|
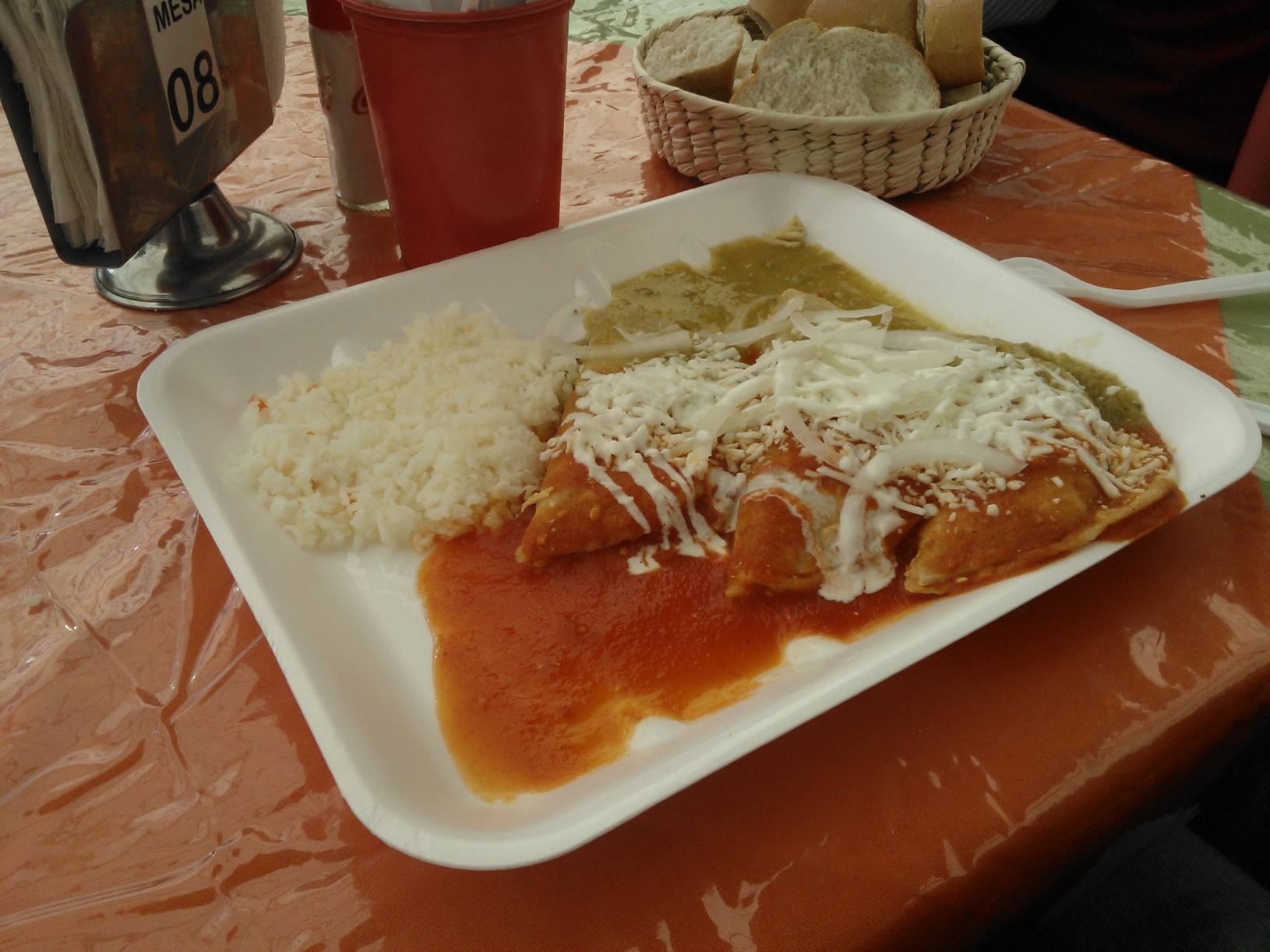
Enchilada
An enchilada (, ) is a Mexican cuisine, Mexican dish consisting of a corn tortilla rolled around a filling and covered with a savory sauce. Enchiladas can be filled with various ingredients, including meats, cheese, beans, potatoes, vegetables, or combinations. Enchilada sauces include chili pepper, chili-based sauces, such as salsa (food), salsa roja, various mole (sauce), moles, tomatillo-based sauces, such as salsa verde, or cheese-based sauces, such as chile con queso. Etymology The Royal Spanish Academy defines the word ''enchilada'', as used in Mexico, as a rolled maize tortilla stuffed with meat and covered with a tomato and Chili pepper, chili sauce. ''Enchilada'' is the past participle of the Mexican Spanish ''enchilar'', "to add chili pepper to"; literally, "to season (or decorate) with chili". History Enchiladas originated in Mexico, where the practice of rolling tortillas around other food dates back at least to Aztec civilization, Aztec times. The people living in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mole (sauce)
Mole (; from Nahuatl ''mōlli'', ), meaning 'sauce', is a traditional sauce and marinade originally used in Mexican cuisine. In contemporary Mexico the term is used for a number of sauces, some quite dissimilar, including ''mole amarillo'' or ''amarillito'' (yellow mole), ''mole chichilo'', ''mole colorado'' or ''coloradito'' (reddish mole), ''mole manchamantel'' or ''manchamanteles'' (tablecloth stainer), ''mole negro'' (black mole), ''mole rojo'' (red mole), ''mole verde'' (green mole), ''mole poblano'', ''mole almendrado'' (mole with almond), ''mole michoacano'', ''mole prieto'', ''mole ranchero'', ''mole tamaulipeco'', ''mole xiqueno'', ''Pipián (sauce), pipián'' (mole with squash seed), ''mole rosa'' (pink mole), ''mole blanco'' (white mole), ''mole estofado'', ''tezmole'', ''clemole'', ''mole de'' olla, chimole, guacamole (mole with avocado) and ''huaxmole'' (mole with Leucaena leucocephala, huaje). The spelling “molé,” often seen on English-language menus, is a hype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corn Tortilla
In Mexico and Central America, a corn tortilla or just tortilla (, ) is a type of thin, unleavened flatbread, made from hominy, that is the whole kernels of maize treated with alkali to improve their nutrition in a process called nixtamalization. A simple dough made of ground hominy, salt and water is then formed into flat discs and cooked on a very hot surface, generally an iron griddle called a comal. A similar flatbread from South America, called an '' arepa'' (made with ground maize, not hominy, and typically much thicker than tortillas), predates the arrival of Europeans to America, and was called ''tortilla'' by the Spanish from its resemblance to traditional Spanish round, unleavened cakes and omelettes. The Aztecs and other Nahuatl-speakers call tortillas tlaxcalli (''Nahuatl Dictionary.'' (1997). Wired Humanities Project. University of Oregon. Retrieved August 29, 2012, frolink). The successful conquest of the Aztec empire by the Spanish and the subsequent colonial e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
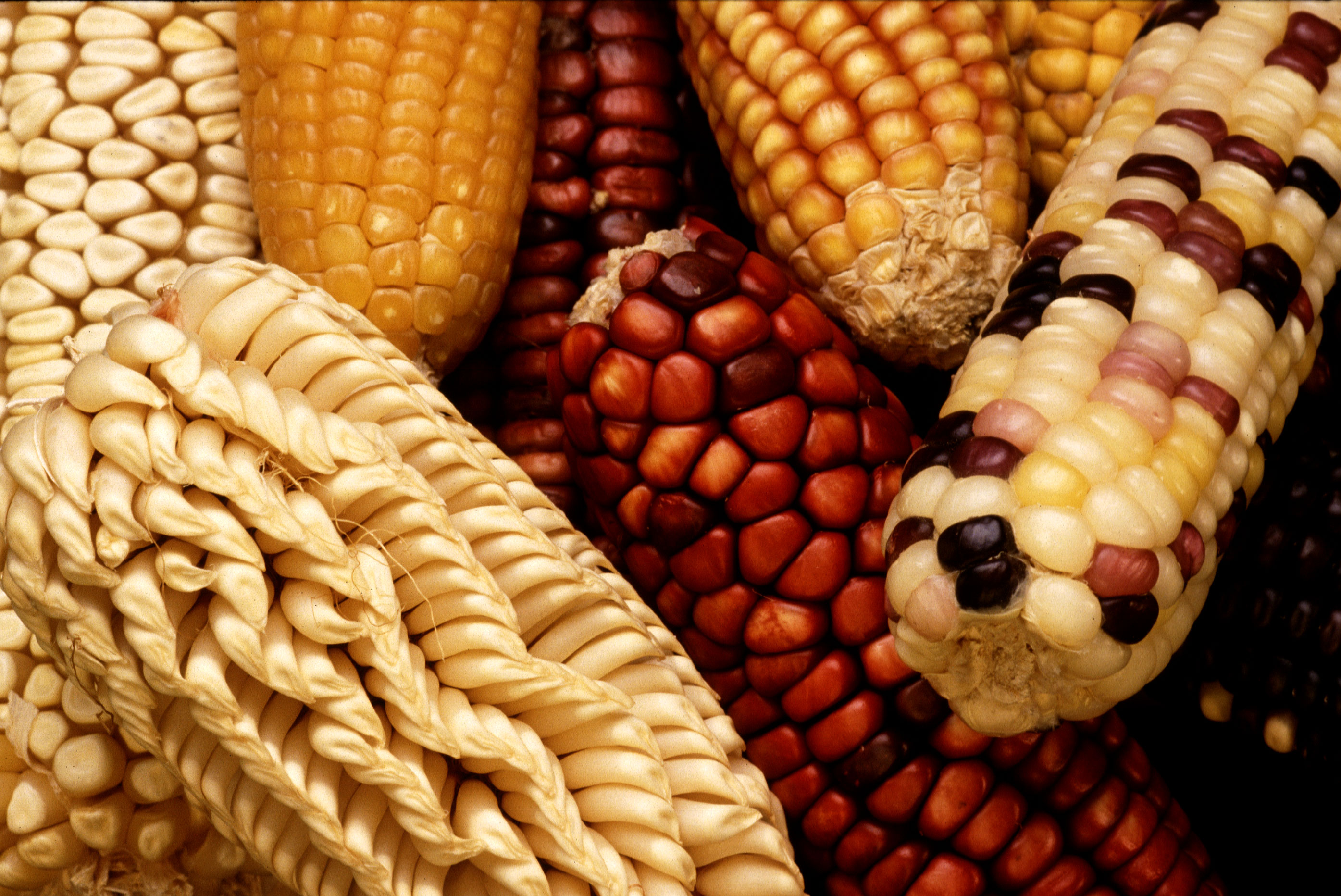
Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears. The ears yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors. Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is used for animal feed, whether as grain or as the whole plant, which can either be baled or made into the more palatable silage. Sugar-rich varieties called sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile Con Queso
Chile con queso (), sometimes simply called queso, is an appetizer or side dish of melted cheese and chili peppers, typically served in Tex-Mex restaurants as a dip for tortilla chips. It can also be added to other dishes such as tacos. Background Chile con queso (also spelled chili con queso) is a part of Tex-Mex and Southwestern cuisine. Chile con queso is probably a derivative of queso flameado from the northern Mexican state of Chihuahua. Chile con queso is predominantly found on the menus of Tex-Mex restaurants in the southwest and western United States. Ingredients Chile con queso is a smooth, creamy sauce, used for dipping, that is made from a blend of melted cheeses (often American cheese, Velveeta or another processed cheese, Monterey Jack or cream cheese), cream, and chili peppers. Many restaurants serve chile con queso with such added ingredients as pico de gallo, black beans, guacamole, and ground beef or pork. Serving Chile con queso is a warm dish, heated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salsa Verde
In Mexican cuisine, Salsa verde () is a spicy green sauce made from tomatillo and green chili peppers. It dates to the Aztec Empire, as documented by the Spanish physician Francisco Hernández, and is distinct from the various medieval European parsley-based green sauces. In the cuisines of Mexico and the Southwestern United States, it is often served with Mexican or Tex-Mex dishes such as enchiladas and chicharrón (, plural ; ; ; ) is a dish generally consisting of fried pork belly or fried pork rinds. may also be made from chicken, mutton, or beef. Name , as a dish with sauces, or as finger-food snacks, are popular in Andalusia and Canarias in ... (pork rinds). The version typical of New Mexico consists mostly of green chile rather than tomatillos. Types This green sauce comes in subtypes: cooked sauce, in which the ingredients are cooked and then ground; roasted salsa, in which the elements are roasted on a and then ground; raw sauce, in which ingredi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salsa (food)
A salsa is any of a variety of sauces used as condiments for tacos and other Mexican cuisine, Mexican and Mexican cuisine in the United States, Mexican-American foods, and as dip (food), dips for tortilla chips. They may be raw or cooked, and are generally served at room temperature. Though the word ''salsa'' means any kind of sauce in Spanish, in English, it refers specifically to these Mexican table sauces, especially to the chunky tomato-and-chili pepper, chili-based pico de gallo, as well as to salsa verde. chips and dip, Tortilla chips with salsa are a ubiquitous appetizer in Mexican-American restaurants, but not in Mexico itself. History The use of salsa as a table dip was popularized by Mexican restaurants in the United States. In the 1980s, tomato-based Mexican-style salsas gained in popularity. In 1992, the dollar value of salsa sales in the United States exceeded those of tomato ketchup. Tomato-based salsas later found competition from salsas made with fruit, corn, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican Cuisine
Mexican cuisine consists of the cuisines and associated traditions of the modern country of Mexico. Its earliest roots lie in Mesoamerican Cuisine, Mesoamerican cuisine. Mexican cuisine's ingredients and methods arise from the area's first agricultural communities, such as those of the Olmecs, Olmec and Maya civilization, Maya, who domesticated maize, created the standard process of nixtamalization, and established foodways. Successive waves of other Mesoamerican groups brought with them their cooking methods. These included the Teotihuacanos, Toltec, Huastec civilization, Huastec, Zapotec civilization, Zapotec, Mixtec, Otomi people, Otomi, Tarascan state, Purépecha, Totonac, Mazatec, Mazahua people, Mazahua, and Nahuas, Nahua. With the Mexica formation of the multi-ethnic Triple Alliance (Aztec Empire), culinary foodways became infused (Aztec cuisine). Today's food staples native to the land include corn (maize), turkey, beans, squash, amaranth, Chia seed, chia, avocados, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquis of the Valley of Oaxaca (December 1485 – December 2, 1547) was a Spanish ''conquistador'' who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of what is now mainland Mexico under the rule of the King of Castile in the early 16th century. Cortés was part of the generation of Spanish explorers and conquistadors who began the first phase of the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Born in Medellín, Spain, to a family of lesser nobility, Cortés chose to pursue adventure and riches in the New World. He went to Hispaniola and later to Cuba, where he received an ''encomienda'' (the right to the labor of certain subjects). For a short time, he served as ''alcalde'' (magistrate) of the second Spanish town founded on the island. In 1519, he was elected captain of the third expedition to the mainland, which he partly funded. His enmity with the governor of Cuba, Diego Velázquez de Cué ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coyoacán
Coyoacán ( ; , Otomi: ) is a borough (''demarcación territorial'') in Mexico City. The former village is now the borough's "historic center". The name comes from Nahuatl and most likely means "place of coyotes", when the Aztecs named a pre-Hispanic village on the southern shore of Lake Texcoco dominated by the Tepanec people. Against Aztec domination, these people allied with the Spanish, who used the area as a headquarters during the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire and made it the first capital of New Spain between 1521 and 1523. The village and later municipality of Coyoacán remained independent of Mexico City through the colonial period into the 19th century. In 1857, the area was incorporated into the then Federal District when this district was expanded. In 1928, the borough was created when the Federal District was divided into sixteen boroughs. The urban expansion of Mexico City reached the borough in the mid-20th century, turning farms, former lakes, and for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernal Díaz Del Castillo
Bernal Díaz del Castillo ( 1492 – 3 February 1584) was a Spanish conquistador who participated as a soldier in the conquest of the Aztec Empire under Hernán Cortés and late in his life wrote an account of the events. As an experienced soldier of fortune, he had already participated in expeditions to Tierra Firme, Cuba, and to Yucatán before joining Cortés. In his later years, Castillo was an encomendero and governor in Guatemala where he wrote his memoirs called '' The True History of the Conquest of New Spain''. He began his account of the conquest almost thirty years after the events and later revised and expanded it in response to Cortés' letters to the king, which Castillo viewed as Cortés taking most of the credit for himself while minimizing the efforts and sacrifices of the other Spaniards and their Indigenous allies such as the Tlaxcaltec during the expedition. In addition to this, Castillo disputed the biography published by Cortés' chaplain Francisco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |