|
Endless Mountains
The Endless Mountains is a geographical, geological, and cultural region in Northeastern Pennsylvania. The Endless Mountains region includes Bradford County, Pennsylvania, Bradford, Sullivan County, Pennsylvania, Sullivan, Susquehanna County, Pennsylvania, Susquehanna, and Wyoming County, Pennsylvania, Wyoming counties. The highest peak in the region is the Elk Hill (Pennsylvania), North Knob of Elk Mountain at . The dissected plateau is a List of subranges of the Appalachian Mountains, subrange of the Appalachian Mountains. Geography Part of the Appalachian Mountains chain, the region does not consist of true mountains, geology, geologically speaking, but instead a dissected plateau that is part of the Allegheny Plateau. The Catskill Mountains are the highest expression of the plateau, located to the east of the Endless Mountains, and separated from them by the Delaware River. The current geography was slightly modified during the last ice age by the Wisconsin Glacier about 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
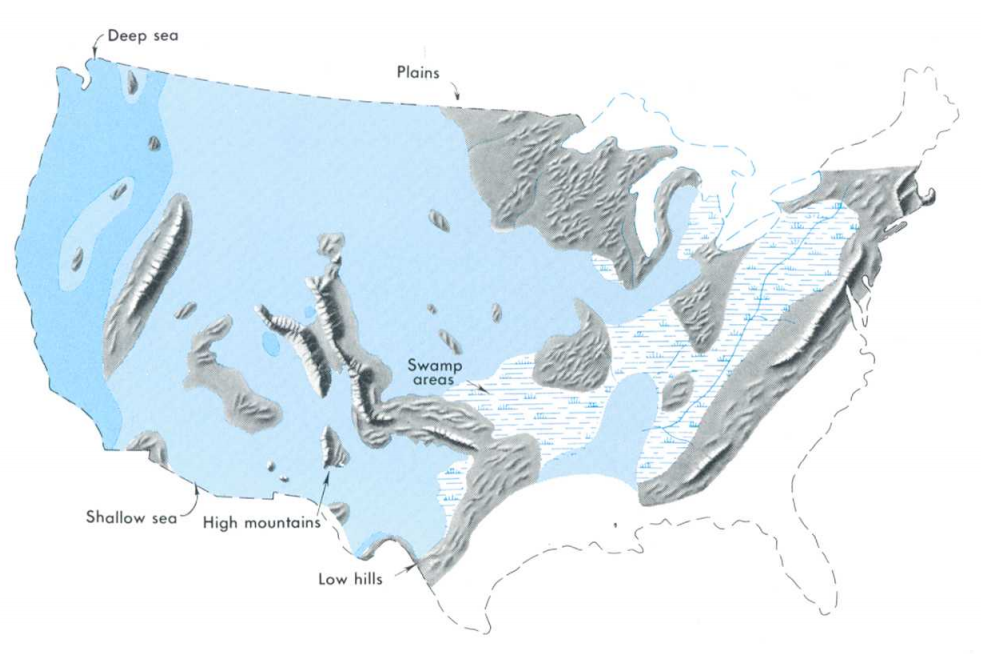
Map Of PA Endless Mountains
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geography, geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacial Striation
Glacial striations or striae are scratches or gouges cut into bedrock by glacial abrasion. These scratches and gouges were first recognized as the result of a moving glacier in the late 18th century when Swiss alpinists first associated them with moving glaciers. They also noted that if they were visible today that the glaciers must also be receding. Glacial striations are usually multiple, straight, and parallel, representing the movement of the glacier using rock fragments and sand grains, embedded in the base of the glacier, as cutting tools. Large amounts of coarse gravel and boulders carried along underneath the glacier provide the abrasive power to cut trough-like ''glacial grooves''. Finer sediments also in the base of the moving glacier further scour and polish the bedrock surface, forming a ''glacial pavement''. Ice itself is not a hard enough material to change the shape of rock but because the ice has rock embedded in the basal surface it can effectively abrade the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incised Meander
A meander is one of a series of regular sinuous curves in the channel of a river or other watercourse. It is produced as a watercourse erodes the sediments of an outer, concave bank ( cut bank or river cliff) and deposits sediments on an inner, convex bank which is typically a point bar. The result of this coupled erosion and sedimentation is the formation of a sinuous course as the channel migrates back and forth across the axis of a floodplain. The zone within which a meandering stream periodically shifts its channel is known as a meander belt. It typically ranges from 15 to 18 times the width of the channel. Over time, meanders migrate downstream, sometimes in such a short time as to create civil engineering challenges for local municipalities attempting to maintain stable roads and bridges.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl Jr., and J.A. Jackson, J.A., eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute. 779 pp. Charlton, R., 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meander
A meander is one of a series of regular sinuous curves in the Channel (geography), channel of a river or other watercourse. It is produced as a watercourse erosion, erodes the sediments of an outer, concave bank (cut bank, cut bank or river cliff) and deposits sediments on an inner, convex bank which is typically a point bar. The result of this coupled erosion and sedimentation is the formation of a sinuous course as the channel migrates back and forth across the axis of a floodplain. The zone within which a meandering stream periodically shifts its channel is known as a meander belt. It typically ranges from 15 to 18 times the width of the channel. Over time, meanders migrate downstream, sometimes in such a short time as to create civil engineering challenges for local municipalities attempting to maintain stable roads and bridges.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl Jr., and J.A. Jackson, J.A., eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River ( ; Unami language, Lenape: ) is a major river located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, crossing three lower Northeastern United States, Northeast states (New York, Pennsylvania and Maryland). At long, it is the longest river on the East Coast of the United States. By Drainage basin, watershed area, it is the 16th-largest river in the United States,Susquehanna River Trail Pennsylvania Fish and Boat Commission, accessed March 25, 2010.Susquehanna River , Green Works Radio, accessed March 25, 2010. and also the longest river in the early 21st-century continental United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peneplain
In geomorphology and geology, a peneplain is a low-relief plain formed by protracted erosion. This is the definition in the broadest of terms, albeit with frequency the usage of peneplain is meant to imply the representation of a near-final (or penultimate) stage of fluvial erosion during times of extended tectonic stability. Peneplains are sometimes associated with the cycle of erosion theory of William Morris Davis, but Davis and other researchers have also used the term in a purely descriptive manner without any theory or particular genesis attached. Discussion 390px, Sketch of a hypothetical peneplain formation after an orogeny. The existence of some peneplains, and peneplanation as a process in nature, is not without controversy, due to a lack of contemporary examples and uncertainty in identifying relic examples. By some definitions, peneplains grade down to a base level represented by sea level, yet in other definitions such a condition is ignored. Geomorphologist K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvanian (geology)
The Pennsylvanian ( , also known as Upper Carboniferous or Late Carboniferous) is, on the International Commission on Stratigraphy, ICS geologic timescale, the younger of two period (geology), subperiods of the Carboniferous Period (or the upper of two system (stratigraphy), subsystems of the Carboniferous System). It lasted from roughly . As with most other geochronology, geochronologic units, the stratum, rock beds that define the Pennsylvanian are well identified, but the exact date of the start and end are uncertain by a few hundred thousand years. The Pennsylvanian is named after the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, where the coal Bed (geology), beds of this age are widespread. The division between Pennsylvanian and Mississippian (geology), Mississippian comes from North American stratigraphy. In North America, where the early Carboniferous beds are primarily marine limestones, the Pennsylvanian was in the past treated as a full-fledged geologic period between the Mississippian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippian Age
The Mississippian ( ), also known as Lower Carboniferous or Early Carboniferous, is a subperiod in the geologic timescale or a subsystem of the geologic record. It is the earlier of two subperiods of the Carboniferous period lasting from roughly 358.9 to 323.2 million years ago. As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Mississippian are well identified, but the exact start and end dates are uncertain by a few million years. The Mississippian is so named because rocks with this age are exposed in the Mississippi Valley. The Mississippian was a period of marine transgression in the Northern Hemisphere: the sea level was so high that only the Fennoscandian Shield and the Laurentian Shield were dry land. The cratons were surrounded by extensive delta systems and lagoons, and carbonate sedimentation on the surrounding continental platforms, covered by shallow seas. In North America, where the interval consists primarily of marine limestones, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, transports it to another location where it is deposit (geology), deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by Solvation, dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and Wind wave, waves; glacier, glacial Plucking (glaciation), plucking, Abrasion (geology), abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; Aeolian processes, wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and Mass wastin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
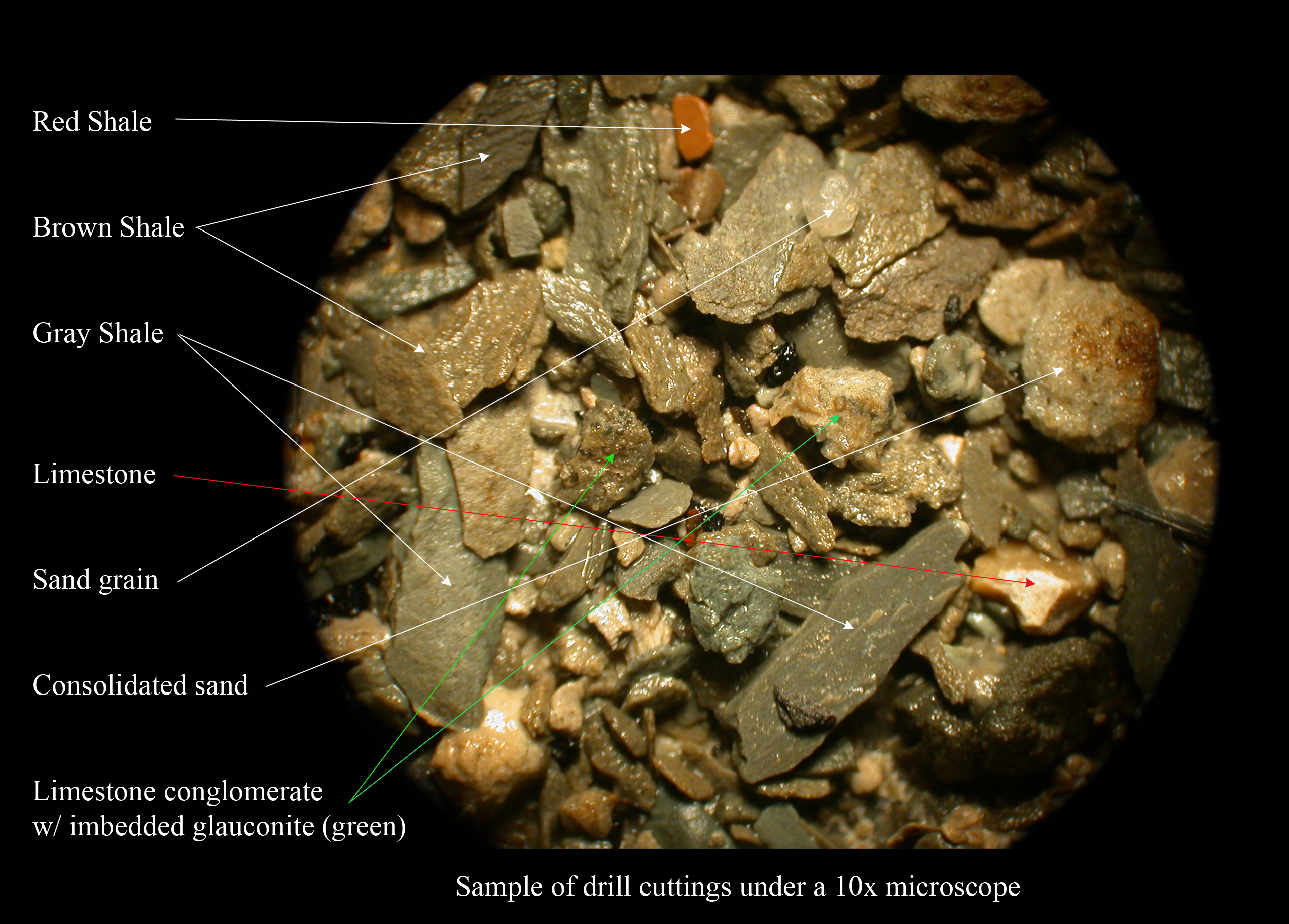
Conglomerate (geology)
Conglomerate () is a sedimentary rock made up of rounded gravel-sized pieces of rock surrounded by finer-grained sediments (such as sand, silt, or clay). The larger fragments within conglomerate are called clasts, while the finer sediment surrounding the clasts is called the matrix. The clasts and matrix are typically cemented by calcium carbonate, iron oxide, silica, or hardened clay. Conglomerates form when rounded gravels deposited by water or glaciers become solidified and cemented by pressure over time. They can be found in sedimentary rock sequences of all ages but probably make up less than 1 percent by weight of all sedimentary rocks. They are closely related to sandstones in origin, and exhibit many of the same types of sedimentary structures, such as tabular and trough cross-bedding and graded bedding.Boggs, S. (2006) ''Principles of Sedimentology and Stratigraphy.'', 2nd ed. Prentice Hall, New York. 662 pp. Friedman, G.M. (2003) ''Classification of sediments and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of Clay mineral, clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g., Kaolinite, kaolin, aluminium, Al2Silicon, Si2Oxygen, O5(hydroxide, OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especially quartz and calcite.Blatt, Harvey and Robert J. Tracy (1996) ''Petrology: Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic'', 2nd ed., Freeman, pp. 281–292 Shale is characterized by its tendency to split into thin layers (Lamination (geology), laminae) less than one centimeter in thickness. This property is called ''Fissility (geology), fissility''. Shale is the most common sedimentary rock. The term ''shale'' is sometimes applied more broadly, as essentially a synonym for mudrock, rather than in the narrower sense of clay-rich fissile mudrock. Texture Shale typically exhibits varying degrees of fissility. Because of the parallel orientation of clay mineral flakes in shale, it breaks in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar, because they are the most resistant minerals to the weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be imparted any color by impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Because sandstone beds can form highly visible cliffs and other topography, topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have become strongly identified with certain regions, such as the red rock deserts of Arches National Park and other areas of the Southwestern United States, American Southwest. Rock formations composed of sandstone usually allow the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |