|
Epi-convergence
In mathematical analysis, epi-convergence is a type of convergence for real-valued and extended real-valued functions. Epi-convergence is important because it is the appropriate notion of convergence with which to approximate minimization problems in the field of mathematical optimization. The symmetric notion of hypo-convergence is appropriate for maximization problems. Mosco convergence In mathematical analysis, Mosco convergence is a notion of convergence for functional (mathematics), functionals that is used in nonlinear, nonlinear analysis and set-valued analysis. It is a particular case of Γ-convergence. Mosco convergence is ... is a generalization of epi-convergence to infinite dimensional spaces. Definition Let X be a metric space, and f_: X \to \mathbb a real-valued function for each natural number n . We say that the sequence (f^) epi-converges to a function f: X \to \mathbb if for each x \in X : \begin & \liminf_ f_(x_n) \geq f(x) \text x_n \to x ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuratowski Convergence
In mathematics, Kuratowski convergence or Painlevé-Kuratowski convergence is a notion of convergence for subsets of a topological space. First introduced by Paul Painlevé in lectures on mathematical analysis in 1902,This is reported in the Commentary section of Chapter 4 of Rockafellar and Wets' text. the concept was popularized in texts by Felix Hausdorff and Kazimierz Kuratowski. Intuitively, the Kuratowski limit of a sequence of sets is where the sets " accumulate". Definitions For a given sequence \_^ of points in a space X, a limit point of the sequence can be understood as any point x \in X where the sequence ''eventually'' becomes arbitrarily close to x. On the other hand, a cluster point of the sequence can be thought of as a point x \in X where the sequence ''frequently'' becomes arbitrarily close to x. The Kuratowski limits inferior and superior generalize this intuition of limit and cluster points to subsets of the given space X. Metric Spaces Let (X,d) be a metric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Analysis
Analysis is the branch of mathematics dealing with continuous functions, limit (mathematics), limits, and related theories, such as Derivative, differentiation, Integral, integration, measure (mathematics), measure, infinite sequences, series (mathematics), series, and analytic functions. These theories are usually studied in the context of Real number, real and Complex number, complex numbers and Function (mathematics), functions. Analysis evolved from calculus, which involves the elementary concepts and techniques of analysis. Analysis may be distinguished from geometry; however, it can be applied to any Space (mathematics), space of mathematical objects that has a definition of nearness (a topological space) or specific distances between objects (a metric space). History Ancient Mathematical analysis formally developed in the 17th century during the Scientific Revolution, but many of its ideas can be traced back to earlier mathematicians. Early results in analysis were i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Series
In mathematics, a series is, roughly speaking, a description of the operation of adding infinitely many quantities, one after the other, to a given starting quantity. The study of series is a major part of calculus and its generalization, mathematical analysis. Series are used in most areas of mathematics, even for studying finite structures (such as in combinatorics) through generating functions. In addition to their ubiquity in mathematics, infinite series are also widely used in other quantitative disciplines such as physics, computer science, statistics and finance. For a long time, the idea that such a potentially infinite summation could produce a finite result was considered paradoxical. This paradox was resolved using the concept of a limit during the 17th century. Zeno's paradox of Achilles and the tortoise illustrates this counterintuitive property of infinite sums: Achilles runs after a tortoise, but when he reaches the position of the tortoise at the beginning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics Of Operations Research
''Mathematics of Operations Research'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed scientific journal established in February 1976. It focuses on areas of mathematics relevant to the field of operations research such as continuous optimization, discrete optimization, game theory, machine learning, simulation methodology, and stochastic models. The journal is published by INFORMS (Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences). the journal has a 2017 impact factor of 1.078. History The journal was established in 1976. The founding editor-in-chief was Arthur F. Veinott Jr. (Stanford University). He served until 1980, when the position was taken over by Stephen M. Robinson, who held the position until 1986. Erhan Cinlar served from 1987 to 1992, and was followed by Jan Karel Lenstra (1993-1998). Next was Gérard Cornuéjols (1999-2003) and Nimrod Megiddo (2004-2009). Finally came Uri Rothblum (2009-2012), Jim Dai (2012-2018), and the current editor-in-chief Katya Scheinberg ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pointwise Convergence
In mathematics, pointwise convergence is one of various senses in which a sequence of functions can converge to a particular function. It is weaker than uniform convergence, to which it is often compared. Definition Suppose that X is a set and Y is a topological space, such as the real or complex numbers or a metric space, for example. A net or sequence of functions \left(f_n\right) all having the same domain X and codomain Y is said to converge pointwise to a given function f : X \to Y often written as \lim_ f_n = f\ \mbox if (and only if) \lim_ f_n(x) = f(x) \text x \text f. The function f is said to be the pointwise limit function of the \left(f_n\right). Sometimes, authors use the term bounded pointwise convergence when there is a constant C such that \forall n,x,\;, f_n(x), Properties This concept is often contrasted with |
Uniform Convergence
In the mathematics, mathematical field of mathematical analysis, analysis, uniform convergence is a Modes of convergence, mode of convergence of functions stronger than pointwise convergence. A sequence of Function (mathematics), functions (f_n) converges uniformly to a limiting function f on a set E as the function domain if, given any arbitrarily small positive number \epsilon, a number N can be found such that each of the functions f_N, f_,f_,\ldots differs from f by no more than \epsilon ''at every point'' x ''in'' E. Described in an informal way, if f_n converges to f uniformly, then how quickly the functions f_n approach f is "uniform" throughout E in the following sense: in order to guarantee that f_n(x) differs from f(x) by less than a chosen distance \epsilon, we only need to make sure that n is larger than or equal to a certain N, which we can find without knowing the value of x\in E in advance. In other words, there exists a number N=N(\epsilon) that could depend on \e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
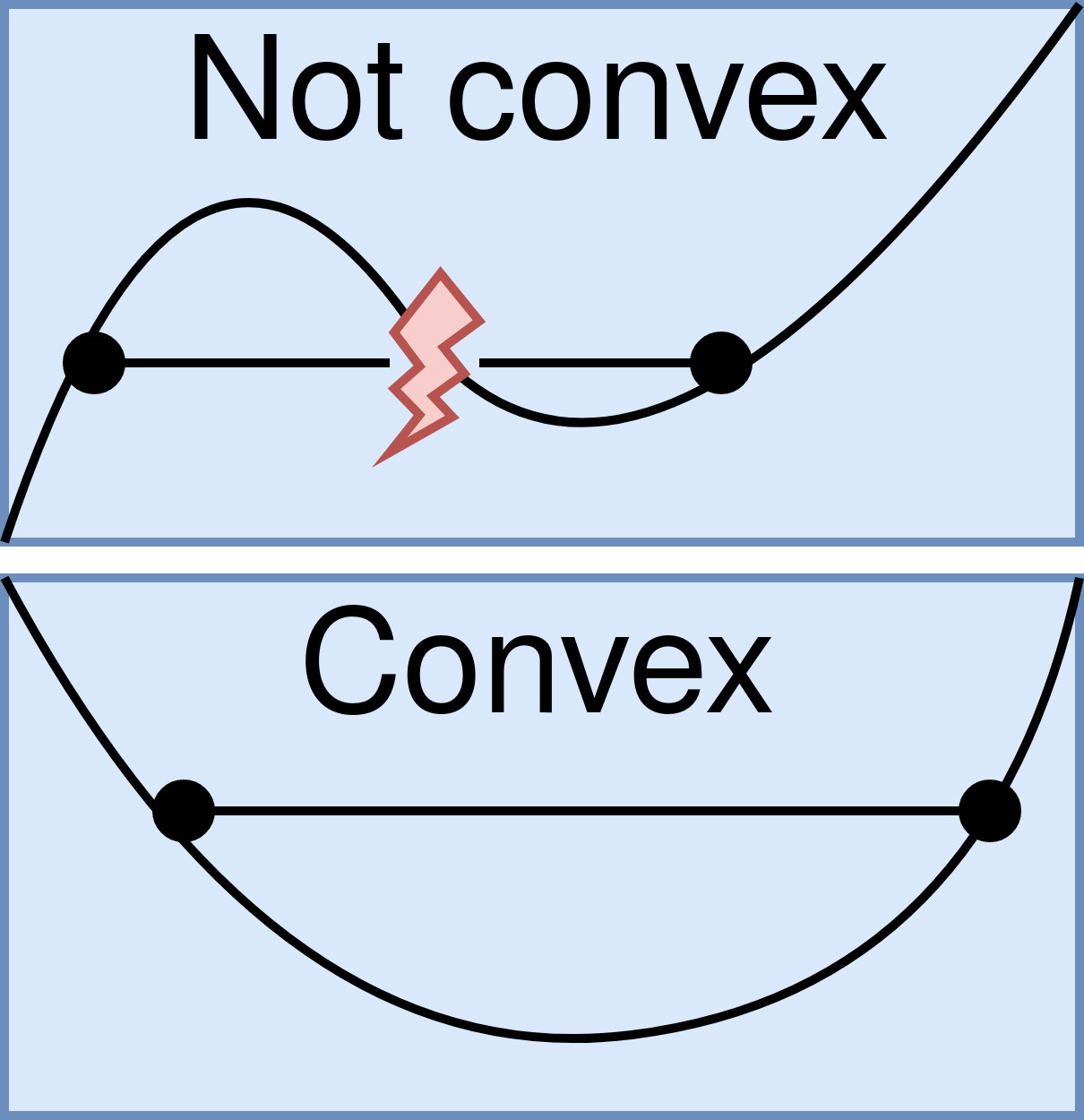
Convex Function
In mathematics, a real-valued function is called convex if the line segment between any two distinct points on the graph of the function lies above the graph between the two points. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. A twice-differentiable function of a single variable is convex if and only if its second derivative is nonnegative on its entire domain. Well-known examples of convex functions of a single variable include a linear function f(x) = cx (where c is a real number), a quadratic function cx^2 (c as a nonnegative real number) and an exponential function ce^x (c as a nonnegative real number). In simple terms, a convex function refers to a function whose graph is shaped like a cup \cup (or a straight line like a linear function), while a concave function's graph is shaped like a cap \cap. Convex functions play an important role in many areas of mathematics. They are especially imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigraph (mathematics)
In mathematics, the epigraph or supergraph of a function f : X \to \infty, \infty/math> valued in the extended real numbers \infty, \infty= \R \cup \ is the set, denoted by \operatorname f, of all points in the Cartesian product X \times \R lying on or above its graph. The strict epigraph \operatorname_S f is the set of points in X \times \R lying strictly above its graph. Importantly, although both the graph and epigraph of f consists of points in X \times \infty, \infty the epigraph consists of points in the subset X \times \R, which is not necessarily true of the graph of f. If the function takes \pm \infty as a value then \operatorname f will be a subset of its epigraph \operatorname f. For example, if f\left(x_0\right) = \infty then the point \left(x_0, f\left(x_0\right)\right) = \left(x_0, \infty\right) will belong to \operatorname f but not to \operatorname f. These two sets are nevertheless closely related because the graph can always be reconstructed from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Convergence
Gamma (uppercase , lowercase ; ''gámma'') is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. In Ancient Greek, the letter gamma represented a voiced velar stop . In Modern Greek, this letter represents either a voiced velar fricative or a voiced palatal fricative (while /g/ in foreign words is instead commonly transcribed as γκ). In the International Phonetic Alphabet and other modern Latin-alphabet based phonetic notations, it represents the voiced velar fricative. History The Greek letter Gamma Γ is a grapheme derived from the Phoenician letter (''gīml'') which was rotated from the right-to-left script of Canaanite to accommodate the Greek language's writing system of left-to-right. The Canaanite grapheme represented the /g/ phoneme in the Canaanite language, and as such is cognate with '' gimel'' ג of the Hebrew alphabet. Based on its name, the letter has been interpreted as an abstract representation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real-valued Function
In mathematics, a real-valued function is a function whose values are real numbers. In other words, it is a function that assigns a real number to each member of its domain. Real-valued functions of a real variable (commonly called ''real functions'') and real-valued functions of several real variables are the main object of study of calculus and, more generally, real analysis. In particular, many function spaces consist of real-valued functions. Algebraic structure Let (X,) be the set of all functions from a set to real numbers \mathbb R. Because \mathbb R is a field, (X,) may be turned into a vector space and a commutative algebra over the reals with the following operations: *f+g: x \mapsto f(x) + g(x) – vector addition *\mathbf: x \mapsto 0 – additive identity *c f: x \mapsto c f(x),\quad c \in \mathbb R – scalar multiplication *f g: x \mapsto f(x)g(x) – pointwise multiplication These operations extend to partial functions from to \mathbb R, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Real Numbers
In mathematics, the affinely extended real number system is obtained from the real number system \R by adding two infinity elements: +\infty and -\infty, where the infinities are treated as actual numbers. It is useful in describing the algebra on infinities and the various limiting behaviors in calculus and mathematical analysis, especially in the theory of measure and integration. The affinely extended real number system is denoted \overline or \infty, +\infty/math> or It is the Dedekind–MacNeille completion of the real numbers. When the meaning is clear from context, the symbol +\infty is often written simply as Motivation Limits It is often useful to describe the behavior of a function f, as either the argument x or the function value f gets "infinitely large" in some sense. For example, consider the function f defined by :f(x) = \frac. The graph of this function has a horizontal asymptote at y = 0. Geometrically, when moving increasingly farther to the right along t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Number
In mathematics, the natural numbers are those numbers used for counting (as in "there are ''six'' coins on the table") and ordering (as in "this is the ''third'' largest city in the country"). Numbers used for counting are called '' cardinal numbers'', and numbers used for ordering are called '' ordinal numbers''. Natural numbers are sometimes used as labels, known as ''nominal numbers'', having none of the properties of numbers in a mathematical sense (e.g. sports jersey numbers). Some definitions, including the standard ISO 80000-2, begin the natural numbers with , corresponding to the non-negative integers , whereas others start with , corresponding to the positive integers Texts that exclude zero from the natural numbers sometimes refer to the natural numbers together with zero as the whole numbers, while in other writings, that term is used instead for the integers (including negative integers). The natural numbers form a set. Many other number sets are built by succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |