|
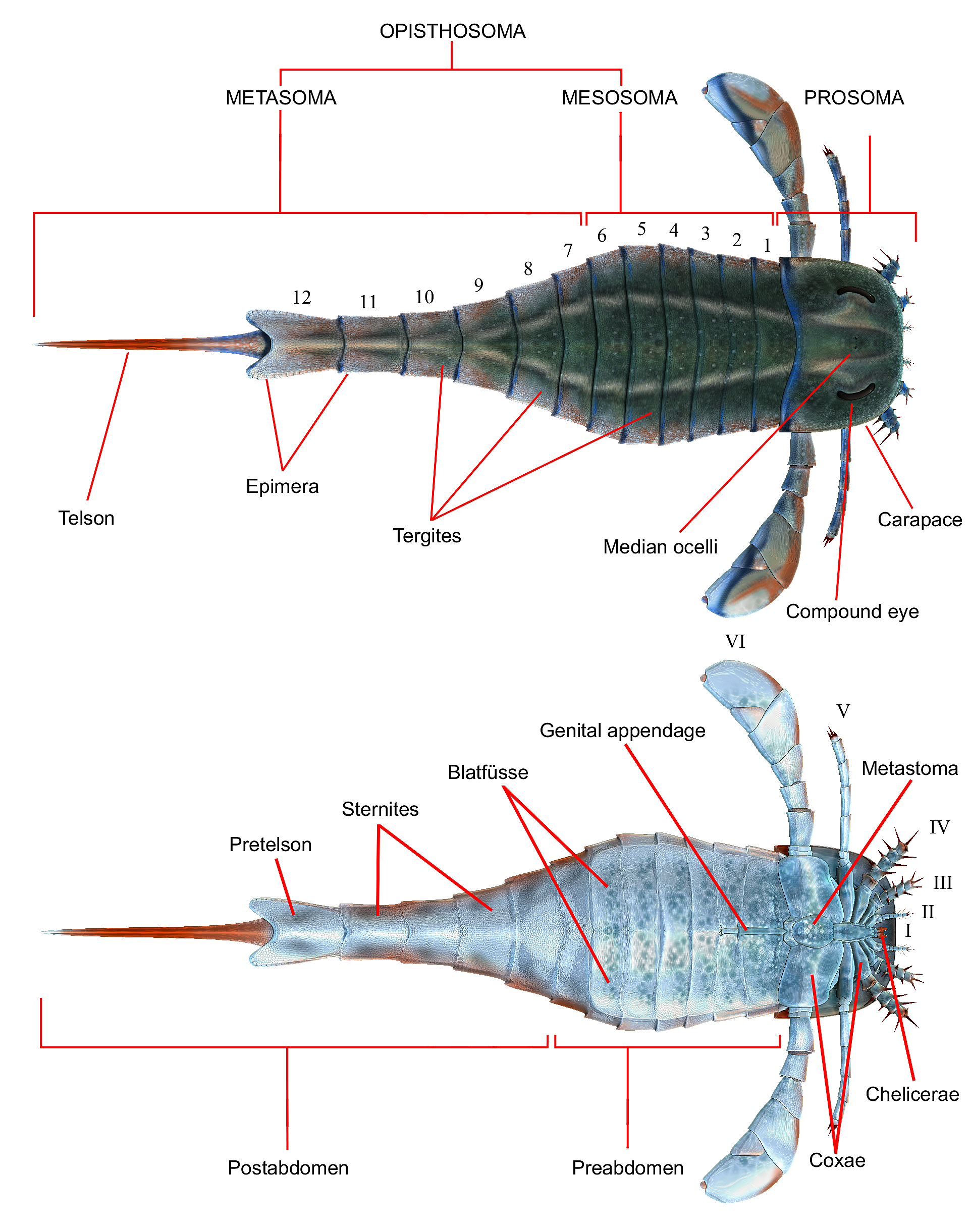
Eramoscorpius
''Eramoscorpius'' is an extinct genus of Silurian scorpions from the Eramosa Member in Ontario. It was likely one of the first semi-terrestrial scorpions. The genus contains a Monotypic taxon, single species, ''Eramoscorpius brucensis''. Description ''Eramoscorpius'' was roughly 17 cm long at largest, with individuals in various size classes. Unusually for most Silurian scorpions, its Arthropod tarsus, tarsi resembled those of modern scorpions, suggesting the ability to walk on land. Most other Silurian scorpions, on the other hand, had tarsi much longer than basitarsi, or pointed crab-like legs, meaning they would have likely walked on their "toes" and therefore would have been rather slow on land. However, the morphology of the wikt:coxosternum, coxosternae still suggests ''Eramoscorpius'' was mainly aquatic. While its sternal morphology resembles the "giant" scorpion ''Praearcturus'', appendages are unknown from that genus, alongside the two differing in the absence of Stomot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eramosa Member
The Eramosa Member is a Silurian stratigraphic unit of the Lockport Formation exposed along the Niagara Escarpment in Ontario and western New York State. In the late nineteenth century it was an important source of building stone in Hamilton, Ancaster and Waterdown, and in the late twentieth century quarries in a similar unit, also called the Eramosa, near Wiarton in the Bruce Peninsula, became an important source of dimension stone at a time when most of the other resources of similar stone were depleted. Work in these quarries led to the discovery of exceptionally well preserved fossils (the Eramosa lagerstätte). On the east Mountain at Hamilton, a well-developed cave system was discovered in the Eramosa and has now been designated as the Eramosa Karst Conservation Area. Stratigraphy The term was first used for a stratigraphic unit by Williams (1915) who named the Eramosa Member of the Lockport Formation for the bituminous dolomites exposed below the Guelph Formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of the Paleozoic Era, and the third of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods ( myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Lung
A book lung is a type of respiration organ used for atmospheric gas-exchange that is present in many arachnids, such as scorpions and spiders. Each of these organs is located inside an open, ventral-abdominal, air-filled cavity (atrium) and connects with its surroundings through a small opening for the purpose of respiration. Structure and function Book lungs are not related to the lungs of modern land-dwelling vertebrates. Their name instead describes their structure and purpose as a case of convergent evolution. Stacks of alternating air pockets and tissue filled with hemolymph give them an appearance similar to a "folded" book. Their number varies from just one pair in most spiders to four pairs in scorpions. The unfolded "pages" (plates) of the book lung are filled with hemolymph. The folds maximize the surface exposed to air, and thereby maximize the amount of gas exchanged with the environment. In most species, no motion of the plates is needed to facilitate this ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic Life Of Ontario
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma at the start of the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest), Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. Some geological timescales divide the Paleozoic informally into early and late sub-eras: the Early Paleozoic consisting of the Cambrian, Ordovician and Silurian; the Late Paleozoic consisting of the Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. The name ''Paleozoic'' was first used by Adam Sedgwick (1785–1873) in 1838 to describe the Cambrian and Ordovician periods. It was redefined by John Phillips (1800–1874) in 1840 to cover the Cambrian to Permian periods. It is derived from the Greek ''palaiós'' (παλαιός, "old") and ''zōḗ'' (ζωή, "life") meaning "ancient lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 2015
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of ''Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Scorpion Genera
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing having spread to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. It is based on an old conception of history that without written records there could be no history. The most common conception today is that history is based on evidence, however the concept of prehistory hasn't been completely discarded. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurian Arthropods Of North America
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of the Paleozoic Era, and the third of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods (myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) became full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruce Peninsula
The Bruce Peninsula is a peninsula in Ontario, Canada, that divides Georgian Bay of Lake Huron from the lake's main basin. The peninsula extends roughly northwestwards from the rest of Southwestern Ontario, pointing towards Manitoulin Island, with which it forms the widest strait joining Georgian Bay to the rest of Lake Huron. The Bruce Peninsula contains part of the geological formation known as the Niagara Escarpment. The entire peninsula and nearby communities to the south along Lake Huron are located within Bruce County, Ontario. The peninsula is a popular tourist destination for camping, hiking and fishing, with two national parks (Bruce Peninsula National Park and Fathom Five National Marine Park), more than half a dozen nature reserves, and the Bruce Peninsula Bird Observatory. The Bruce Trail runs through the region to its northern terminus in the town of Tobermory, Ontario, Tobermory. This region is named after James Bruce, 8th Earl of Elgin (Lord Elgin), Governor Gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomotheca
Stomotheca is the term applied to the feeding apparatus in front of the mouth of harvestmen, and sometimes the related scorpions. Usually it consists of the ''epistome'' ( labrum), two pairs of ''coxapophyses'' (endites, maxillary lobes) and often a '' labium''. (2007): Morphology and Functional Anatomy. In: Pinto-da-Rocha ''et al.'' 2007: 23ff The ''epistome'' is a projection that forms the anterior wall of the stomotheca. Its upper side is hardened and divided by a transverse invagination ( sulcus). The part nearer the groove is sometimes called clypeus, the other one labrum. The area around the mouth is soft and flexible, often with a distal lobe. On the sides, the walls around the mouth are fused to the medial surfaces of the pedipalpal coxae, and a transverse muscle attaches to the inner surfaces of the epistomal walls. ''Coxapophyses'' are extensions from the pedipalps and first pair of legs. While hardened at the base, they end in large soft pads that work as lips. It some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurypterids
Eurypterids, often informally called sea scorpions, are a group of extinct marine arthropods that form the order Eurypterida. The earliest known eurypterids date to the Darriwilian stage of the Ordovician period, 467.3 million years ago. The group is likely to have appeared first either during the Early Ordovician or Late Cambrian period. With approximately 250 species, the Eurypterida is the most diverse Paleozoic chelicerate order. Following their appearance during the Ordovician, eurypterids became major components of marine faunas during the Silurian, from which the majority of eurypterid species have been described. The Silurian genus ''Eurypterus'' accounts for more than 90% of all known eurypterid specimens. Though the group continued to diversify during the subsequent Devonian period, the eurypterids were heavily affected by the Late Devonian extinction event. They declined in numbers and diversity until becoming extinct during the Permian–Triassic extinction event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praearcturus
''Praearcturus'' is an extinct genus of arthropod, most likely a scorpion, known from the Devonian period of what is now Britain. It is the only genus in the family Praearcturidae and contains the single species ''P. gigas''. Taxonomic history The type fossil was discovered in Rowlestone, England, and was described as a giant isopod in 1871 by Henry Woodward. It was later interpreted as a scorpion by Rolfe (1980), who claimed that it was based on the personal communications by L. Størmer (1974) and E. N. Kjellesvig-Waering (1978) and the published figures by Rolfe (1969). While type specimen is from the Lower Devonian of Old Red Sandstone, single tergite remain is known from Lower Devonian of Wyoming and fragmentary cuticles referrable to this genus is known from Famennian of Portishead. Based on comparisons to modern scorpions, the species could have reached a total length of nearly , possibly making it one of the largest scorpions known. However, a 2024 study was uncertain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |