|
Empty Diagonal
The empty diagonal () is a band of low-density population that stretches from the France, French department of the Landes (department), Landes in the southwest to the Meuse (department), Meuse in the northeast. The diagonal's population density is very low compared to the rest of France. Description The low population density (less than 30/km², or 78/mi²) is caused largely by the rural exodus and urbanisation of the 19th and 20th centuries. Some commentators prefer to speak of a "low-density diagonal" () and regard the term "empty diagonal" as both pejorative and exaggerated. Still, Délégation interministérielle à l'aménagement du territoire et à l'attractivité régionale, DATAR used the term and it remains the most common term. The pattern is more readily apparent at the departments of France, departmental level than at the regions of France, regional level. It is part of a broader pattern of low population density that extends into Spain and Portugal and is known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carte Démographique De La France
Carte may refer to: People * Alexander Carte (1805–1881), Irish British zoologist * Anto Carte (1886–1954), Belgian painter * Helen Carte (1852–1913), Scottish British businesswoman * Richard Carte (1808–1891), British flute-maker * Samuel Carte (1652–1740), English antiquarian * Thomas Carte (1686–1754), English historian * Omer Carte Qalib (1930–2020), Somalian politician * Carte Goodwin (born 1974), U.S. politician * Carte Said (born 1997), Italian soccer player Other uses * CARTE Museum (Cartographic Acquisition Research Teaching and Exhibition), Baton Rouge, Louisiana, USA * Carte network, a French resistance network See also * Deidre LaCarte, Canadian dancer * Julio Lacarte Muró (1918–2016), Uruguayan diplomat * * Card (other) * Cart (other) * Cartes (other) * Cartesian (other) * Descartes (other), including ''des Cartes'' * D'Oyly Carte (other) * Carte blanche (other) * À la carte (disam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emmanuel Todd
Emmanuel Todd (; born 16 May 1951) is a French historian, anthropologist, demographer, sociologist and political scientist at the National Institute of Demographic Studies (INED) in Paris. His research examines the different family structures around the world and their relationship with beliefs, ideologies, political systems, and historical events. He has also published a number of political essays, which have received broad coverage in France. Life and works Born in Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Yvelines, Emmanuel Todd is the son of journalist and Anne-Marie Nizan. Todd's paternal grandfather, Julius Oblatt, was of Austrian Jewish background, and his paternal grandmother, Helen Todd, was the illegitimate daughter of British magazine editor Dorothy Todd. Emmanuel Todd's maternal grandfather was the writer Paul Nizan. The historian Emmanuel Le Roy Ladurie, who pioneered microhistory, was a friend of the family and gave him his first history book. Aged 10, Todd wanted to beco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Europe
Europe is often divided into regions and subregions based on geographical, cultural or historical factors. Since there is no universal agreement on Europe's regional composition, the placement of individual countries may vary based on criteria being used. For instance, the Balkans is a distinct geographical region within Europe, but individual countries may alternatively be grouped into Southeast Europe, Southeastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. Regional affiliation of countries may also evolve over time. Malta (island), Malta was considered an island of North Africa for centuries, but is now considered a part of Southern Europe. The exact placement of the Caucasus has also varied since classical antiquity and is now regarded by many as a distinct region within or partly in Europe. Greenland, and partially Iceland, is geographically a part of North America but has been politically and culturally influenced by Northern European countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Banana
The Blue Banana (; ; ; ), also known as the European Megalopolis or the Liverpool–Milan Axis, is a discontinuous corridor of urbanization in Western and Central Europe, with a population of around 100 million. Over time, the region has been referred to by several names, each reflecting its development and significance. Initially, French geographer Roger Brunet, as the leader of RECLUS (Network for the study of changes in locations and spatial units), described the area as 'the European Backbone', which depicted an urban corridor extending from Liverpool to Milan. Characterized by significant industrialization and urbanization, this area has attracted numerous public and private enterprises since the early post-war period, prompting researchers and academics to investigate the factors behind its remarkable development within Europe. It stretches approximately from North West England through the English Midlands across Greater London to the European Metropolis of Lille, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Banana
The Golden Banana or Sun Belt is an area of higher population density lying between Cartagena in the west and Genoa in the east along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea. The area runs along the Mediterranean coast, including the French cities of Nice, Marseille, Montpellier, and Perpignan, and the Spanish cities of Figueres, Barcelona and Valencia. It was defined by the "Europe 2000" report from the European Commission in 1995 similarly to the Blue Banana. Description The region is characterized by its importance in activities related to information and communication technologies, in terms of quality of life and as a top travel destination. At any rate, the Golden Banana can also be understood as an extension of the Blue Banana over the Mediterranean arc. The golden banana has development axes extending into the area of the upper Adriatic around Trieste. This also relates to the trade flows of the maritime Silk Road or the Chinese Belt and Road Initiative and its develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
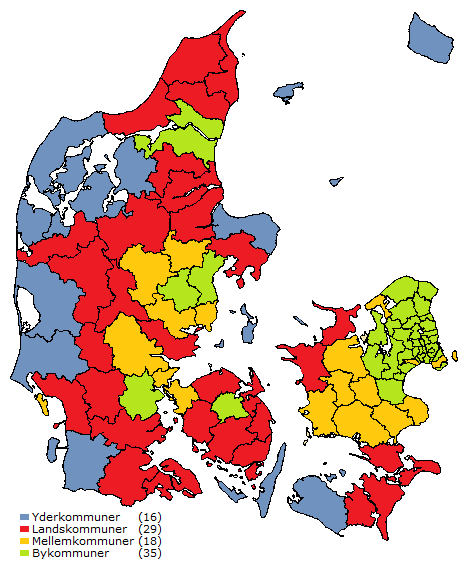
Rotten Banana
The Rotten Banana ( Danish: ''Den rådne banan'') is an informal area of rural Denmark facing significant economic disparities. The term ''Rotten Banana'' traditionally includes an area of Danish municipalities the west coast of Jutland to Lolland-Falster islands in the southeast, forming a crescent shape reminiscent of a banana. This phenomenon has garnered media attention due to the stark economic disparities between these regions and more prosperous urban centers, like Copenhagen, Aarhus, and Odense. The term was coined by Hanne W. Tanvig in the 1990s to draw attention to a contrasting phenomenon to the Blue Banana. The term, which holds a negative connotation, has been falling out of fashion, and media use of the term has declined. Tanvig regrets creating the term. In the time since the term was coined, studies have found that the area with highest unemployment has shrunken to primary west Zealand, Lolland, and Falster. See also * Rust Belt – a term for a region in the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardèche
Ardèche (; , ; ) is a Departments of France, department in Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, Southeastern France. It is named after the river Ardèche (river), Ardèche and had a population of 328,278 as of 2019.Populations légales 2019: 07 Ardèche INSEE Its Prefectures of France, prefecture is in Privas, but its largest city is Annonay. History Prehistory and ancient history Humans have inhabited the area at least since the Upper Paleolithic, as attested by the famous cave paintings at Chauvet Cave, Chauvet Pont d'Arc. The Ardèche river plateau has extensive standing stones (mainly dolmens and some menhirs), erected thousands of years ago. The river has one of Europe's largest canyons, and the caves that dot the cliffs—which go as high as 300 metres (1,00 ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collection Blanche
The Collection Blanche is the great Collection (publishing), collection of French literature published by the Éditions Gallimard. It appeared in 1911, and at the beginning was nourished by the publications of ''Nouvelle Revue Française, La Nouvelle Revue française'' (''La NRF''), the brand "Librairie Gallimard" appeared only after July 1919.Henri Vignes et Pierre Boudrot, ''Bibliographie des éditions de La Nouvelle Revue française'', Paris, Henri Vigne & Éditions des Cendres, 2011, , page 7-18. Since its creation, "La Blanche", which takes its name from the cream color of its cover, has published 6500 titles, of which 3800 are still available today. In addition to the "NRF" logo originally designed by Jean Schlumberger (writer), Jean Schlumberger, the graphic charter of this collection - a black border surrounding two red edges - is inspired by the éditions de , with its first title, ''L'Otage'' by Paul Claudel, published 26 May 1911. Apart from classic literature like ''I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Éditions Gallimard
Éditions Gallimard (), formerly Éditions de la Nouvelle Revue Française (1911–1919) and Librairie Gallimard (1919–1961), is one of the leading French book publishers. In 2003, it and its subsidiaries published 1,418 titles. Founded by Gaston Gallimard in 1911, the publisher is now majority-owned by his grandson Antoine Gallimard. Éditions Gallimard is a subsidiary of Groupe Madrigall, the third largest French publishing group. History The publisher was founded on 31 May 1911 in Paris by Gaston Gallimard, André Gide, and Jean Schlumberger as ''Les Éditions de la Nouvelle Revue Française'' (NRF). From its 31 May 1911 founding until June 1919, Nouvelle Revue Française published one hundred titles including ''La Jeune Parque'' by Paul Valéry. NRF published the second volume of ''In Search of Lost Time'', In the Shadow of Young Girls in Flower, which became the first Prix Goncourt-awarded book published by the company. Nouvelle Revue Française adopted the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Péju
Pierre Péju (born 1946) is a French philosopher, novelist and essayist. Born in Lyon, he studied at the Sorbonne. He has published a number of works in different literary genres, the best-known of which are two prize-winning novels ''Le rire de l’ogre'' and ''La petite Chartreuse''. Both titles are studied in French schools and lycees, and both have been translated into English, the former by Euan Cameron Euan Cameron is the Henry Luce III Professor of Reformation Church History at Union Theological Seminary. He has a D.Phil from the University of Oxford. His work focuses on the Reformation and religion in the Late Middle Ages The late Middle ... and the latter ('' The Girl from the Chartreuse'') by Ina Rilke. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Peju, Pierre 20th-century French writers 21st-century French writers 20th-century French essayists Prix du Livre Inter winners French art critics Writers from Lyon 1946 births Living people 20th-century French male writers F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorraine
Lorraine, also , ; ; Lorrain: ''Louréne''; Lorraine Franconian: ''Lottringe''; ; ; is a cultural and historical region in Eastern France, now located in the administrative region of Grand Est. Its name stems from the medieval kingdom of Lotharingia (855–959 AD), which in turn was named after either Emperor Lothair I or King Lothair II. Lorraine, originally the southern or "upper" part of this kingdom, came to be ruled by the Holy Roman Empire as the Duchy of Lorraine before the Kingdom of France annexed it in 1766. From 1982 until January 2016, Lorraine was an administrative region of France. In 2016, under a reorganisation, it became part of the new region Grand Est. As a region in modern France, Lorraine consisted of the four departments Meurthe-et-Moselle, Meuse, Moselle and Vosges (from a historical point of view the Haute-Marne department is also located in the region), containing 2,337 communes. Metz is the regional prefecture. The largest metropolitan area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |