|
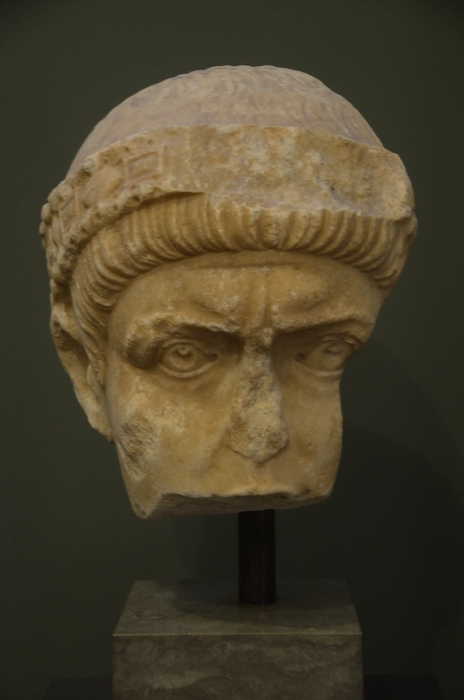
Equitius (consul)
Equitius, or Aequitius, was ''magister militum'' (or master of soldiers) in Illyricum in the Roman Empire. Career Born in Pannonia, he served together with the future Emperor Valentinian I as ''scutarius'' (or guardsman). Being one of Valentinian's principal supporters, the new Emperor made Equitius ''magister militum'' in Illyricum in 364. When Procopius rose up against Valentinian, Equitius remained loyal to the Emperor. Procopius sent envoys to the Illyrian troops to secure their support, but Equitius had them captured and killed. Valentinian appointed Equitius consul in 374. In 375, when Valentinian died, Equitius was one of the generals who elevated the deceased emperor's second son, Valentinian II Valentinian II (; 37115 May 392) was a Roman emperor in the western part of the Roman Empire between AD 375 and 392. He was at first junior co-ruler of his half-brother, then was sidelined by a usurper, and finally became sole ruler after 388, ..., as emperor.Ps-Aurelius Vict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, on the west by Noricum and upper Roman Italy, Italy, and on the southward by Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and upper Moesia. It included the modern regions western Hungary, western Slovakia, eastern Austria, northern Croatia, north-western Serbia, northern Slovenia, and northern Bosnia and Herzegovina. Background In the Early Iron Age, Transdanubia was inhabited by the Pannonians or Pannonii, a collection of Illyrians, Illyrian tribes. The Celts invaded in the Late Iron Age and Gallo-Roman culture, Gallo-Roman historian Pompeius Trogus writes that the Celts were met with heavy resistance from the locals and were not able to overrun the southern part of Transdanubia. Some tribes advanced as far as Delphi, with the Scordisci settling in Syrmia (279 BC) upon being forced to withdraw. The arrival of the Celts in Transdanubia disrupted the flow of amber from the Balti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magister Militum
(Latin for "master of soldiers"; : ) was a top-level military command used in the late Roman Empire, dating from the reign of Constantine the Great. The term referred to the senior military officer (equivalent to a war theatre commander, the emperor remaining the supreme commander) of the empire. The office continued to exist end evolve during the early Byzantine Empire. In Greek language, Greek sources, the term is translated either as ''strategos#Byzantine use, strategos'' or as ''stratelates'' (although these terms were also used non-technically to refer to commanders of different ranks). Establishment and development of the command The office of ''magister militum'' was created in the early 4th century, most likely when the Western Roman emperor Constantine the Great defeated all other contemporary Roman emperors, which gave him control over their respective armies. Because the Praetorian Guards and their leaders, the praetorian prefect, Praetorian Prefects, had suppor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetorian Prefecture Of Illyricum
The praetorian prefecture of Illyricum (; , also termed simply the prefecture of Illyricum) was one of four praetorian prefectures into which the Later Roman Empire, Late Roman Empire was divided. The administrative centre of the prefecture was Sirmium (375–379), and, after 379, Thessalonica.Thessalonica 1910 Catholic Encyclopedia 1910 Catholic Encyclopedia It took its name from the older Illyricum (Roman province), province of Illyricum, which in turn was named after ancient Illyria, and in its greatest expanse encompassed Pannonia, Noricum, Crete, and most of the Balkans, Balkan peninsula except for Diocese of Thrace, Thrace. Administrative history Unlike the other three "classical" ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valentinian I
Valentinian I (; 32117 November 375), also known as Valentinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 364 to 375. He ruled the Western Roman Empire, Western half of the empire, while his brother Valens ruled the Byzantine Empire, East. During his reign, he fought successfully against the Alamanni, Quadi, and Sarmatians, strengthening the border fortifications and conducting campaigns across the Rhine and Danube. His general Count Theodosius, Theodosius defeated a revolt in Africa (Roman province), Africa and the Great Conspiracy, a coordinated assault on Roman Britain by Picts, Scoti, and Saxons. Valentinian founded the Valentinian dynasty, with his sons Gratian and Valentinian II succeeding him in the western half of the empire. Early life Valentinian was born in 321 at Cibalae (now Vinkovci, Croatia) in southern Pannonia into a family of Illyro-Roman origin. Valentinian and his younger brother Valens were the sons of Gratianus Funarius, Gratianus (nicknamed Funarius), a military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scutarius
A scutarius in ancient Rome was any of the various types of gladiator who used a large shield called a samnite shield, which is named after another type of gladiator—a samnite. In Latin, the shield was called a '' scutum''—where the name ''scutarius'' comes from. Due to having a large shield, ''scutarii'' would wear shin armour (''ocrea'') on their shield leg. This piece of armour would be smaller than the two ''ocreae'' worn by '' parmularii,'' who carried a smaller, though still somewhat large, shield. Scutarii also usually carried short swords and wore visored helmets. Scutarii and parmularii are mentioned by Marcus Aurelius in his ''Meditations'' as two factions at the gladiator fights—both as gladiators and people who supported those gladiators. A scutarius could also refer to a guard armed with a scutum, as well as someone who made shields. See also * List of Roman gladiator types There were many different types of gladiators in ancient Rome. Some of the first g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procopius (usurper)
Procopius (; Ancient Greek: Προκόπιος; July 325 – 27 May 366) was a Roman usurper against Valens. Life Procopius was born in July 325, in Corycus, Cilicia (now Turkey). On his mother's side, Procopius was a maternal cousin to Emperor Julian, since their maternal grandfather was Julius Julianus. His first wife was probably Artemisia. The Roman general of the 5th century Procopius and his son, the Emperor Anthemius, were among his descendants, the first being the son of his son Procopius. During the reign of Constantius II, he served as ''tribunus et notarius'' for a long period of time. By 358, the emperor trusted him enough to send him with Lucillianus as an envoy to the Sassanid court. His career granted him the opportunity to build many important connections, as well as to help him understand the structure of the imperial government. Persian campaign When Julian departed from Constantinople in the spring of 362, his objective was clear: to launch a swift, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valentinian II
Valentinian II (; 37115 May 392) was a Roman emperor in the western part of the Roman Empire between AD 375 and 392. He was at first junior co-ruler of his half-brother, then was sidelined by a usurper, and finally became sole ruler after 388, albeit with limited ''de facto'' powers. A son of emperor Valentinian I and empress Justina, he was raised to the imperial office at the age of four by military commanders upon his father's death. Until 383, Valentinian II remained a junior partner to his older half-brother Gratian in ruling the Western empire, while the East was governed by his uncle Valens until 378 and Theodosius I from 379. When the usurper emperor Magnus Maximus killed Gratian in 383, the court of Valentinian II in Milan became the locus of confrontations between adherents to Nicene and Arian Christianity. In 387, Maximus invaded Italy, spurring Valentinian II and his family to escape to Thessalonica where they successfully sought Theodosius's aid. Theodosius def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valens
Valens (; ; 328 – 9 August 378) was Roman emperor from 364 to 378. Following a largely unremarkable military career, he was named co-emperor by his elder brother Valentinian I, who gave him the Byzantine Empire, eastern half of the Roman Empire to rule. In 378, Valens was defeated and killed at the Battle of Adrianople against the invading Goths, which astonished contemporaries and marked the beginning of barbarian encroachment into Roman territory. As emperor, Valens continually faced threats both internal and external. He defeated, after some dithering, the usurper Procopius (usurper), Procopius in 366, and campaigned against the Goths across the Danube in 367 and 369. In the following years, Valens focused on the eastern frontier, where he faced the perennial threat of Sasanian Empire, Persia, particularly in Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Armenia, as well as additional conflicts with the Saracens and Isaurians. Domestically, he inaugurated the Aqueduct of Valens in Cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Late Imperial Roman Consuls
This is a list of consuls known to have held office, from the beginning of the Roman Republic to the latest use of the title in Imperial times, together with those magistrates of the Republic who were appointed in place of consuls, or who superseded consular authority for a limited period. Background Republican consuls From the establishment of the Republic to the time of Augustus, the consuls were the chief magistrates of the Roman state. Traditionally, two were simultaneously appointed for a year-long term, so that the executive power of the state was not vested in a single individual, as it had been under the kings. As other ancient societies dated historical events according to the reigns of their kings, it became customary at Rome to date events by the names of the consuls in office when the events occurred, rather than (for instance) by counting the number of years since the foundation of the city, although that method could also be used. If a consul died during his year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gratian
Gratian (; ; 18 April 359 – 25 August 383) was emperor of the Western Roman Empire from 367 to 383. The eldest son of Valentinian I, Gratian was raised to the rank of ''Augustus'' as a child and inherited the West after his father's death in 375. He nominally shared the government with his infant half-brother Valentinian II, who was also acclaimed emperor in Pannonia on Valentinian's death. The East was ruled by his uncle Valens, who was later succeeded by Theodosius I. Gratian subsequently led a campaign across the Rhine, attacked the Lentienses, and forced the tribe to surrender. That same year, the eastern emperor Valens was killed fighting the Goths at the Battle of Adrianople, which led to Gratian elevating Theodosius to replace him in 379. Gratian favoured Nicene Christianity over traditional Roman religion, issuing the Edict of Thessalonica, refusing the office of '' pontifex maximus'', and removing the Altar of Victory from the Roman Senate's Curia Julia. The city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |