|
Epikeratophakia
Epikeratophakia (also known as epikeratoplasty and onlay lamellar keratoplasty) is a refractive surgical procedure in which a lamella of a donor cornea is transplanted onto the anterior surface of the patient's cornea. A lamellar disc from a donor cornea is placed over the de-epithelialized host cornea and sutured into a prepared groove on the host cornea. Indications include treatment of keratoconus, refractive errors like myopia and high hypermetropia including aphakia, which cannot be corrected with conservative methods. __TOC__ Complications Common complications of epikeratophakia include delayed post operative visual recovery, reduced best corrected visual acuity, prolonged epithelial defects and irregular astigmatism Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. The lens and cornea of an eye without astigmatism are nearly spherical, with only a single radius of curvature, and any refractive errors .... His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratoconus
Keratoconus is an eye disorder in which the cornea, the transparent front part of the eye, gradually thins and bulges outward into a cone shape. This causes distorted vision, including blurry vision, double vision, increased nearsightedness, irregular astigmatism, and light sensitivity, which can reduce Quality of life (healthcare), quality of life. Both eyes are usually affected. The cause is not fully understood but likely involves a combination of heredity, genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors. Having a parent, sibling, or child with keratoconus increases risk significantly. Environmental risk factors include frequent eye rubbing and atopy, allergies. Diagnosis is typically made with corneal topography, which maps the shape of the cornea and reveals characteristic changes. In early stages, vision is often corrected with glasses or soft contact lenses. As the condition progresses, rigid or scleral contact lenses may be needed. In 2016, the FDA approved corneal col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Surgery
Refractive surgery is an optional eye surgery used to improve the refractive state of the eye and decrease or eliminate dependency on glasses or contact lenses. This can include various methods of surgical remodeling of the cornea ( keratomileusis), lens implantation or lens replacement. The most common methods today use excimer lasers to reshape the curvature of the cornea. Refractive eye surgeries are used to treat common vision disorders such as myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia and astigmatism. History The first theoretical work on the potential of refractive surgery was published in 1885 by Hjalmar August Schiøtz, an ophthalmologist from Norway. In 1930, the Japanese ophthalmologist Tsutomu Sato made the first attempts at performing this kind of surgery, hoping to correct the vision of military pilots. His approach was to make radial cuts in the cornea, correcting effects by up to 6 diopters. The procedure unfortunately produced a high rate of corneal degeneration, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornea
The cornea is the transparency (optics), transparent front part of the eyeball which covers the Iris (anatomy), iris, pupil, and Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and Lens (anatomy), lens, the cornea Refraction, refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is approximately 43 dioptres. The cornea can be reshaped by surgical procedures such as LASIK. While the cornea contributes most of the eye's focusing power, its Focus (optics), focus is fixed. Accommodation (eye), Accommodation (the refocusing of light to better view near objects) is accomplished by changing the geometry of the lens. Medical terms related to the cornea often start with the prefix "''wikt:kerat-, kerat-''" from the Ancient Greek, Greek word κέρας, ''horn''. Structure The cornea has myelinated, unmyelinated nerve endings sensitive to touch, temperature and chemicals; a to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Error
Refractive error is a problem with focus (optics), focusing light accurately on the retina due to the shape of the eye and/or cornea. The most common types of refractive error are myopia, near-sightedness, hyperopia, far-sightedness, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Near-sightedness results in far away objects being blurred vision, blurry, far-sightedness and presbyopia result in close objects being blurry, and astigmatism causes objects to appear stretched out or blurry. Other symptoms may include double vision, headaches, and eye strain. Near-sightedness is due to the length of the eyeball being too long; far-sightedness the eyeball too short; astigmatism the cornea being the wrong shape, while presbyopia results from aging of the lens of the eye such that it cannot change shape sufficiently. Some refractive errors occur more often among those whose parents are affected. Diagnosis is by eye examination. Refractive errors are corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
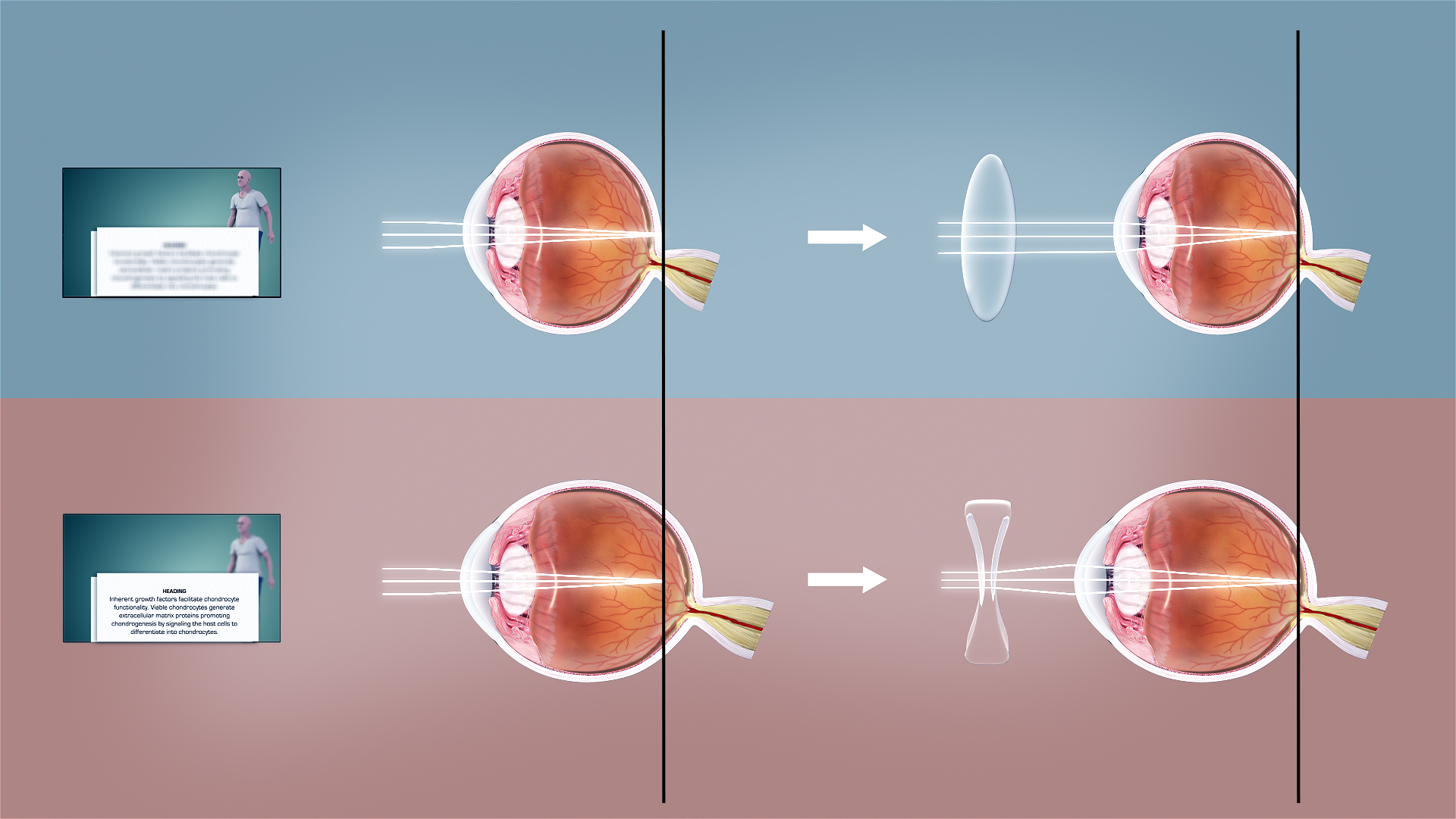
Myopia
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness and short-sightedness, is an eye condition where light from distant objects focuses in front of, instead of on, the retina. As a result, distant objects appear blurry, while close objects appear normal. Other symptoms may include headaches and eye strain. Severe myopia is associated with an increased risk of macular degeneration, retinal detachment, cataracts, and glaucoma. Myopia results from the length of the eyeball growing too long or less commonly the lens being too strong. It is a type of refractive error. Diagnosis is by the use of cycloplegics during eye examination. Tentative evidence indicates that the risk of myopia can be decreased by having young children spend more time outside. This decrease in risk may be related to natural light exposure. Myopia can be corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or by refractive surgery. Eyeglasses are the simplest and safest method of correction. Contact lenses can provide a rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypermetropia
Far-sightedness, also known as long-sightedness, hypermetropia, and hyperopia, is a condition of the eye where distant objects are seen clearly but near objects appear blurred. This blur is due to incoming light being focused behind, instead of on, the retina due to insufficient accommodation by the lens. Minor hypermetropia in young patients is usually corrected by their accommodation, without any defects in vision. But, due to this accommodative effort for distant vision, people may complain of eye strain during prolonged reading. If the hypermetropia is high, there will be defective vision for both distance and near. People may also experience accommodative dysfunction, binocular dysfunction, amblyopia, and strabismus. Newborns are almost invariably hypermetropic, but it gradually decreases as the newborn gets older. There are many causes for this condition. It may occur when the axial length of eyeball is too short or if the lens or cornea is flatter than normal. Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphakia
Aphakia is the absence of the lens of the eye, due to surgical removal, such as in cataract surgery, a perforating wound or ulcer, or congenital anomaly. It causes a loss of ability to maintain focus ( accommodation), high degree of farsightedness ( hyperopia), and a deep anterior chamber. Complications include detachment of the vitreous or retina, and glaucoma. Babies are rarely born with aphakia. Occurrence most often results from surgery to remove a congenital cataract. Congenital cataracts usually develop as a result of infection of the fetus or genetic reasons. It is often difficult to identify the exact cause of these cataracts, especially if only one eye is affected. People with aphakia have relatively small pupils and their pupils dilate to a lesser degree. Causes Surgical removal of a lens, mainly in cataract surgery, is the most common cause of aphakia. Spontaneous traumatic absorption or congenital absence of lens matter is rare. Traumatic subluxation or disloca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of visual perception, vision, but technically rates an animal's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity depends on optical and neural factors. Optical factors of the eye influence the sharpness of an image on its retina. Neural factors include the health and functioning of the retina, of the neural pathways to the brain, and of the interpretative faculty of the brain. The most commonly referred-to visual acuity is ''distance acuity'' or ''far acuity'' (e.g., "20/20 vision"), which describes someone's ability to recognize small details at a far distance. This ability is compromised in people with myopia, also known as short-sightedness or near-sightedness. Another visual acuity is ''Near visual acuity, near acuity'', which describes someone's ability to recognize small details at a near distance. This ability is compromised in people with hyperopia, also known as long-sightedness or far-sightedness. A com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astigmatism
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. The lens and cornea of an eye without astigmatism are nearly spherical, with only a single radius of curvature, and any refractive errors present can be corrected with simple glasses. In an eye with astigmatism, either the lens or the cornea is slightly egg-shaped, with higher curvature in one direction than the other. This gives distorted or blurred vision at any distance and requires corrective lenses that apply different optical powers at different rotational angles. Astigmatism can lead to symptoms that include eyestrain, headaches, and trouble driving at night. Astigmatism often is present at birth, but can change or develop later in life. If it occurs in early life and is left untreated, it may result in amblyopia. The cause of astigmatism is unclear, although it is believed to be partly related to genetic factors. The underlying mechanism involves an irregular c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jose Barraquer
José Ignacio Barraquer Moner (24 January 1916 – 13 February 1998) was a Spanish Ophthalmology, ophthalmologist and Invention, inventor born in Barcelona who did most of his life's work in Bogotá, Colombia. His original pioneering investigations on corneal transplants and correction of corneal refraction led him to be designated as “Father of modern Refractive Surgery”. His ophthalmological surgical techniques and inventions are now in routine use by the ophthalmic community. Biography He was born in Barcelona, first son of Ignacio Barraquer (March 25, 1884 – May 13, 1965) and Josefa Moner Raguer (1893-1987). His grandfather, José Antonio Barraquer i Roviralta (1852-1924) was a pioneer of modern ophthalmology in Spain and a great histopathologist, and the brother of Lluis Barraquer i Roviralta (1855-1928), a pioneer of neurology and the founder, in 1882, of the first department of clinical neurology and electrotherapy in Spain; his son Lluis Barraquer Ferré (1887-19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |