the literature. SLC7A11 plays an important role in glutathione production throughout nervous and non-nervous tissues. In the nervous system, SLC7A11 regulates synaptic activity by stimulating extrasynaptic receptors and performs nonvesicular glutamate release. This gene is highly expressed by astrocytes and couples the uptake of one molecule of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-dependent Anion Channel
Voltage-dependent anion channels, or mitochondrial porins, are a class of porin ion channel located on the outer mitochondrial membrane. There is debate as to whether or not this channel is expressed in the cell surface membrane. This major protein of the outer mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes forms a voltage-dependent anion-selective channel (VDAC) that behaves as a general diffusion pore for small hydrophilic molecules. The channel adopts an open conformation at low or zero membrane potential and a closed conformation at potentials above 30–40 mV. VDAC facilitates the exchange of ions and molecules between mitochondria and cytosol and is regulated by the interactions with other proteins and small molecules. Structure This protein contains about 280 amino acids and forms a beta barrel which spans the mitochondrial outer membrane. Since its discovery in 1976, extensive function and structure analysis of VDAC proteins has been conducted. A prominent feature of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VDAC2
Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''VDAC2'' gene on chromosome 10. This protein is a voltage-dependent anion channel and shares high structural homology with the other VDAC isoforms. VDACs are generally involved in the regulation of cell metabolism, mitochondrial apoptosis, and spermatogenesis. Additionally, VDAC2 participates in cardiac contractions and pulmonary circulation, which implicate it in cardiopulmonary diseases. VDAC2 also mediates immune response to infectious bursal disease (IBD). Structure The three VDAC isoforms in human are highly conserved, particularly with respect to their 3D structure. VDACs form a wide β-barrel structure, inside of which the N-terminal resides to partially close the pore. The sequence of the VDAC2 isoform contains an abundance of cysteines, which allow for the formation of disulfide bridges and, ultimately, affect the flexibility of the β-barrel. VDACs also contain a mito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VDAC3
Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 3 (VDAC3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''VDAC3'' gene on chromosome 8. The protein encoded by this gene is a voltage-dependent anion channel and shares high structural homology with the other VDAC isoforms. Nonetheless, VDAC3 demonstrates limited pore-forming ability and, instead, interacts with other proteins to perform its biological functions, including sperm flagella assembly and centriole assembly. Mutations in VDAC3 have been linked to male infertility, as well as Parkinson's disease. Structure The three VDAC isoforms in human are highly conserved, particularly with respect to their 3D structure. VDACs form a wide β-barrel structure, inside of which the N-terminal resides to partially close the pore. The sequence of the VDAC3 isoform contains an abundance of cysteines, which allow for the formation of disulfide bridges and, ultimately, affect the flexibility of the β-barrel. VDACs also contain a mitocho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiporter
An antiporter (also called exchanger or counter-transporter) is an integral membrane protein that uses secondary active transport to move two or more molecules in opposite directions across a phospholipid membrane. It is a type of cotransporter, which means that uses the Exergonic reaction, energetically favorable movement of one molecule down its electrochemical gradient to power the Endergonic reaction, energetically unfavorable movement of another molecule up its electrochemical gradient. This is in contrast to symporters, which are another type of cotransporter that moves two or more ions in the same direction, and primary active transport, which is directly powered by Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Transport may involve one or more of each type of solute. For example, the Sodium-calcium exchanger, Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, found in the plasma membrane of many cells, moves three sodium ions in one direction, and one calcium ion in the other. As with sodium in this example, antiport ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine
Cysteine (; symbol Cys or C) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine enables the formation of Disulfide, disulfide bonds, and often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. Cysteine is chiral, but both D and L-cysteine are found in nature. LCysteine is a protein monomer in all biota, and D-cysteine acts as a signaling molecule in mammalian nervous systems. Cysteine is named after its discovery in urine, which comes from the urinary bladder or cyst, from Ancient Greek, Greek κύστις ''kýstis'', "bladder". The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide bond, disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. In this case, the symbol Cyx is sometimes used. The deprotonated form can generally be described by the symbol Cym as well. When used as a food additive, cysteine has the E number E920. Cysteine is Genetic code, encoded by the codo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutathione
Glutathione (GSH, ) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources such as reactive oxygen species, free radicals, peroxides, lipid peroxides, and heavy metals. It is a tripeptide with a gamma peptide linkage between the carboxyl group of the glutamate side chain and cysteine. The carboxyl group of the cysteine residue is attached by normal peptide linkage to glycine. Biosynthesis and occurrence Glutathione biosynthesis involves two adenosine triphosphate-dependent steps: *First, γ-glutamylcysteine is synthesized from L-glutamate and L-cysteine. This conversion requires the enzyme glutamate–cysteine ligase (GCL, glutamate cysteine synthase). This reaction is the rate-limiting step in glutathione synthesis. *Second, glycine is added to the C-terminal of γ-glutamylcysteine. This condensation is ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid Peroxidation
Lipid peroxidation, or lipid oxidation, is a complex chemical process that leads to oxidative degradation of lipids, resulting in the formation of peroxide and hydroperoxide derivatives.{{Cite journal , last1=Ayala , first1=Antonio , last2=Muñoz , first2=Mario F. , last3=Argüelles , first3=Sandro , date=2014 , title=Lipid Peroxidation: Production, Metabolism, and Signaling Mechanisms of Malondialdehyde and 4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal , journal=Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity , language=en , volume=2014 , pages=1–31 , doi=10.1155/2014/360438 , doi-access=free , issn=1942-0900 , pmc=4066722 , pmid=24999379 It occurs when free radicals, specifically reactive oxygen species (ROS), interact with lipids within cell membranes, typically polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) as they have carbon–carbon double bonds. This reaction leads to the formation of lipid radicals, collectively referred to as lipid peroxides or lipid oxidation products (LOPs), which in turn react with other ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Death
Cell death is the event of a biological cell ceasing to carry out its functions. This may be the result of the natural process of old cells dying and being replaced by new ones, as in programmed cell death, or may result from factors such as diseases, localized injury, or the death of the organism of which the cells are part. Apoptosis or Type I cell-death, and Autophagy (cellular), autophagy or Type II cell-death are both forms of programmed cell death, while necrosis is a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury. The term "cell necrobiology" has been used to describe the life processes associated with morphological, biochemical, and molecular changes which predispose, precede, and accompany cell death, as well as the consequences and tissue response to cell death. The word is derived from the Greek language, Greek νεκρό meaning "death", βìο meaning "life", and logos, λόγος meaning "the study of". The term was initially coined to bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Drugs
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and informal natural comparisons ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |