|
Enotikon
The tie is a symbol in the shape of an arc similar to a large breve, used in Greek, phonetic alphabets, and Z notation. It can be used between two characters with spacing as punctuation, non-spacing as a diacritic, or (underneath) as a proofreading mark. It can be above or below, and reversed. Its forms are called tie, double breve, enotikon or papyrological hyphen, ligature tie, and undertie. Uses Cyrillic transliteration In the ALA-LC romanization for Russian, a tie symbol is placed over some combinations of Latin letters that are represented by a single letter in the Cyrillic alphabet, e.g., T͡S for Ц and i͡a for Я. This is not uniformly applied, however; some letters corresponding to common digraphs in English, such as SH for Ш and KH for Х do not employ the tie. In practice, the tie ligature is often omitted. Greek The enotikon (, ''henōtikón'', "uniter", from "a serving to unite or unify"), papyrological hyphen, or Greek hyphen was a low tie mark fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanization Of Greek
Romanization of Greek is the transliteration ( letter-mapping) or transcription (sound-mapping) of text from the Greek alphabet into the Latin alphabet. History The conventions for writing and romanizing Ancient Greek and Modern Greek differ markedly. The sound of the English letter B () was written as in ancient Greek but is now written as the digraph , while the modern sounds like the English letter V () instead. The Greek name became Johannes in Latin and then John in English, but in modern Greek has become ; this might be written as Yannis, Jani, Ioannis, Yiannis, or Giannis, but not Giannes or Giannēs as it would be for ancient Greek. The word might variously appear as Hagiοs, Agios, Aghios, or Ayios, or simply be translated as " Holy" or "Saint" in English forms of Greek placenames. Traditional English renderings of Greek names originated from Roman systems established in antiquity. The Roman alphabet itself was a form of the Cumaean alphabet derived f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyphen
The hyphen is a punctuation mark used to join words and to separate syllables of a single word. The use of hyphens is called hyphenation. The hyphen is sometimes confused with dashes (en dash , em dash and others), which are wider, or with the minus sign , which is also wider and usually drawn a little higher to match the crossbar in the plus sign . As an Orthography, orthographic concept, the hyphen is a single entity. In character encoding for use with computers, it is represented in Unicode by any of several character (computing), characters. These include the dual-use hyphen-minus, the soft hyphen, the #Nonbreaking hyphens, nonbreaking hyphen, and an unambiguous form known familiarly as the "Unicode hyphen", shown at the top of the infobox on this page. The character most often used to represent a hyphen (and the one produced by the key on a keyboard) is called the "hyphen-minus" by Unicode, deriving from the original ASCII standard, where it was called "hyphen(minus)". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypodiastole
The hypodiastole (Greek: , , ), also known as a diastole,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "diastole, ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1895. was an interpunct developed in late Ancient and Byzantine Greek texts before the separation of words by spaces was common. In the then used, a group of letters might have separate meanings as a single word or as a pair of words. The papyrological hyphen () showed a group of letters should be read together as a single word, and the hypodiastole showed that they should be taken separately. Compare "" ("whatever") to "" ("...that..."). The hypodiastole was similar in appearance to the comma and was eventually entirely conflated with it. In Modern Greek, () refers to the comma in its role as a decimal separator, and words such as are written with standard commas. A separate Unicode point, ISO/IEC 10646 standard (U+2E12) (⸒), exists for the hypodiastole but is intended only to reproduce its historical occurrence in Greek texts.N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc (geometry)
In mathematics, a curve (also called a curved line in older texts) is an object similar to a line (geometry), line, but that does not have to be Linearity, straight. Intuitively, a curve may be thought of as the trace left by a moving point (geometry), point. This is the definition that appeared more than 2000 years ago in Euclid's Elements, Euclid's ''Elements'': "The [curved] line is […] the first species of quantity, which has only one dimension, namely length, without any width nor depth, and is nothing else than the flow or run of the point which […] will leave from its imaginary moving some vestige in length, exempt of any width." This definition of a curve has been formalized in modern mathematics as: ''A curve is the image (mathematics), image of an interval (mathematics), interval to a topological space by a continuous function''. In some contexts, the function that defines the curve is called a ''parametrization'', and the curve is a parametric curve. In this artic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
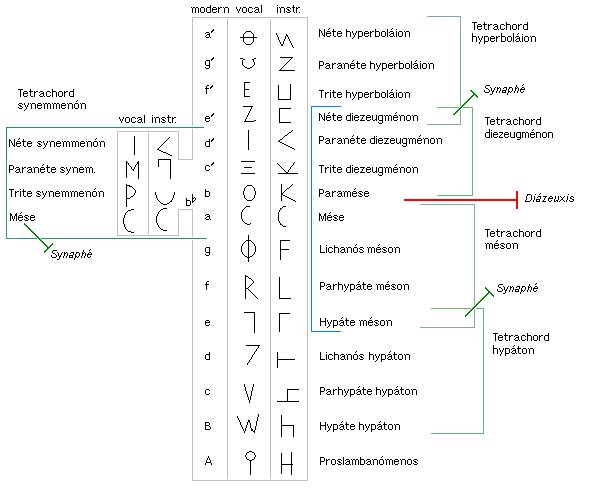
Greek Musical Notation
The musical system of ancient Greece evolved over a period of more than 500 years from simple scale (music), scales of tetrachords, or divisions of the perfect fourth, into several complex systems encompassing tetrachords and octaves, as well as octave scales divided into seven to thirteen intervals. Any discussion of the music of ancient Greece, theoretical, philosophical or aesthetic, is fraught with two problems: there are few examples of written music, and there are many, sometimes fragmentary, theoretical and philosophical accounts. The empirical research of scholars like Richard Crocker, C. André Barbera, and John Chalmers has made it possible to look at the ancient Greek systems as a whole without regard to the tastes of any one ancient theorist. The primary genera they examine are those of Pythagoras and the Pythagoreanism, Pythagorean school, Archytas, Aristoxenus, Aristoxenos, and Ptolemy (including his versions of the genera of Didymus the Musician, Didymos and Eratost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slur (music)
A slur is a symbol in Western culture, Western musical notation indicating that the note (music), notes it embraces are to be played without separation (that is, with legato articulation (music), articulation). A slur is denoted with a curved line (geometry), line generally placed over the notes if the stem (music), stems point downward, and under them if the stems point upwards. The example below shows two measures in with a slur for each measure: : \relative c'' Performance Slurs mean different things for different instruments: *For bow (music), bowed string instruments, the notes should be played in one bow stroke. * For plucked string instruments, such as guitars, the notes should be played without plucking the individual strings (hammer-ons and pull-offs). * For wind instruments, the notes should be played without re-articulating each note (tonguing), except for the slide trombone (and other instruments that control the pitch with a slide), on which only certain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colon (punctuation)
The colon, , is a punctuation mark consisting of two equally sized dots aligned vertically. A colon often precedes an explanation, a list, or a quoted sentence. It is also used between hours and minutes in time, between certain elements in medical journal citations, between chapter and verse in Bible citations, between two numbers in a ratio, and, in the US, for salutations in business letters and other formal letters. History In Ancient Greek, in rhetoric and prosody, the term (', 'limb, member of a body') did not refer to punctuation, but to a member or section of a complete thought or passage; see also '' Colon (rhetoric)''. From this usage, in palaeography, a colon is a clause or group of clauses written as a line in a manuscript.''Oxford English Dictionary'', 1st ed. "colon, ''n.2''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1891. In the 3rd century BC, Aristophanes of Byzantium is alleged to have devised a punctuation system, in which the end of such a was thought to oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overline
An overline, overscore, or overbar, is a typographical feature of a horizontal and vertical, horizontal line drawn immediately above the text. In old mathematical notation, an overline was called a ''vinculum (symbol), vinculum'', a notation for grouping symbols which is expressed in modern notation by parentheses, though it persists for symbols under a radical sign. The original use in Ancient Greek was to indicate compositions of Greek alphabet, Greek letters as Greek numerals. In Latin, it indicates Roman numerals multiplied by a thousand and it forms medieval abbreviations (sigla). Marking one or more words with a continuous line above the characters is sometimes called ''overstriking'', though overstriking generally refers to printing one character on top of an already-printed character. An overline, that is, a single line above a chunk of text, should not be confused with the macron (diacritic), macron, a diacritical mark placed above (or sometimes below) ''individual'' le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synalepha
A synalepha or synaloepha is the merging of two syllables into one, especially when it causes two words to be pronounced as one. The original meaning in Ancient Greek is more general than modern usage and includes coalescence of vowels within a word. Similarly, synalepha most often refers to elision (as in English contraction), but it can also refer to coalescence by other metaplasms: synizesis, synaeresis or crasis. W. Sidney Allen, ''Vox Graeca'', chart of "Types of vowel-junction", p. 98. Examples Spanish, Portuguese and Italian use synalepha, which is important in counting syllables in poetry. An example is in this hendecasyllable (11-syllable line) by Garcilaso de la Vega: : ''Los cabellos que al oro oscurecían.'' :: The hair that endarkened the gold. The words ''que'' and ''al'' form one syllable in counting them because of synalepha. The same thing happens with ''-ro'' and ''os-'' and so the line has eleven syllables (syllable boundaries are shown by a dot): : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Engraving
Music engraving is the art of drawing music notation at high quality for the purpose of mechanical reproduction. The term ''music copying'' is almost equivalent—though ''music engraving'' implies a higher degree of skill and quality, usually for publication. The name of the process originates in plate engraving, a widely used technique dating from the late sixteenth century. The term ''engraving'' is now used to refer to any high-quality method of drawing music notation, particularly on a computer ("computer engraving" or "computer setting") or by hand ("hand engraving"). Traditional engraving techniques Elements of music engraving style Mechanical music engraving began in the middle of the fifteenth century. As musical composition increased in complexity, so too did the technology required to produce accurate Sheet music, musical scores. Unlike literary printing, which mainly contains printed words, music engraving communicates several different types of information simul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melisma
Melisma (, , ; from , plural: ''melismata''), informally known as a vocal run and sometimes interchanged with the term roulade, is the singing of a single syllable of text while moving between several different notes in succession. Music sung in this style is referred to as ''melismatic'', as opposed to ''syllabic'', in which each syllable of text is matched to a single note. History General The term ''melisma'' may be used to describe music of any genre, including baroque singing, opera, and later gospel. Within the tradition of religious Jewish music, melisma is still commonly used in the chanting of Torah, readings from the Prophets, and in the body of a service. Melisma is prevalent in many forms of Gregorian chant (see e.g. Jubilus) as well as late-medieval sacred polyphony, notably in works by Guillaume de Machaut, John Dunstaple, and many early Tudor composers represented in the Eton, Caius, and Lambeth choirbooks. Today, melisma is commonly used in Middle Eastern, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
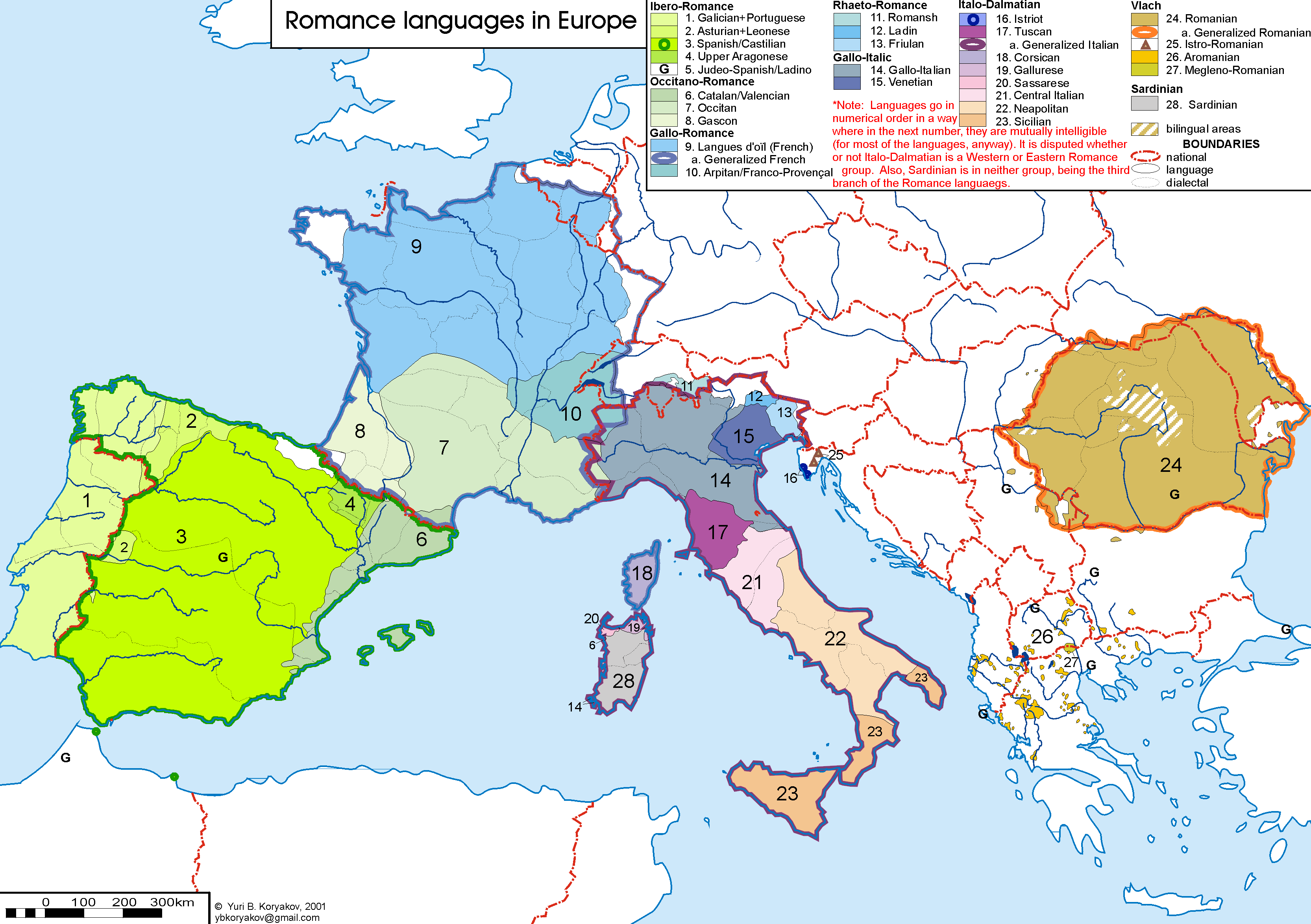
Romance Languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The five list of languages by number of native speakers, most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are: * Spanish language, Spanish (489 million): official language in Spain, Mexico, Equatorial Guinea, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, SADR, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico and most of Central America, Central and South America * French language, French (310 million): official in 26 countries * Portuguese language, Portuguese (240 million): official in Portugal, Brazil, Portuguese-speaking African countries, Portuguese-speaking Africa, Timor-Leste and Macau * Italian language, Italian (67 million): official in Italy, Vatican City, San Marino, Switzerland; mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |