|
Environmental Persistent Pharmaceutical Pollutant
The term environmental persistent pharmaceutical pollutants (EPPP) was first suggested in the nomination in 2010 of pharmaceuticals and environment as an emerging issue in a Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management ( SAICM) by the International Society of Doctors for the Environment (ISDE). The occurring problems from EPPPs are in parallel explained under environmental impact of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCP). The European Union summarizes pharmaceutical residues with the potential of contamination of water and soil together with other micropollutants under "priority substances". Background Pharmaceuticals comprise one of the few groups of chemicals that are specifically designed to act on living cells. They present a special risk when they persist in the environment. With the exception of watercourses downstream of sewage treatment plants, the concentration of pharmaceuticals in surface and ground water is generally low. Concentrations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an ''aquifer'' when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock become completely saturated with water is called the ''water table''. Groundwater is Groundwater recharge, recharged from the surface; it may discharge from the surface naturally at spring (hydrosphere), springs and Seep (hydrology), seeps, and can form oasis, oases or wetlands. Groundwater is also often withdrawn for agricultural, municipal, and industrial use by constructing and operating extraction water well, wells. The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is ''hydrogeology'', also called groundwater hydrology. Typically, groundwater is thought o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
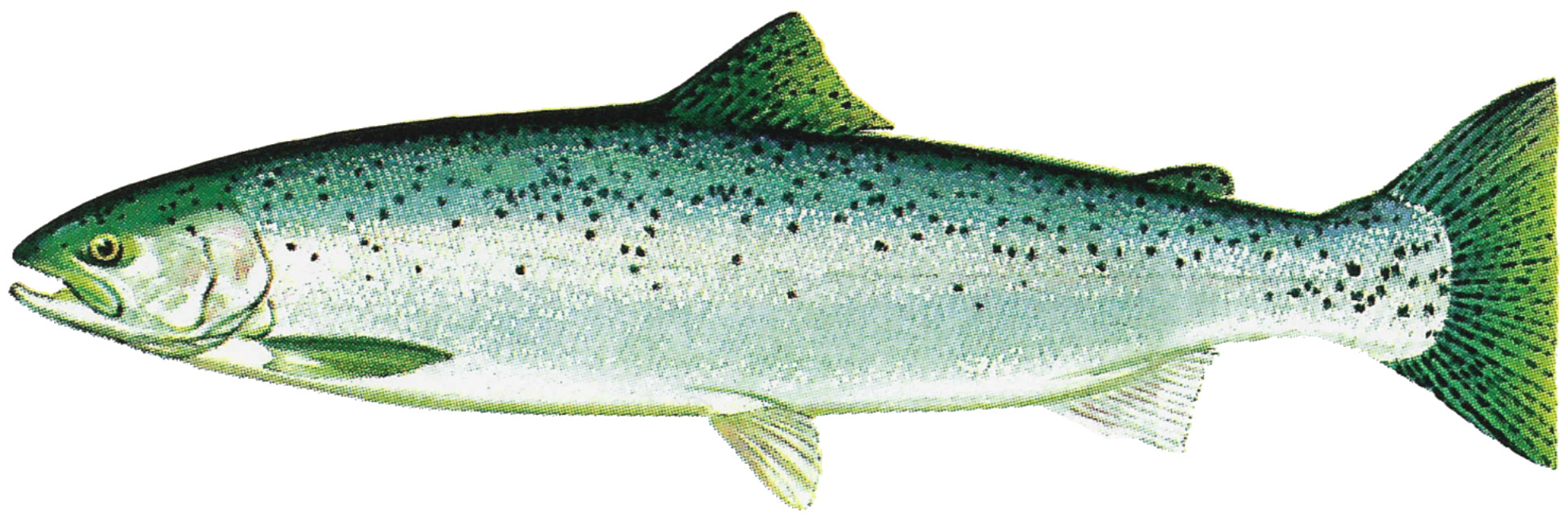
Rainbow Trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributary, tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in North America and Asia. The steelhead (sometimes called steelhead trout) is an Fish migration#Classification, anadromous (sea-run) form of the coastal rainbow trout or Columbia River redband trout that usually returns to freshwater to Spawn (biology), spawn after living two to three years in the ocean. Adult freshwater stream rainbow trout average between , while lake-dwelling and anadromous forms may reach . Coloration varies widely based on subspecies, forms, and habitat. Adult fish are distinguished by a broad reddish stripe along the lateral line, from gills to the tail, which is most vivid in breeding males. Wild-caught and Fish hatchery, hatchery-reared forms of the species have been transplanted and introduced for food or sport in at least 45 countries and every continent except Antarctica. Introductions to locations outside their nativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levonorgestrel
Levonorgestrel is a hormonal medication used in a number of birth control methods. It is combined with an estrogen to make combination birth control pills. As an emergency birth control, sold under the brand names Plan B One-Step and Julie, among others, it is useful within 72 hours of unprotected sex. The more time that has passed since sex, the less effective the medication becomes. Levonorgestrel works by preventing or delaying ovulation so an egg cannot be released. The dosage used for emergency contraception is ineffective when ovulation has already occurred, and has been found to have no effect on implantation. It decreases the chances of pregnancy by 57–93%. In an intrauterine device (IUD), such as Mirena among others, it is effective for the long-term prevention of pregnancy. A levonorgestrel-releasing implant is also available in some countries. Common side effects include nausea, breast tenderness, headaches, and increased, decreased, or irregular menstru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackwater (waste)
Blackwater in a sanitation context denotes wastewater from toilets which likely contains pathogens that may spread by the fecal–oral route. Blackwater can contain Human feces, feces, urine, water and toilet paper from flush toilets. Blackwater is distinguished from greywater, which comes from sinks, baths, washing machines, and other household appliances apart from toilets. Greywater results from washing food, clothing, dishes, as well as from showering or bathing. Blackwater and greywater are kept separate in "ecological buildings", such as autonomous buildings. Recreational vehicles often have separate holding tanks for greywater from showers and sinks, and blackwater from the toilet. Definition According to one source: Water coming from domestic equipment other than toilets (e.g., bathtubs, showers, sinks, washing machines) is called greywater. In some sanitation systems, it is preferred to keep the greywater separate from blackwater to reduce the amount of water that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
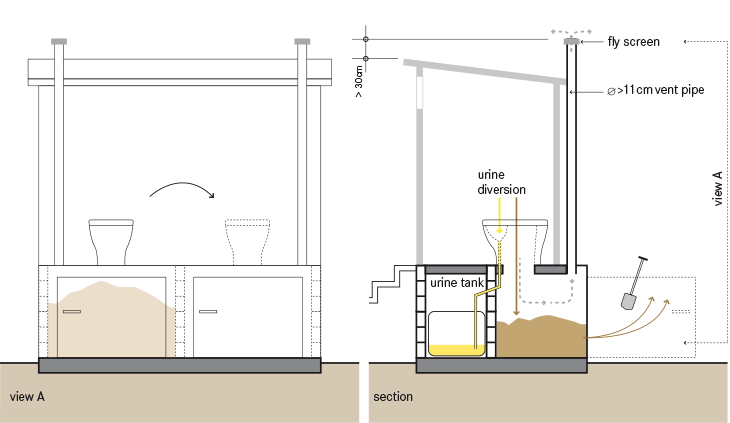
Urine-diverting Dry Toilet
A urine-diverting dry toilet (UDDT) is a type of dry toilet with urine diversion that can be used to provide safe, affordable sanitation in a variety of contexts worldwide. The separate collection of feces and urine without any flush water has many advantages, such as odor-free operation and pathogen reduction by drying. While dried feces and urine harvested from UDDTs can be and routinely are used in agriculture (respectively, as a soil amendment and nutrient-rich fertilizer—this practice being known as reuse of excreta in agriculture), many UDDT installations do not apply any sort of recovery scheme. The UDDT is an example of a technology that can be used to achieve a sustainable sanitation system. This dry excreta management system (or "dry sanitation" system) is an alternative to pit latrines and flush toilets, especially where water is scarce, a connection to a sewer system and centralized wastewater treatment plant is not feasible or desired, fertilizer and soil condit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wastewater
Wastewater (or waste water) is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of domestic, industrial, commercial or agricultural activities, surface runoff / storm water, and any sewer inflow or sewer infiltration". In everyday usage, wastewater is commonly a synonym for sewage (also called domestic wastewater or municipal wastewater), which is wastewater that is produced by a community of people. As a generic term, wastewater may also describe water containing contaminants accumulated in other settings, such as: * Industrial wastewater: waterborne waste generated from a variety of industrial processes, such as manufacturing operations, mineral extraction, power generation, or water and wastewater treatment. * Cooling water, is released with potential thermal pollution after use to condense steam or reduce machinery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diclofenac
Diclofenac, sold under the brand name Voltaren among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain and inflammatory diseases such as gout. It can be taken orally (swallowed by mouth), inserted rectally as a suppository, injected intramuscularly, injected intravenously, applied to the skin topically, or through eye drops. Improvements in pain last up to eight hours. It is also available as the fixed-dose combination diclofenac/misoprostol (Arthrotec) to help protect the stomach; however, proton pump inhibitors such as omeprazole are typically first-line since they are at least as effective as misoprostol, but with better tolerability. Common side effects include abdominal pain, gastrointestinal bleeding, nausea, dizziness, headache, and swelling. Serious side effects may include heart disease, stroke, kidney problems, and stomach ulceration. Use is not recommended in the third trimester of pregnancy. It is likely safe during breast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microgram
In the metric system, a microgram or microgramme is a unit of mass equal to one millionth () of a gram. The unit symbol is μg according to the International System of Units (SI); the recommended symbol in the United States and United Kingdom when communicating medical information is mcg. In μg, the prefix symbol for micro- is the Greek letter μ (mu). Abbreviation and symbol confusion When the Greek lowercase "μ" (mu) is typographically unavailable, it is occasionally – although not properly – replaced by the Latin lowercase "u". The United States–based Institute for Safe Medication Practices (ISMP) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommend that the symbol μg should not be used when communicating medical information due to the risk that the prefix μ (micro-) might be misread as the prefix m (milli-), resulting in a thousandfold overdose. The ISMP recommends the non- SI symbol mcg instead. However, the abbreviation mcg is also the symbol for an o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocontrast Agent
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography (contrast CT), projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically iodine, or more rarely barium sulfate. The contrast agents absorb external X-rays, resulting in decreased exposure on the X-ray detector. This is different from radiopharmaceuticals used in nuclear medicine which emit radiation. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) functions through different principles and thus MRI contrast agents have a different mode of action. These compounds work by altering the magnetic properties of nearby hydrogen nuclei. Types and uses Radiocontrast agents used in X-ray examinations can be grouped in positive (iodinated agents, barium sulfate), and negative agents (air, carbon dioxide, methylcellulose). Iodine (circulatory system) Iodinated contrast contains iodine. It is the main type of radiocontrast used for intra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meuse
The Meuse or Maas is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a total length of . History From 1301, the upper Meuse roughly marked the western border of the Holy Roman Empire with the France in the Middle Ages, Kingdom of France, after Count Henry III, Count of Bar, Henry III of Bar had to receive the western part of the County of Bar (''Barrois mouvant'') as a French fief from the hands of King Philip IV of France, Philip IV. In 1408, a Burgundian army led by John the Fearless went to the aid of John III, Duke of Bavaria, John III against the citizens of Liège, who were in open revolt. After the Battle of Othée, battle, which saw the men from Liège defeated, John ordered the drowning in the Meuse of burghers and noblemen in Liège whose loyalties he suspected. The border remained relatively stable until the annexation of the Three Bishoprics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Switzerland border, Swiss-Austrian border. From Lake Constance downstream, it forms part of the Germany-Switzerland border, Swiss-German border. After that the Rhine defines much of the Franco-German border. It then flows in a mostly northerly direction through the German Rhineland. Finally, the Rhine turns to flow predominantly west to enter the Netherlands, eventually emptying into the North Sea. It drains an area of 185,000 km2. Its name derives from the Gaulish language, Gaulish ''Rēnos''. There are two States of Germany, German states named after the river, North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate, in addition to several districts of Germany, districts (e.g. Rhein-Sieg-Kreis, Rhein-Sieg). The departments of France, department ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |