|
Erasmus Smith
Erasmus Smith (1611–1691) was an English merchant and a landowner with possessions in England and Ireland. Having acquired significant wealth through trade and land transactions, he became a philanthropist in the sphere of education, treading a path between idealism and self-interest during a period of political and religious turbulence. His true motivations remain unclear. Smith's family owned manors in Leicestershire and held Protestant beliefs. He became a merchant, supplying provisions to the armies of the Puritan Oliver Cromwell – during Cromwell's suppression of rebellion in Ireland — and an alderman of the City of London. His financial and landowning status was greatly enhanced by benefiting from his father's subscription to the Adventurers' Act from which he gained extensive landholdings in Ireland as a reward, and from his own speculative practice of buying additional subscriptions from other investors. During the period of Cromwell's rule and the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erasmus Smith 1611-1691 By John Michael Wright
Desiderius Erasmus Roterodamus ( ; ; 28 October c. 1466 – 12 July 1536), commonly known in English as Erasmus of Rotterdam or simply Erasmus, was a Dutch Christian humanist, Catholic priest and Catholic theology, theologian, educationalist, Menippean satire, satirist, and philosopher. Through his Works of Erasmus, works, he is considered one of the most influential thinkers of the Northern Renaissance and one of the major figures of Dutch and Western culture. Erasmus was an important figure in classical scholarship who wrote in a spontaneous, copious and natural Latin style. As a Catholic priest developing Philology, humanist techniques for working on texts, he prepared pioneering new Vulgate, Latin and Biblical Greek, Greek scholarly editions of the Novum Instrumentum omne, New Testament and of the Church Fathers, with annotations and commentary that were immediately and vitally influential in both the Protestant Reformation and the Catholic Reformation. He also wrote ''De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinity College, Dublin
Trinity College Dublin (), officially titled The College of the Holy and Undivided Trinity of Queen Elizabeth near Dublin, and legally incorporated as Trinity College, the University of Dublin (TCD), is the sole constituent college of the University of Dublin in the Republic of Ireland. Founded by Queen Elizabeth I in 1592 through a royal charter, it is one of the extant seven " ancient universities" of Great Britain and Ireland. Trinity contributed to Irish literature during the Georgian and Victorian eras, and areas of the natural sciences and medicine. Trinity was established to consolidate the rule of the Tudor monarchy in Ireland, with Provost Adam Loftus christening it after Trinity College, Cambridge. Built on the site of the former Priory of All Hallows demolished by King Henry VIII, it was the Protestant university of the Ascendancy ruling elite for over two centuries, and was therefore associated with social elitism for most of its history. Trinity has three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Louth
County Louth ( ; ) is a coastal Counties of Ireland, county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. Louth is bordered by the counties of County Meath, Meath to the south, County Monaghan, Monaghan to the west, County Armagh, Armagh to the north and County Down, Down to the north-east, across Carlingford Lough. It is the List of Irish counties by area, smallest county in Ireland by land area and the List of Irish counties by population, 17th most populous, with just over 139,100 residents 2022 census of Ireland, as of 2022. The county is named after the village of Louth, County Louth, Louth. Louth County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority for the county. History County Louth is named after the Louth, County Louth, village of Louth, which in turn is named after Lugh, a god of the ancient Irish. Historically, the placename has had various spellings; , , and ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardee (Parliament Of Ireland Constituency)
Ardee was a constituency represented in the Irish House of Commons from 1378 to 1801. History Ardee in County Louth was enfranchised as a borough constituency in 1378. In 1665 the Lord Lieutenant (James Butler, 1st Duke of Ormonde) wrote to the Portreeve of Ardee recommending Sir Robert Byron, as Burgess in Parliament for Ardee, in the room of Captain John Chambers, "removed" and Colonel Brent Moore, in the "stead of Lieutenant John Ruxton, removed". In the Patriot Parliament of 1689 summoned by King James II, Ardee was represented by two members. It continued to send two Members of Parliament to the Irish House of Commons until the Parliament of Ireland was merged into the Parliament of the United Kingdom on 1 January 1801. The constituency was disenfranchised on 31 December 1800. The borough was represented in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom as part of the county constituency of Louth. Electoral system and electorate The parliamentary representatives of the bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish House Of Commons
The Irish House of Commons was the lower house of the Parliament of Ireland that existed from 1297 until the end of 1800. The upper house was the Irish House of Lords, House of Lords. The membership of the House of Commons was directly elected, but on a highly restrictive franchise, similar to the unreformed House of Commons in contemporary Great Britain. Catholic Church in Ireland, Catholics were disqualified from sitting in the Irish parliament from 1691, even though they comprised the vast majority of the Irish population. The Irish executive, known as the Dublin Castle administration, under the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, was not answerable to the House of Commons but to the British government. However, the Chief Secretary for Ireland was usually a member of the Irish parliament. In the Commons, business was presided over by the Speaker of the Irish House of Commons, Speaker. From 1 January 1801, it ceased to exist and was succeeded by the House of Commons of the United Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pound Sterling
Sterling (symbol: £; currency code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound is the main unit of sterling, and the word '' pound'' is also used to refer to the British currency generally, often qualified in international contexts as the British pound or the pound sterling. Sterling is the world's oldest currency in continuous use since its inception. In 2022, it was the fourth-most-traded currency in the foreign exchange market, after the United States dollar, the euro, and the Japanese yen. Together with those three currencies and the renminbi, it forms the basket of currencies that calculate the value of IMF special drawing rights. As of late 2022, sterling is also the fourth most-held reserve currency in global reserves. The Bank of England is the central bank for sterling, issuing its own banknotes and regulating issuance of banknotes by private banks in Scotland and Northern Ireland. Sterling banknotes issu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
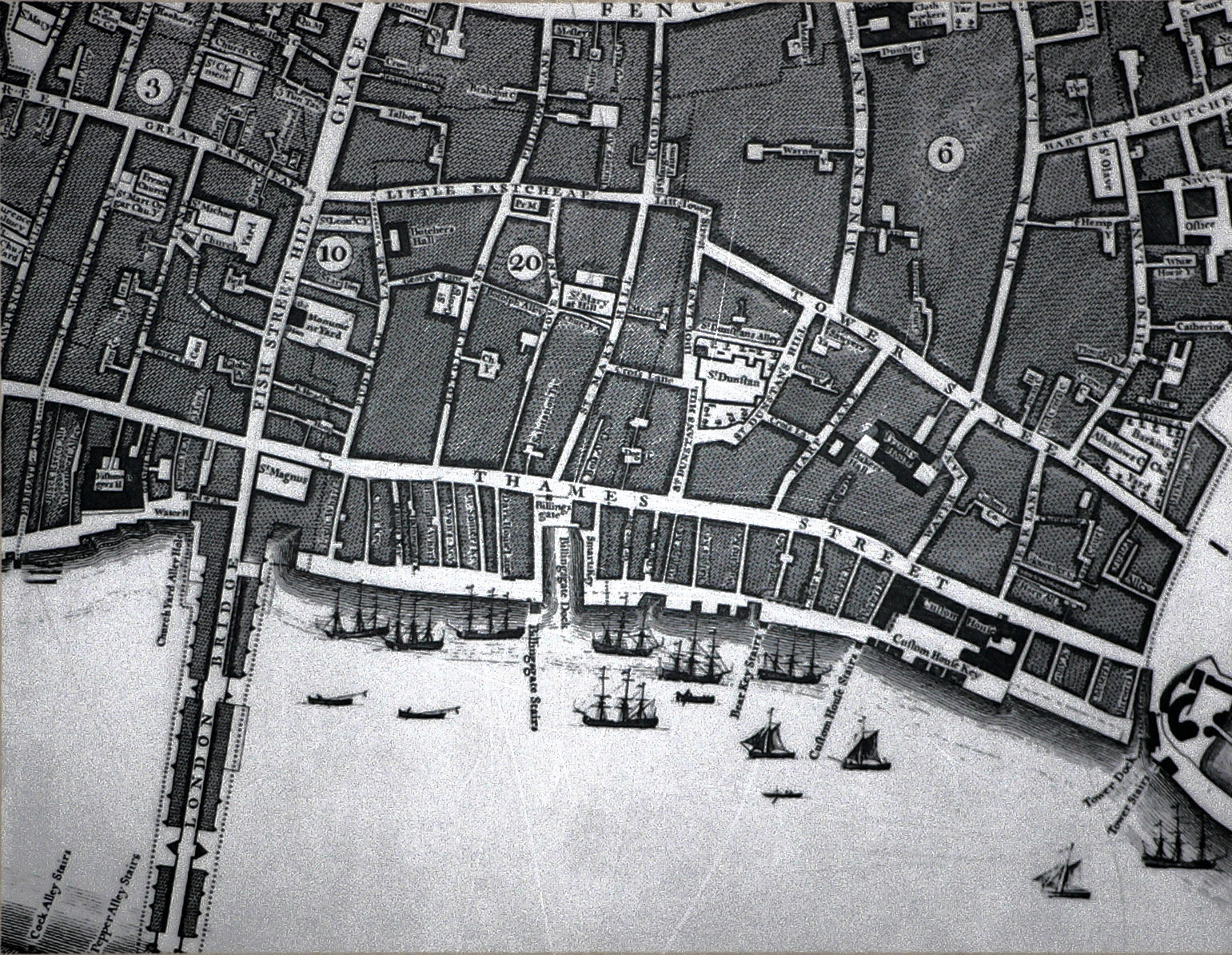
Billingsgate
Billingsgate is one of the 25 Wards of the City of London. This small City Ward is situated on the north bank of the River Thames between London Bridge and Tower Bridge in the south-east of the Square Mile. The modern Ward extends south to the Thames, west to Lovat Lane and Rood Lane, north to Fenchurch Street and Dunster Court, and east to Mark Lane and St Dunstan's Hill. History Legendary origin Billingsgate's most ancient historical reference is as a water gate to the city of Trinovantum (the name given to London in medieval British legend), as mentioned in the ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' (Eng: ''History of the Kings of Britain'') written 1136 by Geoffrey of Monmouth. This work describes how Belinus, a legendary king of Britain said to have held the throne from about 390 BC, erected London's first fortified water gate: Historical origin Originally known as ''Blynesgate'' and ''Byllynsgate'', its name apparently derives from its origins as a water gate on the Tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grocers' Company
The Worshipful Company of Grocers is one of the 111 livery companies of the City of London, ranking second in order of precedence. Established in 1345 for merchants engaged in the grocery trade, it is one of the Great Twelve City Livery Companies. History Founded in the 14th century by members of the ''Guild of Pepperers'', dating from 1180, the company was responsible for maintaining standards for the purity of spices and for setting of certain weights and measures. Its membership until 1617 included suppliers of medicinal spices and herbs when the Worshipful Society of Apothecaries was formed. The guild was known as the ''Company of Grossers'' from 1373 until 1376 when it was renamed the ''Company of Grocers of London''. In 1428, two years after building its first hall in Old Jewry, the company was granted a royal charter by King Henry VI of England. A Great Twelve City Livery Company, the Grocers rank second in the order of precedence after the Mercers. It is said tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apprenticeship
Apprenticeship is a system for training a potential new practitioners of a trade or profession with on-the-job training and often some accompanying study. Apprenticeships may also enable practitioners to gain a license to practice in a regulated occupation. Most of their training is done while working for an employer who helps the apprentices learn their trade or profession, in exchange for their continued labor for an agreed period after they have achieved measurable competencies. Apprenticeship lengths vary significantly across sectors, professions, roles and cultures. In some cases, people who successfully complete an apprenticeship can reach the " journeyman" or professional certification level of competence. In other cases, they can be offered a permanent job at the company that provided the placement. Although the formal boundaries and terminology of the apprentice/journeyman/master system often do not extend outside guilds and trade unions, the concept of on-the-job trai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Smith (preacher)
Henry Smith (c. 1560 – 1591?) was an English clergyman, widely regarded as "the most popular Puritan preacher of Elizabethan London." His sermons at St. Clement Danes drew enormous crowds, and earned him a reputation as "Silver Tongued" Smith. The collected editions of his sermons, and especially his tract, "God's Arrow Against Atheists," were among the most frequently reprinted religious writings of the Elizabethan age. Life Despite his popularity in the Elizabethan period, considerable uncertainty surrounds Smith's biography. Probably born in Leicestershire around 1560, Smith may have enrolled during the 1570s in colleges at both Cambridge and Oxford, but seems not to have taken a degree. He was, in any case, by 1589 among London's most popular preachers; however in that year, Smith seems to have contracted an illness which according to Charles Henry Cooper's ''Athenae Cantabrigienses'' caused him to devote his remaining time to preparing his writings for publication: Dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry VII Of England
Henry VII (28 January 1457 – 21 April 1509), also known as Henry Tudor, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from his seizure of the crown on 22 August 1485 until his death in 1509. He was the first monarch of the House of Tudor. Henry was the son of Edmund Tudor, 1st Earl of Richmond, and Lady Margaret Beaufort. His mother was a great-granddaughter of John of Gaunt, an English prince who founded the Lancastrian cadet branch of the House of Plantagenet. His father was the half-brother of the Lancastrian king Henry VI. Edmund Tudor died three months before his son was born, and Henry was raised by his uncle Jasper Tudor, a Lancastrian, and William Herbert, a supporter of the Yorkist branch of the House of Plantagenet. During Henry's early years, his uncles and the Lancastrians fought a series of civil wars against the Yorkist claimant, Edward IV. After Edward retook the throne in 1471, Henry spent 14 years in exile in Brittany. He attained the throne when his f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |