|
Energy Planning
Energy planning has a number of different meanings, but the most common meaning of the term is the process of developing long-range policies to help guide the future of a local, national, regional or even the global energy system. Energy planning is often conducted within governmental organizations but may also be carried out by large energy companies such as electric utilities or oil and gas producers. These oil and gas producers release greenhouse gas emissions. Energy planning may be carried out with input from different stakeholders drawn from government agencies, local utilities, academia and other interest groups. Since 1973, the art and science of energy modeling, on which energy planning is based, has developed significantly. Energy models can be classified into three groups: descriptive, normative, and futuristic forecasting. Energy planning is often conducted using integrated approaches that consider both the provision of energy supplies and the role of energy efficienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Utility
An electric utility is a company in the electric power industry (often a public utility) that engages in electricity generation and distribution of electricity for sale generally in a regulated market. The electrical utility industry is a major provider of energy in most countries. Electric utilities include investor owned, publicly owned, cooperatives, and nationalized entities. They may be engaged in all or only some aspects of the industry. Electricity markets are also considered electric utilities—these entities buy and sell electricity, acting as brokers, but usually do not own or operate generation, transmission, or distribution facilities. Utilities are regulated by local and national authorities. Electric utilities are facing increasing demandsBy Candace Lombardi, CNET. �Utilities: Green tech good for planet, bad for business” February 23, 2010. including aging infrastructure, reliability, and regulation. In 2009, the French company EDF was the world's largest produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable atoms survive. The term is also used more generally to characterize any type of exponential (or, rarely, non-exponential) decay. For example, the medical sciences refer to the biological half-life of drugs and other chemicals in the human body. The converse of half-life (in exponential growth) is doubling time. The original term, ''half-life period'', dating to Ernest Rutherford's discovery of the principle in 1907, was shortened to ''half-life'' in the early 1950s. Rutherford applied the principle of a radioactive element's half-life in studies of age determination of rocks by measuring the decay period of radium to lead-206. Half-life is constant over the lifetime of an exponentially decaying quantity, and it is a characteristic u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merit Order
The merit order is a way of ranking available sources of energy, especially electrical generation, based on ascending order of price (which may reflect the order of their short-run marginal costs of production) and sometimes pollution, together with amount of energy that will be generated. In a centralized management, the ranking is so that those with the lowest marginal costs are the first ones to be brought online to meet demand, and the plants with the highest marginal costs are the last to be brought on line. Dispatching generation in this way, known as economic dispatch, minimizes the cost of production of electricity. Sometimes generating units must be started out of merit order, due to transmission congestion, system reliability or other reasons. In environmental dispatch, additional considerations concerning reduction of pollution further complicate the power dispatch problem. The basic constraints of the economic dispatch problem remain in place but the model is optimiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Load
The base load (also baseload) is the minimum level of demand on an electrical grid over a span of time, for example, one week. This demand can be met by unvarying power plants, dispatchable generation, or by a collection of smaller intermittent energy sources, depending on which approach has the best mix of cost, availability and reliability in any particular market. The remainder of demand, varying throughout a day, is met by dispatchable generation which can be turned up or down quickly, such as load following power plants, peaking power plants, or energy storage. Power plants that do not change their power output quickly, such as large coal or nuclear plants, are generally called baseload power plants. Donald G. Fink, H. Wayne Beatty (ed), ''Standard Handbook for Electrical Engineers'', Eleventh Edition, Mc-Graw Hill, 1978 , pp. 12-16 through 12-18 Historically, most or all of base load demand was met with baseload power plants, whereas new capacity based around renewables of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission System Operator
File:Electricity grid simple- North America.svg, 380px, Simplified diagram of AC electricity grid from generation stations to consumers rect 2 243 235 438 Power station rect 276 317 412 556 Transformer rect 412 121 781 400 Electric power transmission rect 800 0 980 165 Transformer desc bottom-left A transmission system operator (TSO) is an entity entrusted with transporting energy in the form of natural gasEuropean Network of Transmission System Operators for Gas '' ENTSO-G''. Retrieved: 2 October 2010. or electrical power on a national or regional level, using fixed [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Various common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of an electric charge, which can be either positive or negative, produces an electric field. The movement of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. When a charge is placed in a location with a non-zero electric field, a force will act on it. The magnitude of this force is given by Coulomb's law. If the charge moves, the electric field would be doing work on the electric charge. Thus we can speak of electric potential at a certain point in space, which is equal to the work done by an external agent in carrying a u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Power Plant
A virtual power plant (VPP) is a cloud-based distributed power plant that aggregates the capacities of heterogeneous distributed energy resources (DER) for the purposes of enhancing power generation, trading or selling power on the electricity market, and demand side options for load reduction. DER assets in a VPP can include photovoltaic solar, energy storage, electric vehicle chargers, and demand-responsive devices (such as water heaters, thermostats, and appliances) with examples of virtual power plants existing in the United States, Europe, and Australia. Power generation A virtual power plant is a system that integrates several types of power sources to give a reliable overall power supply. The sources often form a cluster of different types of dispatchable and non-dispatchable, controllable or flexible load (CL or FL) distributed generation (DG) systems that are controlled by a central authority and can include microCHPs, natural gas-fired reciprocating engines, small-scale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Resource Assessment
Wind resource assessment is the process by which wind power developers estimate the future energy production of a wind farm. Accurate wind resource assessments are crucial to the successful development of wind farms. History Modern wind resource assessments have been conducted since the first wind farms were developed in the late 1970s. The methods used were pioneered by developers and researchers in Denmark, where the modern wind power industry first developed. Wind resource maps High resolution mapping of wind power resource potential has traditionally been carried out at the country level by government or research agencies, in part due to the complexity of the process and the intensive computing requirements involved. However, in 2015 the Technical University of Denmark, under framework of the Clean Energy Ministerial, launched the Global Wind Atlas (version 1.0) to provide freely available data on wind resource potential globally. The Global Wind Atlas was relaunched in N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Renewable Energy
Variable renewable energy (VRE) or intermittent renewable energy sources (IRES) are renewable energy sources that are not dispatchable due to their fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power, as opposed to controllable renewable energy sources, such as dammed hydroelectricity or biomass, or relatively constant sources, such as geothermal power. The use of small amounts of intermittent power has little effect on grid operations. Using larger amounts of intermittent power may require upgrades or even a redesign of the grid infrastructure. Options to absorb large shares of variable energy into the grid include using storage, improved interconnection between different variable sources to smooth out supply, using dispatchable energy sources such as hydroelectricity and having overcapacity, so that sufficient energy is produced even when weather is less favourable. More connections between the energy sector and the building, transport and industrial sectors may also help ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Power Forecasting
A wind power forecast corresponds to an estimate of the expected production of one or more wind turbines (referred to as a wind farm) in the near future, up to a year. Forecast are usually expressed in terms of the available power of the wind farm, occasionally in units of energy, indicating the power production potential over a time interval. Time scales of forecasts Forecasting of the wind power generation may be considered at different time scales, depending on the intended application: * ''very short-term'' forecasts (from seconds up to minutes) are used for the real-time turbine control and electrical grid management, as well as for market clearing; * ''short-term'' forecasts (from 30 minutes up to hours) are used for dispatch planning, intelligent load shedding decisions; * ''medium-term'' forecasts (from 6 hours up to a day) are used for to make decisions for switching the turbine on or off for safety or conditions on the market; * ''long-term'' forecasts (from a day up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
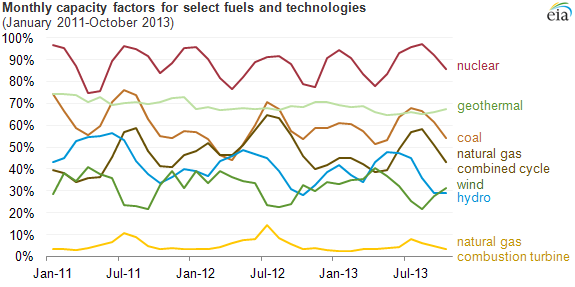
Capacity Factor
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full nameplate capacity over the relevant period. The capacity factor can be calculated for any electricity producing installation, such as a fuel consuming power plant or one using renewable energy, such as wind or the sun. The average capacity factor can also be defined for any class of such installations, and can be used to compare different types of electricity production. The actual energy output during that period and the capacity factor vary greatly depending on a range of factors. The capacity factor can never exceed the availability factor, or uptime during the period. Uptime can be reduced due to, for example, reliability issues and maintenance, scheduled or unscheduled. Other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Energy Software
Specialized wind energy software applications aid in the development and operation of wind farms. Pre-feasibility and feasibility analysis The RETScreen software wind power model is designed to evaluate energy production and savings, costs, emission reductions, financial viability and risk for central-grid, isolated-grid and off-grid wind energy projects, for multi-turbine and single-turbine hybrid systems. Developed by the Government of Canada, the software is free, multilingual, and includes links to wind energy resource maps. The Wind Data Generator (WDG) is a Wind Energy Software tool capable of running WRF (Weather Research and Forecasting) model to create a wind atlas and to generate wind data at resolutions of 3 km to 10 km. Turbine design Software helps design wind turbines. There are several aero-elastic packages that are used in this design process. FOCUS6 aids in the design of wind turbines and turbine components such as rotor blades. It was developed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |