|
Epistrategos
''Epistrategos'' (; ) was a senior military and administrative office in Ptolemaic Egypt, which was retained during the subsequent Roman period as well. Each ''epistrategos'' were responsible for an epistrategy (). Under Ptolemaic rule, a Greek '' strategos'' was appointed to each of the Egyptian nomes, originally as garrison commander for the Greek troops, but soon eclipsing the nomarch and assuming administrative duties as well. Gradually, a number of nomes began being placed under the authority of a single ''strategos'', and under Ptolemy II Philadelphus (), the office of ''epistrategos'' of the "''Chora''" (i.e. the interior country) was established, with authority over the other ''strategoi'' in the entirety of Egypt beyond the capital, Alexandria. Later, a second ''epistrategos'' was created for the Thebaid. As with most of the Ptolemaic system, the office was retained after the Roman takeover in 30 BC, with a layer of Roman officials under the augustal prefect grafted o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategos
''Strategos'' (), also known by its Linguistic Latinisation, Latinized form ''strategus'', is a Greek language, Greek term to mean 'military General officer, general'. In the Hellenistic world and in the Byzantine Empire, the term was also used to describe a military governor. In the modern Hellenic Army, it is the highest officer rank. Etymology ''Strategos'' is a compound of two Greek words: ''stratos'' and ''agos''. ''Stratos'' (στρατός) means 'army', literally 'that which is spread out', coming from the proto-Indo-European root *stere-, 'to spread'. ''Agos'' (ἀγός) means 'leader', from ''agein'' (ἄγειν), 'to lead', from the pelasgic root *ag-, 'to drive, draw out or forth, move'. Classical Greece Athens In its most famous attestation, in Classical Athens, the office of ''strategos'' existed already in the 6th century BC, but it was only with the reforms of Cleisthenes in 501 BC that it assumed its most recognizable form: Cleisthenes instituted a boa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Egypt
Roman Egypt was an imperial province of the Roman Empire from 30 BC to AD 642. The province encompassed most of modern-day Egypt except for the Sinai. It was bordered by the provinces of Crete and Cyrenaica to the west and Judaea, later Arabia Petraea, to the East. Egypt was conquered by Roman forces in 30 BC and became a province of the new Roman Empire upon its formation in 27 BC. Egypt came to serve as a major producer of grain for the empire and had a highly developed urban economy. It was by far the wealthiest Roman province outside of Italy. The population of Roman Egypt is unknown, although estimates vary from . Alexandria, its capital, was the largest port and second largest city of the Roman Empire. Three Roman legions garrisoned Egypt in the early Roman imperial period, with the garrison later reduced to two, alongside formations of the Roman army. The major town of each '' nome'' (administrative region) was known as a metropolis and gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemaic Kingdom
The Ptolemaic Kingdom (; , ) or Ptolemaic Empire was an ancient Greek polity based in Ancient Egypt, Egypt during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 305 BC by the Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general Ptolemy I Soter, a Diadochi, companion of Alexander the Great, and ruled by the Ptolemaic dynasty until the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC. Reigning for nearly three centuries, the Ptolemies were the longest and final Dynasties of ancient Egypt, dynasty of ancient Egypt, heralding a distinct era of Hellenistic religion, religious and cultural syncretism between Greek and Egyptian culture. Alexander the Great conquered Thirty-first Dynasty of Egypt, Persian-controlled Egypt in 332 BC during Wars of Alexander the Great, his campaigns against the Achaemenid Empire. Death of Alexander the Great, Alexander's death in 323 BC was followed by the Empire of Alexander the Great, rapid unraveling of the Macedonian Empire amid competing claims by the ''diadochi'', his closest fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nome (Egypt)
A nome (, from , ''nomós'', "district") was a territorial division in ancient Egypt. Each nome was ruled by a nomarch (, "Great Chief"). The number of nomes changed through the various periods of the history of ancient Egypt. Etymology The term ''nome'' comes from Ancient Greek νομός ''nomós'' meaning "pasture" extended to "dwelling" and "district"; the Ancient Egyptian term was ( /sɛpɑt/). Today's use of the Ancient Greek rather than the Ancient Egyptian term came about during the Ptolemaic period, when the use of Greek was widespread in Egypt. The availability of Greek records on Egypt influenced the adoption of Greek terms by later historians. History Dynastic Egypt The division of ancient Egypt into nomes can be traced back to prehistoric Egypt (before 3100 BC). These nomes originally existed as autonomous city-states, but later began to unify. According to ancient tradition, the ruler Menes completed the final unification. Not only did the division into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomarch
A nomarch (, Great Chief) was a provincial governor in ancient Egypt; the country was divided into 42 provinces, called Nome (Egypt), nomes (singular , plural ). A nomarch was the government official responsible for a nome. Etymology The term ''nome'' is derived from ''nomós'' "province, district". ''Nomarch'' is derived from ''nomárkhēs'': "province" + "ruler". Egyptian history The division of the Egyptian kingdom into nomes can be documented as far back as the reign of Djoser of the Third Dynasty of Egypt, 3rd Dynasty in the early Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom, c. 2670 BCE, and potentially dates even further back to the Prehistoric Egypt, Predynastic kingdoms of the Nile valley. The earliest topographical lists of the nomes of Upper and Lower Egypt date back to the reign of Nyuserre Ini, of the mid Fifth Dynasty of Egypt, 5th Dynasty, from which time the nomarchs no longer lived at royal capital but stayed in their nomes. The power of the nomarchs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy II Philadelphus
Ptolemy II Philadelphus (, ''Ptolemaîos Philádelphos'', "Ptolemy, sibling-lover"; 309 – 28 January 246 BC) was the pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 284 to 246 BC. He was the son of Ptolemy I, the Macedonian Greek general of Alexander the Great who founded the Ptolemaic Kingdom after the death of Alexander, and Queen Berenice I, originally from Macedon. During Ptolemy II's reign, the material and literary splendour of the Alexandrian court was at its height. He promoted the Museum and Library of Alexandria. In addition to Egypt, Ptolemy's empire encompassed much of the Aegean and Levant. He pursued an aggressive and expansionist foreign policy with mixed success. From 275 to 271 BC, he led the Ptolemaic Kingdom against the rival Seleucid Empire in the First Syrian War and extended Ptolemaic power into Cilicia and Caria, but lost control of Cyrenaica after the defection of his half-brother Magas. In the Chremonidean War (–261 BC), Ptolemy confronted Antigonid Maced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile Delta, Nile River delta. Founded in 331 BC by Alexander the Great, Alexandria grew rapidly and became a major centre of Hellenic civilisation, eventually replacing Memphis, Egypt, Memphis, in present-day Greater Cairo, as Egypt's capital. Called the "Bride of the Mediterranean" and "Pearl of the Mediterranean Coast" internationally, Alexandria is a popular tourist destination and an important industrial centre due to its natural gas and petroleum, oil pipeline transport, pipelines from Suez. The city extends about along the northern coast of Egypt and is the largest city on the Mediterranean, the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second-largest in Egypt (after Cairo), the List of largest cities in the Arab world, fourth- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebaid
The Thebaid or Thebais (, ''Thēbaïs'') was a region in ancient Egypt, comprising the 13 southernmost nome (Egypt), nomes of Upper Egypt, from Abydos, Egypt, Abydos to Aswan. Pharaonic history The Thebaid acquired its name from its proximity to the ancient Egyptian capital of Thebes, Egypt, Thebes (Luxor). During the Ancient Egyptian dynasties this region was dominated by Thebes and its priesthood at the temple of Amun at Karnak. In Ptolemaic dynasty, Ptolemaic Egypt, the Thebaid formed a single administrative district under the ''Epistrategos'' of Thebes, who was also responsible for overseeing navigation in the Red Sea and the Indian Ocean. The capital of Ptolemais in Thebaide, Ptolemaic Thebaid was Ptolemais Hermiou, a Hellenistic colony on the Nile which served as the center of royal political and economic control in Upper Egypt. Roman province(s) During the Roman Empire, Diocletian created the province of ''Thebais'', guarded by the Roman legion, legions Legio I Maxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustal Prefect
During the Roman Empire, the governor of Roman Egypt ''(praefectus Aegypti)'' was a prefect who administered the Roman province of Egypt with the delegated authority ''(imperium)'' of the emperor. Egypt was established as a Roman province in consequence of the Battle of Actium, where Cleopatra as the last independent ruler of Egypt and her Roman ally Mark Antony were defeated by Octavian, the adopted heir of the assassinated Roman dictator Julius Caesar. Octavian then rose to supreme power with the title Augustus, ending the era of the Roman Republic and installing himself as ''princeps'', the so-called "leading citizen" of Rome who in fact acted as an autocratic ruler. Although senators continued to serve as governors of most other provinces (the senatorial provinces), especially those annexed under the Republic, the role of Egypt during the civil war with Antony and its strategic and economic importance prompted Augustus to ensure that no rival could secure ''Aegyptus'' as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Citizens
Citizenship in ancient Rome () was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, traditions, and cultural practices. There existed several different types of citizenship, determined by one's gender, class, and political affiliations, and the exact duties or expectations of a citizen varied throughout the history of the Roman Empire. History The oldest document currently available that details the rights of citizenship is the Twelve Tables, ratified 449 BC. Much of the text of the Tables only exists in fragments, but during the time of Ancient Rome the Tables would be displayed in full in the Roman Forum for all to see. The Tables detail the rights of citizens in dealing with court proceedings, property, inheritance, death, and (in the case of women) public behavior. Under the Roman Republic, the government conducted a census every fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equestrian Order
The (; , though sometimes referred to as " knights" in English) constituted the second of the property/social-based classes of ancient Rome, ranking below the senatorial class. A member of the equestrian order was known as an (). Description During the Roman Kingdom and the first century of the Roman Republic, legionary cavalry was recruited exclusively from the ranks of the patricians, who were expected to provide six (hundreds) of cavalry (300 horses for each consular legion). Around 400BC, 12 more of cavalry were established and these included non-patricians (plebeians). Around 300 BC the Samnite Wars obliged Rome to double the normal annual military levy from two to four legions, doubling the cavalry levy from 600 to 1,200 horses. Legionary cavalry started to recruit wealthier citizens from outside the 18 . These new recruits came from the first class of commoners in the Centuriate Assembly organisation, and were not granted the same privileges. By the time of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
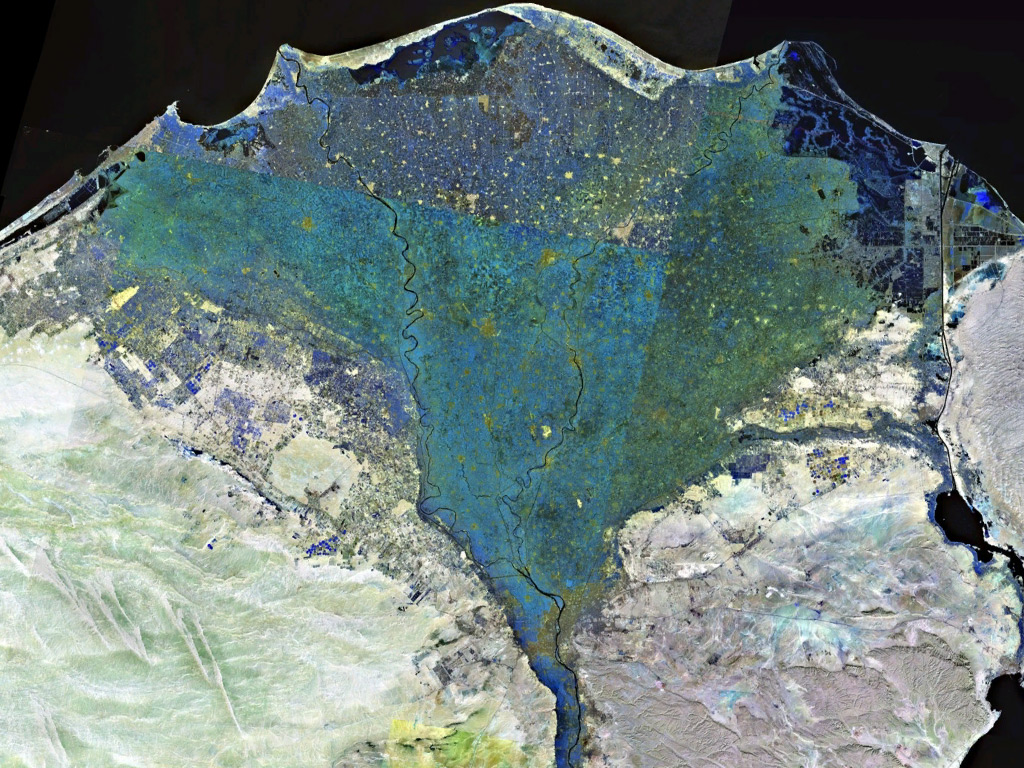
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta (, or simply , ) is the River delta, delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's larger deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east; it covers of the Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributary, distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same names. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood management, flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |