|
English Folk Dance And Song Society
The English Folk Dance and Song Society (EFDSS, or pronounced 'EFF-diss') is an organisation that promotes English folk music and folk dance. EFDSS was formed in 1932 when two organisations merged: the Folk-Song Society and the English Folk Dance Society. Karpeles, Maud and Frogley, Alain (2007–2011)'English Folk Dance and Song Society' In: ''Grove Music Online'', Oxford Music Online. Retrieved 24 October 2011. . The EFDSS, a member-based organisation, was incorporated in 1935 and became a registered charity in 1963. History The Folk-Song Society, founded in London in 1898, focused on collecting and publishing folk songs, primarily of Britain and Ireland although there was no formal limitation. Participants included: Lucy Broadwood, George Butterworth, George Gardiner, Anne Gilchrist, Percy Grainger, Henry Hammond, Ella Leather, Kate Lee, Susan Lushington, May Elliot Hobbs, Cecil Sharp, Ralph Vaughan Williams and Mary Augusta Wakefield. The English Folk Dance Socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonprofit Organization
A nonprofit organization (NPO), also known as a nonbusiness entity, nonprofit institution, not-for-profit organization, or simply a nonprofit, is a non-governmental (private) legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public, or social benefit, as opposed to an entity that operates as a business aiming to generate a Profit (accounting), profit for its owners. A nonprofit organization is subject to the non-distribution constraint: any revenues that exceed expenses must be committed to the organization's purpose, not taken by private parties. Depending on the local laws, charities are regularly organized as non-profits. A host of organizations may be non-profit, including some political organizations, schools, hospitals, business associations, churches, foundations, social clubs, and consumer cooperatives. Nonprofit entities may seek approval from governments to be Tax exemption, tax-exempt, and some may also qualify to receive tax-deductible contributions, but an enti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kate Lee (English Singer)
Kate Lee, born Catharine Anna Spooner (9 March 1859 – 25 July 1904), was an English singer and folksong collector, one of the founders of the English Folk Dance and Song Society, Folk-Song Society in 1898. Early life and education She was born in Rufford, Nottinghamshire, Rufford, Nottinghamshire, one of the ten children of Lucius Henry Spooner and Margaret Skottowe Parker Spooner. Her father was a land agent who died in 1874; her mother was from Ireland. Her cousins included William Archibald Spooner, who gave his name to the "spoonerism". Spooner entered the Royal Academy of Music in January 1876 with the ambition to become a singer. After marriage and motherhood, Lee resumed her studies at the Royal College of Music from 1887 to 1889. Career Lee had a short but busy professional singing career. She sang in a Drury Lane production of ''Die Walküre'' in 1894, and had her debut concert the following year. She also sang at campaign events when her husband ran for a seat i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratford-upon-Avon
Stratford-upon-Avon ( ), commonly known as Stratford, is a market town and civil parish in the Stratford-on-Avon (district), Stratford-on-Avon district, in the county of Warwickshire, in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands region of England. It is situated on the River Avon, Warwickshire, River Avon, north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and south-west of Warwick. The town is the southernmost point of the Arden, Warwickshire, Arden area at the northern extremity of the The Cotswolds, Cotswolds. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 British census Stratford had a population of 30,495. Stratford was inhabited originally by Celtic Britons, Britons before Anglo-Saxons and remained a village before the lord of the manor, John of Coutances, set out plans to develop it into a town in 1196. In that same year, Stratford was granted a charter from King Richard I to hold a weekly Marketplace, market in the town, giving it its status as a market town. As a result, Strat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folk Festival
A folk festival celebrates traditional folk crafts and folk music. This list includes folk festivals worldwide, except those with only a partial focus on folk music or arts. Folk festivals may also feature folk dance or ethnic foods. Handicrafting has long been exhibited at such events and festival-like gatherings, as it has its roots in the rural crafts. Like folk art, handicraft output often has cultural, political, and/or religious significance. Folk art encompasses art produced from an indigenous culture or by peasants or other laboring tradespeople. In contrast to fine art, folk art is primarily utilitarian and decorative rather than purely aesthetic, and is often sold at festivals by tradespeople or practicing amateurs.West, Shearer (general editor), ''The Bullfinch Guide to Art History'', page 440, Bloomsbury Publishing Plc, United Kingdom, 1996. As at folk festivals, such art and handicraft may also appear at historical reenactments and events such as Renaissance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
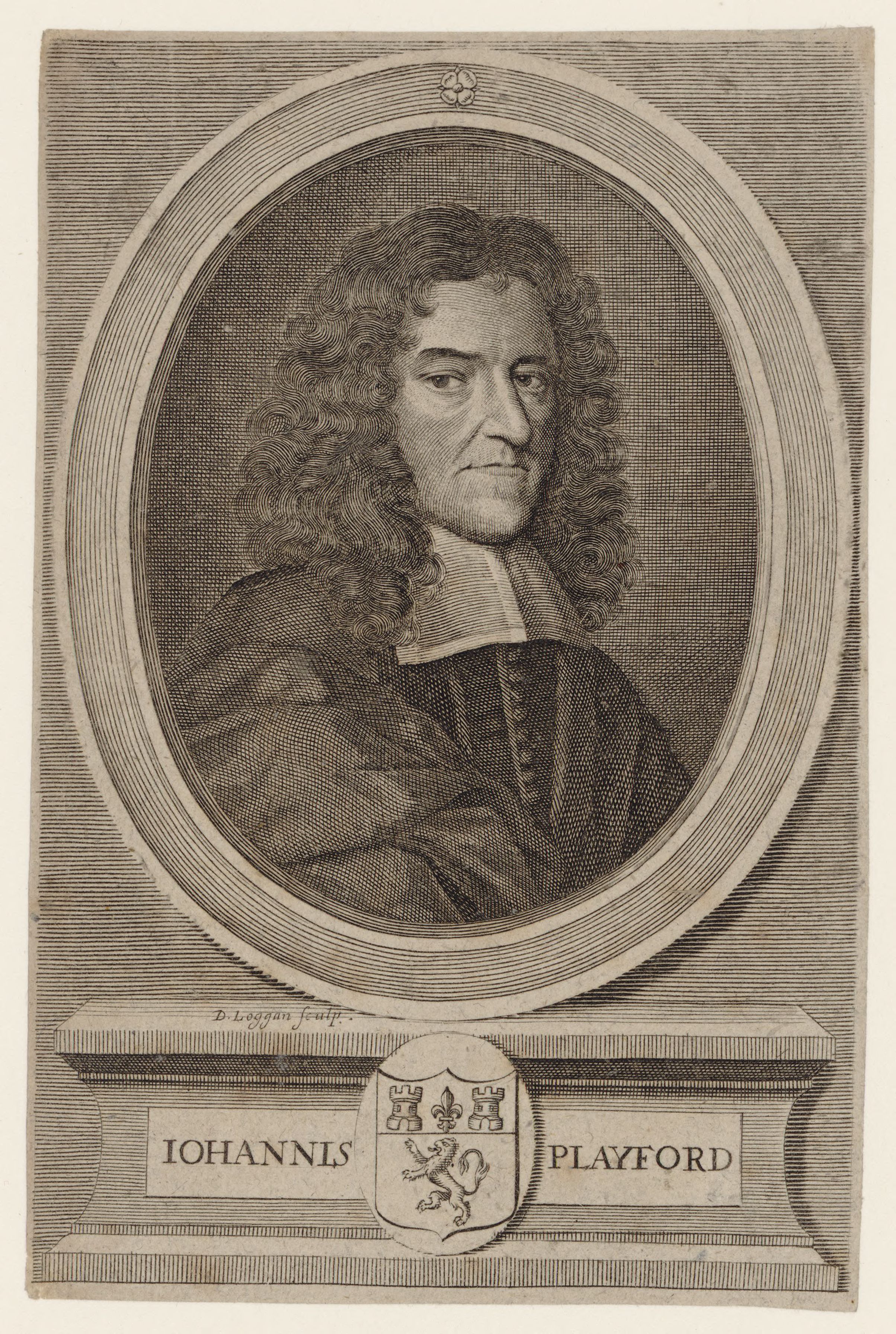
John Playford
John Playford (1623–1686) was a London bookseller, publisher, minor composer and member of the Stationers' Company. He published books on music theory, instruction books for several instruments and psalters with tunes for singing in churches. He is perhaps best known today for his publication of '' The English Dancing Master'' in 1651. Biography Playford was born in Norwich, the younger son of John Playford. He served an apprenticeship in London with publisher John Benson from 1639/40 to 1647, after which he remained in the capital, opening a shop in the porch of Temple Church. Playford was clerk to the church, and probably resided with his wife Hannah over the shop until 1659. He was, it appears (from the title-pages of his publications) temporarily in partnership with John Benson in 1652, and with Zachariah Watkins in 1664 and 1665. Under the Commonwealth (1649–60), and for some years of Charles II's reign, Playford almost monopolised the business of music publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Dances
Social dances are dances that have social functions and context. Social dances are intended for participation rather than performance. They are often danced merely to socialise and for entertainment, though they may have ceremonial, competitive and erotic functions. Many social dances of European origin are in recent centuries partner dances ''(see Ballroom dance)'' but elsewhere there may instead be circle dances or line dances. Social dance in western cultures The types of dance performed in social gatherings change with social values. Social dance music of the 14th century has been preserved in manuscript, though without proper choreography, for dances such as the '' ballo'', carol, '' stampita'', '' saltarello'', '' trotto'' and '' roto''. The 15th century is the first period from which written records of dances exist. A manuscript from Brussels highlights the Burgundian court dance, which spread all over Europe, referred to as the basse dance in which a large group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sword Dances
Weapon dances incorporating swords or similar weapons are recorded throughout world history. There are various traditions of Solo dance, solo and mock-battle (Pyrrhic dance, Pyrrhic) sword dances in Africa, Asia and Europe. Some traditions use sticks or clubs in place of bladed weapons, while most modern performers employ dulled sword replica, replications to avoid injury. Forms General types of sword dance include: *solo dancers around swords – such as the traditional Scottish sword dances. This general form also encompasses non-sword dances such as the bacca pipes jig in Cotswold morris dance, *mock-battle dances, including many stick dances from non-sword traditions, and such common continental dances as Bouffons or Mattachins as described by Thoinot Arbeau in 1588. *hilt-and-point sword dances – where the dancers are linked together by their swords in a chain. These form the basis for rapper sword and Long Sword dance, long sword forms. China and Vietnam Sword ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
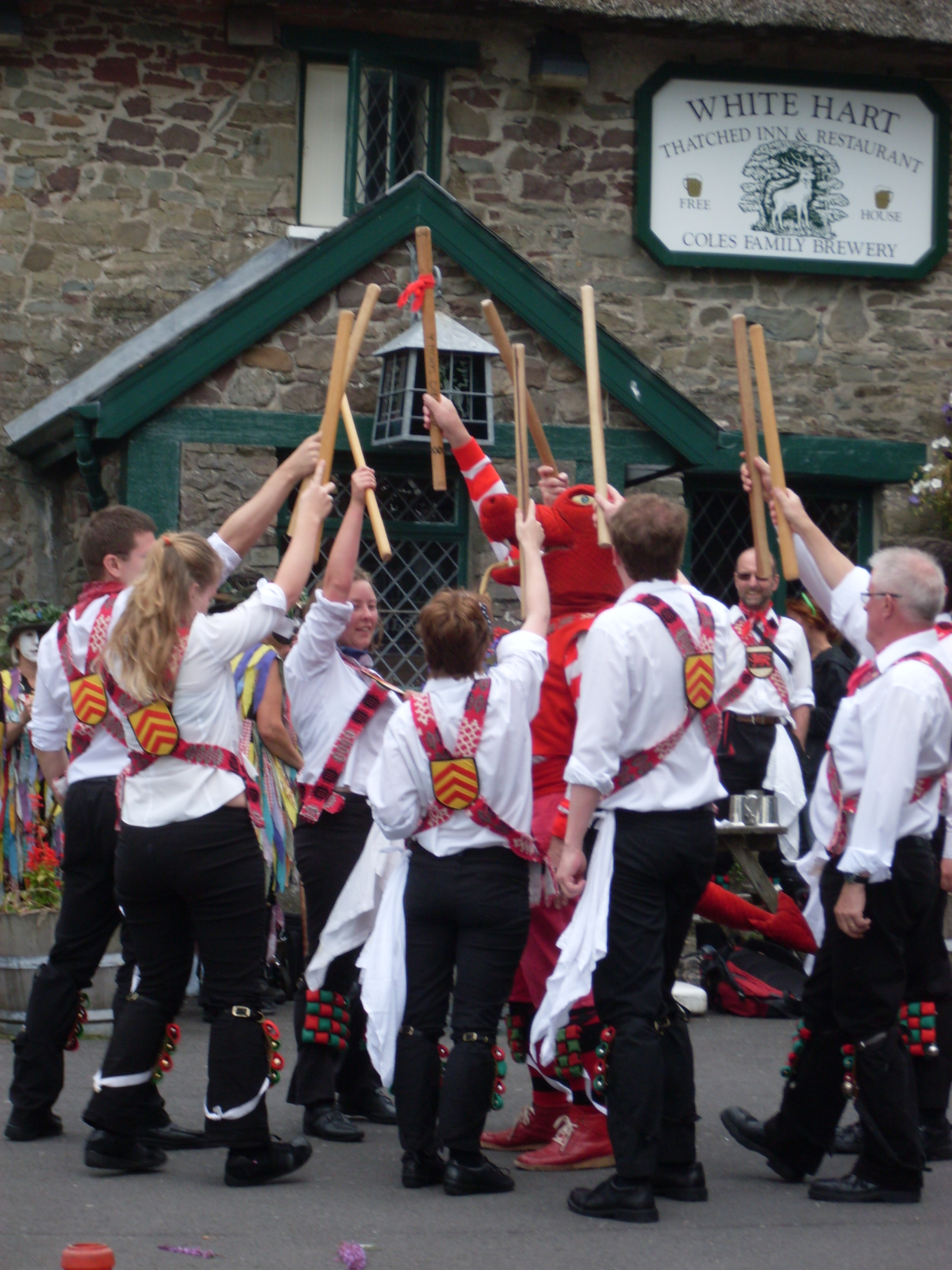
Morris Dance
Morris dancing is a form of English folklore, English folk dance. It is based on rhythmic stepping and the execution of choreographed figures by a group of dancers in costume, usually wearing bell pads on their shins, their shoes or both. A band or single musician, also costumed, will accompany them. Sticks, swords, handkerchiefs, and a variety of other implements may be wielded by the dancers. Morris dancing first appeared in England in the Middle Ages, England in the 15th century. Its earliest surviving mention dates to 1448 and records the payment of seven shillings to Morris dancers by the Goldsmiths' Company in London. The term ''Morris'' derives from the Spanish language, Spanish term , although Morris dancing has no known historical connection to the Moors. Three prominent groups organise and support Morris in England: Morris Ring, Morris Federation and Open Morris; all three organisations have members from other countries as well. There are around 150 Morris sides (or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
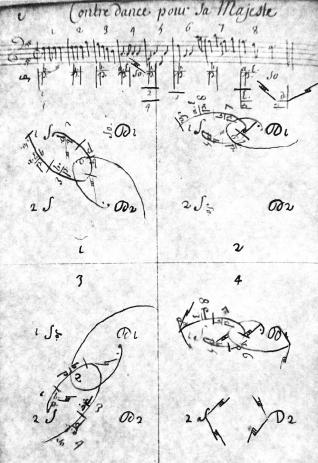
English Country Dances
A country dance is any of a very large number of social dances of a type that originated in England in the British Isles; it is the repeated execution of a predefined sequence of figures, carefully designed to fit a fixed length of music, performed by a group of people, usually in couples, in one or more sets. The figures involve interaction with your partner and/or with other dancers, usually with a progression so that you dance with everyone in your set. It is common in modern times to have a "caller" who teaches the dance and then calls the figures as you dance. Country dances are done in many different styles. As a musical form written in or time, the contredanse was used by Beethoven and Mozart. Beethoven's 6 Ecosaises WoO83 are dated to 1806. Mozart's 6 Ländlerische Tänze, K.606 are dated to 1791. Introduced to South America by French immigrants, Country Dance had great influence upon Latin American music as contradanza. The ''Anglais'' (from the French word meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maud Karpeles
Maud Karpeles OBE, (12 November 1885 – 1 October 1976) was a British collector of folksongs and dance teacher. Early life and education Maud Pauline Karpeles was born at Lancaster Gate in Bayswater, London, in 1885. She was the third of five children. Her father, Joseph Nicolaus Karpeles, was a German immigrant who was born in Hamburg, and naturalised as a British subject in 1881. He worked as a tea merchant and stockbroker. Her mother, Emily Karpeles (née Raphael), was born in London. Both her parents were Jewish but nonreligious. Her family moved to Westbourne Terrace, Paddington, when she was about ten. Like her sisters, Karpeles went to boarding school in Tunbridge Wells, where she learned to play the violin and piano, and studied German. In 1906, she spent six months at the Hochschule für Musik in Berlin, taking piano lessons and going to concerts. Volunteer work After returning to England, Karpeles was a volunteer with the Invalid Children's Aid Association. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Augusta Wakefield
Mary Augusta Wakefield (19 August 1853 – 16 September 1910) was a British composer, contralto, festival organiser, and writer. Biography Early life Wakefield was born in Kendal, where her paternal ancestors had been members of the Quakers, Quaker community before converting to Anglicanism. Her parents William Henry Wakefield and Augusta Hagarty Wakefield had four sons (including the cricketer William Wakefield (cricketer), William Wakefield) and two other daughters. Her mother was from an Irish-American background. In the 1860s her father took over the family business, which included a bank and a Powder mill, gunpowder mill. In 1868, he built Sedgwick House, Cumbria, Sedgwick House a few miles outside Kendal. (The family gunpowder mill started in Sedgwick, Cumbria, Sedgwick in the 18th century, but production had moved to a new site in 1850). As a child, Wakefield learned traditional Anglo-Scottish border, border folksongs from her nurses, which she later included in her c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Vaughan Williams
Ralph Vaughan Williams ( ; 12 October 1872– 26 August 1958) was an English composer. His works include operas, ballets, chamber music, secular and religious vocal pieces and orchestral compositions including nine symphonies, written over sixty years. Strongly influenced by Tudor music and English folk-song, his output marked a decisive break in British music from its German classical music, German-dominated style of the 19th century. Vaughan Williams was born to a well-to-do family with strong moral views and a progressive social outlook. Throughout his life he sought to be of service to his fellow citizens, and believed in making music as available as possible to everybody. He wrote many works for amateur and student performance. He was musically a late developer, not finding his true voice until his late thirties; his studies in 1907–1908 with the French composer Maurice Ravel helped him clarify the textures of his music and free it from Music of Germany, Teutonic inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |