|
Equity Risk
Equity risk is "the financial risk involved in holding equity in a particular investment." Equity risk is a type of market risk that applies to investing in shares. The market price of stocks fluctuates all the time, depending on supply and demand. The risk of losing money due to a reduction in the market price of shares is known as equity risk. The measure of risk used in the equity markets is typically the standard deviation of a security's price over a number of periods. The standard deviation will delineate the normal fluctuations one can expect in that particular security above and below the mean, or average. However, since most investors would not consider fluctuations above the average return as "risk," some economists prefer other means of measuring it. Equity risk premium (ERP) is defined as "excess return that an individual stock or the overall stock market provides over a risk-free rate." equity risk premium (ERP) is the difference between the return on a market por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Risk
Financial risk is any of various types of risk associated with financing, including financial transactions that include company loans in risk of default. Often it is understood to include only downside risk, meaning the potential for financial loss and uncertainty about its extent. Modern portfolio theory initiated by Harry Markowitz in 1952 under his thesis titled "Portfolio Selection" is the discipline and study which pertains to managing market and financial risk. In modern portfolio theory, the variance (or standard deviation In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation of the values of a variable about its Expected value, mean. A low standard Deviation (statistics), deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean ( ...) of a portfolio is used as the definition of risk. Types According to Bender and Panz (2021), financial risks can be sorted into five different categories. In their study, they apply an algorith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equity (finance)
In finance, equity is an ownership interest in property that may be subject to debts or other liabilities. Equity is measured for accounting purposes by subtracting liabilities from the value of the assets owned. For example, if someone owns a car worth $24,000 and owes $10,000 on the loan used to buy the car, the difference of $14,000 is equity. Equity can apply to a single asset, such as a car or house, or to an entire business. A business that needs to start up or expand its operations can sell its equity in order to raise cash that does not have to be repaid on a set schedule. When liabilities attached to an asset exceed its value, the difference is called a deficit and the asset is informally said to be "underwater" or "upside-down". In government finance or other non-profit settings, equity is known as "net position" or "net assets". Origins The term "equity" describes this type of ownership in English because it was regulated through the system of equity law that devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
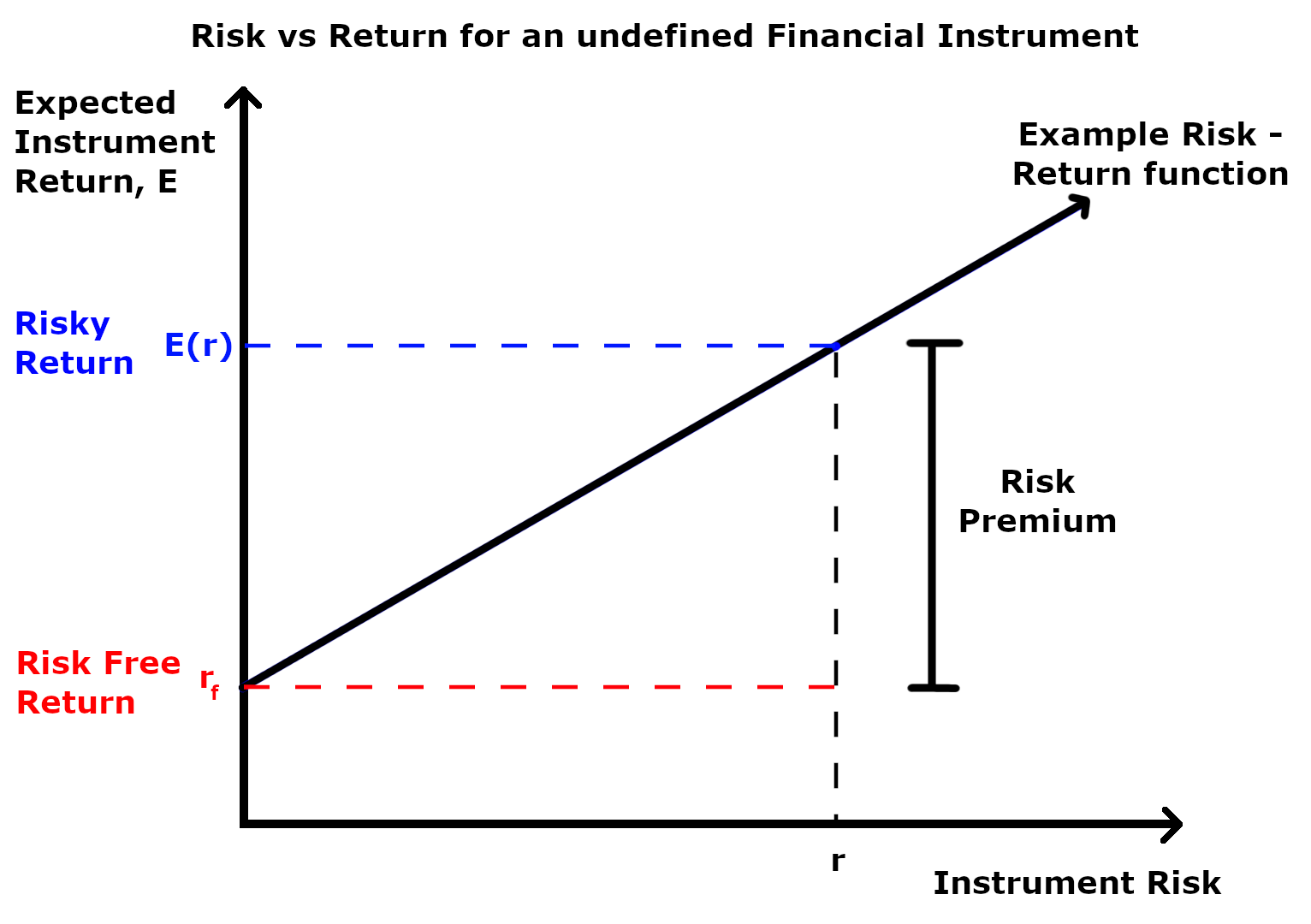
Risk Premium
A risk premium is a measure of excess return that is required by an individual to compensate being subjected to an increased level of risk. It is used widely in finance and economics, the general definition being the expected risky Rate of return, return less the Risk-free interest rate, risk-free return, as demonstrated by the formula below. Risk \ premium = E(r) - r_f Where E(r) is the risky expected rate of return and r_f is the risk-free return. The inputs for each of these variables and the ultimate interpretation of the risk premium value differs depending on the application as explained in the following sections. Regardless of the application, the market premium can be volatile as both comprising variables can be impacted independent of each other by both cyclical and abrupt changes. This means that the market premium is dynamic in nature and ever-changing. Additionally, a general observation regardless of application is that the risk premium is larger during economic do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Share Capital
A corporation's share capital, commonly referred to as capital stock in the United States, is the portion of a corporation's equity that has been derived by the issue of shares in the corporation to a shareholder, usually for cash. ''Share capital'' may also denote the number and types of shares that compose a corporation's share structure. Definition In accounting, the share capital of a corporation is the nominal value of issued shares (that is, the sum of their par values, sometimes indicated on share certificates). If the allocation price of shares is greater than the par value, as in a rights issue, the shares are said to be sold at a premium (variously called share premium, additional paid-in capital or paid-in capital in excess of par). This equation shows the constituents that make up a company's real share capital: : \sum\text \times \text This is differentiated from share capital in the accounting sense, as it presents nominal share capital and does not take t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk Premium
A risk premium is a measure of excess return that is required by an individual to compensate being subjected to an increased level of risk. It is used widely in finance and economics, the general definition being the expected risky Rate of return, return less the Risk-free interest rate, risk-free return, as demonstrated by the formula below. Risk \ premium = E(r) - r_f Where E(r) is the risky expected rate of return and r_f is the risk-free return. The inputs for each of these variables and the ultimate interpretation of the risk premium value differs depending on the application as explained in the following sections. Regardless of the application, the market premium can be volatile as both comprising variables can be impacted independent of each other by both cyclical and abrupt changes. This means that the market premium is dynamic in nature and ever-changing. Additionally, a general observation regardless of application is that the risk premium is larger during economic do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock Market
A stock market, equity market, or share market is the aggregation of buyers and sellers of stocks (also called shares), which represent ownership claims on businesses; these may include ''securities'' listed on a public stock exchange as well as stock that is only traded privately, such as shares of private companies that are sold to investors through equity crowdfunding platforms. Investments are usually made with an investment strategy in mind. Size of the market The total market capitalization of all publicly traded stocks worldwide rose from US$2.5 trillion in 1980 to US$111 trillion by the end of 2023. , there are 60 stock exchanges in the world. Of these, there are 16 exchanges with a market capitalization of $1 trillion or more, and they account for 87% of global market capitalization. Apart from the Australian Securities Exchange, these 16 exchanges are all in North America, Europe, or Asia. By country, the largest stock markets as of January 2022 are in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |