|
Eolipotes
''Eolipotes'' is an extinct genus of marine river dolphin of the family Lipotidae. It is the oldest known member of the family, having lived in what is now Japan during the Tortonian stage of the Late Miocene. Fossils of this animal are known from the Tochigi prefecture ( Ogane or Tanokura Formation) and the Gunma prefecture ( Haraichi Formation). ''Eolipotes'' was a small cetacean, with the skull indicating a length of around . In spite of its name, ''Eolipotes''has been found to be more closely related to the genus '' Parapontoporia'', which could indicate that some species of ''Paraprotoporia'' and the baiji became freshwater animals independently from one another. However it is also possible that they all evolved from ancestors that already inhabited estuaries, with ''Eolipotes'' simply becoming more marine. The genus only includes a single species: ''E. japonicus''. History and naming ''Eolipotes'' was described in 2024 on the basis of two fossil specimens discovered in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipotidae
Lipotidae is a family of river dolphins containing the possibly extinct baiji of China and the fossil genus '' Parapontoporia'' from the Late Miocene and Pliocene of the Pacific coast of North America. The genus '' Prolipotes'', which is based on a mandible fragment from Neogene coastal deposits in Guangxi, China, has been classified as an extinct relative of the baiji, but is dubious. The oldest known member of the family is '' Eolipotes'' from the Late Miocene of Japan. The only species of the Lipotidae family that has flourished until recent times is the baiji (''Lipotes vexillifer''), which lives in the Yangtze River The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ... system, but its population has declined drastically since the second half of the 20th century due to the severe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Miocene
The Late Miocene (also known as Upper Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch made up of two faunal stage, stages. The Tortonian and Messinian stages comprise the Late Miocene sub-epoch, which lasted from 11.63 Ma (million years ago) to 5.333 Ma. The evolution of ''Homo'' The gibbons (family Hylobatidae) and orangutans (genus ''Pongo'') were the first groups to split from the line leading to the hominins, including humans, then gorillas (genus ''Gorilla''), and finally chimpanzees and bonobos (genus ''Pan (genus), Pan''). The splitting date between hominin and chimpanzee lineages is placed by some between 4 and 8 million years ago, that is, during the Late Miocene. References External links GeoWhen Database - Late Miocene Miocene, .03 Miocene geochronology, 03 Messinian, * Tortonian, * {{geochronology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tochigi Prefectural Museum
is a prefectural museum in the city of Utsunomiya, Japan. The collection relates to the history and natural history of Tochigi Prefecture. The museum opened in 1982. See also * Shimotsuke Province * List of Historic Sites of Japan (Tochigi) This list is of the Monuments of Japan, Historic Sites of Japan located within the Prefectures of Japan, Prefecture of Tochigi Prefecture, Tochigi. National Historic Sites As of 24 June 2024, thirty-nine Sites have been Cultural Properties of Ja ... References External links *Tochigi Prefectural Museum*Tochigi Prefectural Museum Museums in Tochigi Prefecture Utsunomiya History museums in Japan Prefectural museums Museums established in 1982 1982 establishments in Japan {{Japan-museum-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
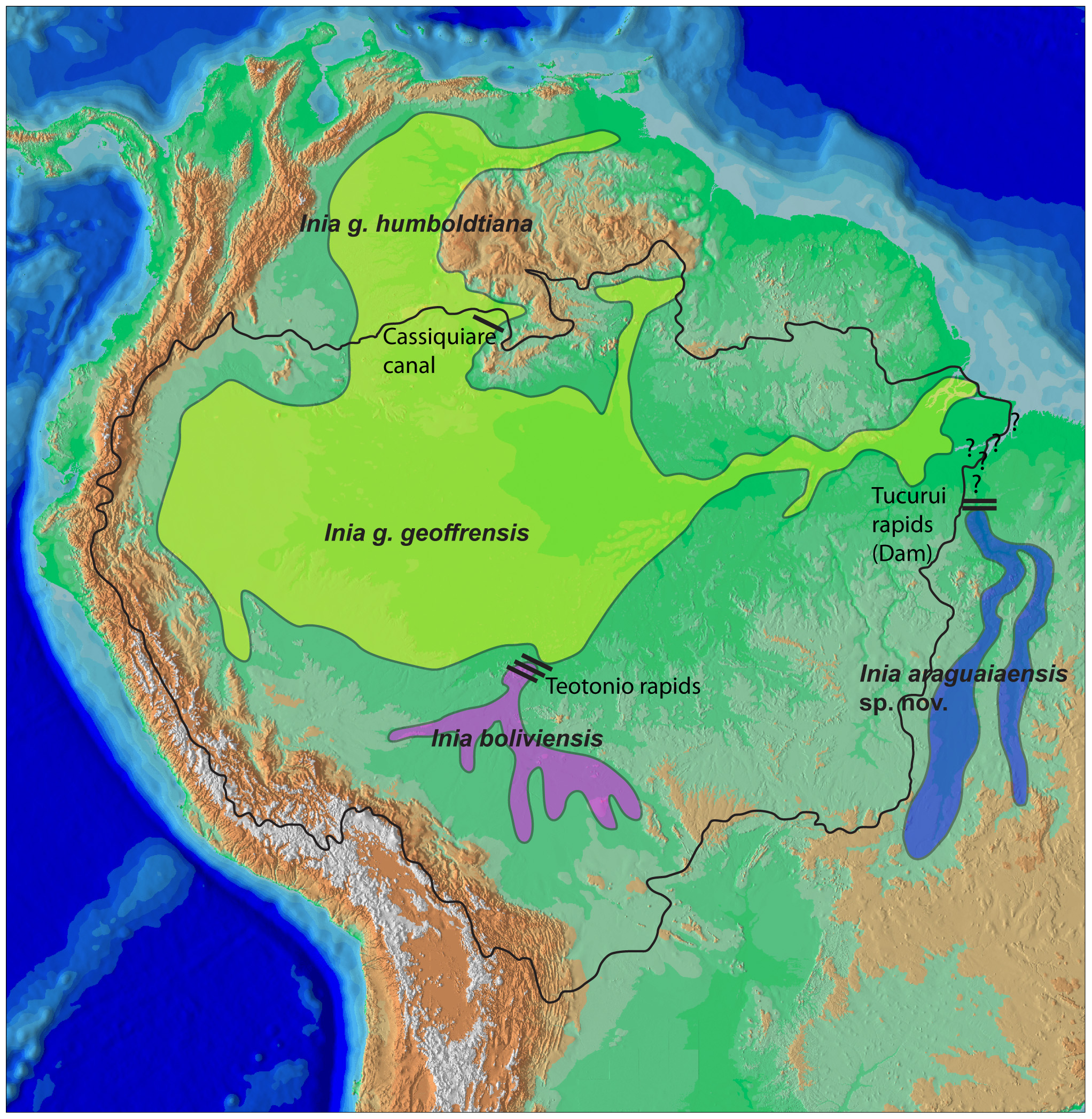
Inioidea
River dolphins are a polyphyletic group of fully aquatic mammals that reside exclusively in freshwater or brackish water. They are an informal grouping of dolphins, which itself is a paraphyletic group within the infraorder Cetacea. Extant river dolphins are placed in two superfamilies, Platanistoidea and Inioidea. They comprise the families Platanistidae (the South Asian dolphins), the possibly extinct Lipotidae (Yangtze River dolphin), Iniidae (the Amazonian dolphins) and Pontoporiidae. There are five extant species of river dolphins. River dolphins, alongside other cetaceans, belong to the clade Artiodactyla, with even-toed ungulates, and their closest living relatives the hippopotamuses, from which they diverged about 40 million years ago. Specific types of dolphins can be pink. River dolphins are relatively small compared to other dolphins, having evolved to survive in warm, shallow water and strong river currents. They range in size from the long South Asian river dolp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex (anatomy)
In arthropod and vertebrate anatomy, the vertex (or ''cranial vertex'') is the highest point of the head. In humans, the vertex is formed by four bones of the skull: the frontal bone, the two parietal bones, and the occipital bone. These bones are connected by the coronal suture between the frontal and parietal bones, the sagittal suture between the two parietal bones, and the lambdoid suture between the parietal and occipital bones. ''Vertex baldness'' refers to a form of male pattern baldness in which the baldness is limited to the vertex, resembling a tonsure. In childbirth, ''vertex birth'' refers to the common head-first presentation of the baby, as opposed to the buttocks-first position of a breech birth. In entomology, the color and shape of an insect's vertex and the structures arising from it are commonly used in identifying species. See also *Calvaria (skull) * Crown (anatomy) *Male pattern baldness Pattern hair loss (also known as androgenetic alopecia (AGA)) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Bone
In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is an unpaired bone which consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, part of the bony orbital cavity holding the eye, and part of the bony part of the nose respectively. The name comes from the Latin word ''frons'' (meaning "forehead"). Structure The frontal bone is made up of two main parts. These are the squamous part, and the orbital part. The squamous part marks the vertical, flat, and also the biggest part, and the main region of the forehead. The orbital part is the horizontal and second biggest region of the frontal bone. It enters into the formation of the roofs of the orbital and nasal cavities. Sometimes a third part is included as the nasal part of the frontal bone, and sometimes this is included with the squamous part. The nasal part is between the brow ridges, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurhinodelphinidae
Eurhinodelphinidae is an extinct family of toothed whales which lived from the Oligocene to the Miocene. Members of the family possessed an elongated jaw similar in appearance to a swordfish. Taxonomy *Family Eurhinodelphinidae **'' Ceterhinops'' **''Eurhinodelphis'' **'' Iniopsis'' **''Mycteriacetus ''Mycteriacetus'' is an extinct genus of dolphin from the Early Miocene (Burdigalian) of northeastern Italy. The type species is ''M. bellunensis''. Etymology ''Mycteriacetus'' is named after the Yellow-billed stork (''Mycteria ibis'') because t ...'' ** '' Phocaenopsis'' **'' Schizodelphis'' **'' Vanbreenia'' **'' Xiphiacetus'' **'' Ziphiodelphis'' References Prehistoric toothed whales Prehistoric mammal families {{paleo-whale-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
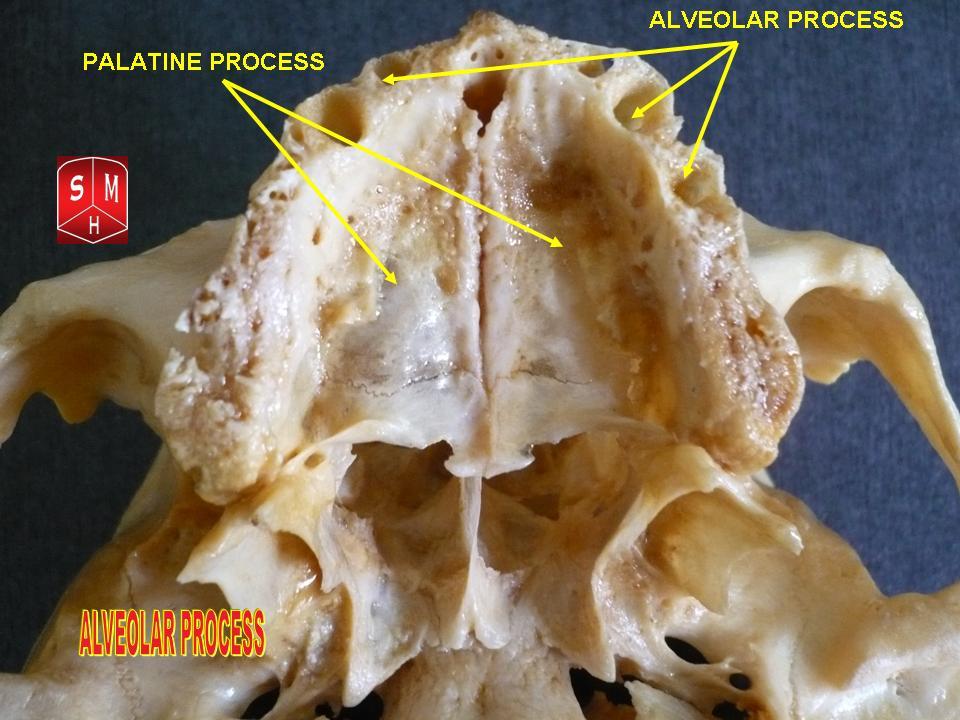
Dental Alveoli
Dental alveoli (singular ''alveolus'') are sockets in the jaws in which the roots of teeth are held in the alveolar process with the periodontal ligament. The lay term for dental alveoli is tooth sockets. A joint that connects the roots of the teeth and the alveolus is called a ''gomphosis'' (plural ''gomphoses''). Alveolar bone is the bone that surrounds the roots of the teeth forming bone sockets. In mammals, tooth sockets are found in the maxilla, the premaxilla, and the mandible. Etymology 1706, "a hollow", especially "the socket of a tooth", from Latin alveolus "a tray, trough, basin; bed of a small river; small hollow or cavity", diminutive of alvus "belly, stomach, paunch, bowels; hold of a ship", from PIE root *aulo- "hole, cavity" (source also of Greek aulos "flute, tube, pipe"; Serbo-Croatian, Polish, Russian ulica "street", originally "narrow opening"; Old Church Slavonic uliji, Lithuanian aulys "beehive" (hollow trunk), Armenian yli "pregnant"). The word was extended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxillae
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Anatomy Structure The maxilla is a paired bone - the two maxillae unite with each other at the intermaxillary suture. The maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla: pyramid-shaped; has an orbital, a nasal, an infratemporal, and a facial surface; contains the maxillary sinus. * Four processes: ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process It has three surfaces: * the anterior, posterior, medial Features of the maxilla include: * the infr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Bone
The nasal bones are two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and by their junction, form the bridge of the upper one third of the nose. Each has two surfaces and four borders. Structure There is heavy variation in the structure of the nasal bones, accounting for the differences in sizes and shapes of the nose seen across different people. Angles, shapes, and configurations of both the bone and cartilage are heavily varied between individuals. Broadly, most nasal bones can be categorized as "V-shaped" or "S-shaped" but these are not scientific or medical categorizations. When viewing anatomical drawings of these bones, consider that they are unlikely to be accurate for a majority of people. The two nasal bones are joined at the midline internasal suture and make up the bridge of the nose. Surfaces The ''outer surface'' is concavo-convex from above downward, convex from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baiji
The baiji (''Lipotes vexillifer'') is a probably extinct species of freshwater dolphin native to the Yangtze river system in China. It is thought to be the first dolphin species driven to extinction due to the impact of humans. This dolphin is listed as "critically endangered: possibly extinct" by the IUCN, has not been seen in 20 years, and several surveys of the Yangtze have failed to find it. The species is also called the Chinese river dolphin, Yangtze river dolphin, Yangtze dolphin, and whitefin dolphin. The genus name ''Lipotes'' means "left behind" and the species epithet ''vexillifer'' means "flag bearer". It is nicknamed the "Goddess of the Yangtze" and was regarded as the goddess of protection by local fishermen and boatmen. It is not to be confused with the Chinese white dolphin (''Sousa chinensis'') or the finless porpoise (''Neophocaena phocaenoides''). This is the only species in the genus ''Lipotes''. The baiji population declined drastically in decades as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annaka Group
file:The remains of the Usui Magistrate’s office.jpg, 240px, Edo-period Usui Magistrate's office in Annaka is a Cities of Japan, city located in Gunma Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 47,911 in 24,749 households, and a population density of 210 persons per square kilometre. The total area of the city is . Geography Annaka is located in the southwestern portion of Gunma Prefecture at the very northernmost point of the Kantō Plain, bordered by Nagano Prefecture to the west. The Usui Pass connects Annaka with neighboring Karuizawa, Nagano. *Mountains: Chausuyama (596 m), Mount Myōgi (1,103 m) *Rivers: Usigawa, Tsukumogawa *Lakes: Sakamoto Dam, Nakagi Dam Surrounding municipalities Gunma Prefecture * Shimonita, Gunma, Shimonita * Takasaki, Gunma, Takasaki * Tomioka, Gunma, Tomioka Nagano Prefecture * Karuizawa, Nagano, Karuizawa Climate Annaka has a Humid continental climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by warm summers and cold winters with heavy s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |