|
Employee Stock Options
Employee stock options (ESO or ESOPs) is a label that refers to compensation contracts between an employer and an employee that carries some characteristics of financial options. Employee stock options are commonly viewed as an internal agreement providing the possibility to participate in the share capital of a company, granted by the company to an employee as part of the employee's remuneration package. Regulators and economists have since specified that ESOs are compensation contracts. These nonstandard contracts exist between employee and employer, whereby the employer has the liability of delivering a certain number of shares of the employer stock, when and if the employee stock options are exercised by the employee. The contract length varies, and often carries terms that may change depending on the employer and the current employment status of the employee. In the United States, the terms are detailed within an employer's "Stock Option Agreement for Incentive Equity P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Options (finance)
In finance, an option is a contract which conveys to its owner, the ''holder'', the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset or instrument at a specified strike price on or before a specified date, depending on the style of the option. Options are typically acquired by purchase, as a form of compensation, or as part of a complex financial transaction. Thus, they are also a form of asset (or contingent liability) and have a valuation that may depend on a complex relationship between underlying asset price, time until expiration, market volatility, the risk-free rate of interest, and the strike price of the option. Options may be traded between private parties in '' over-the-counter'' (OTC) transactions, or they may be exchange-traded in live, public markets in the form of standardized contracts. Definition and application An option is a contract that allows the holder the right to buy or sell an underlying asset or financial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incentive Stock Option
Incentive stock options (ISOs), are a type of employee stock option that can be granted only to employees and confer a U.S. tax benefit. ISOs are also sometimes referred to as statutory stock options by the IRS. ISOs have a strike price, which is the price a holder must pay to purchase one share of the stock. ISOs may be issued both by public companies and private companies, with ISOs being common as a form of executive compensation for public companies, and common as a form of equity compensation in private start-up companies. The tax benefit is that on exercise, the individual does not pay ordinary income tax nor employment taxes on the difference between the exercise price and the strike price of the shares issued (but may owe a substantial alternative minimum tax if the shares are not sold in the same year, especially if the difference between exercise price and strike price is large, on the order of $50,000 or more). Rather, if the shares are held for 1 year from the date of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corporate Action
A corporate action is an event initiated by a public company that brings or could bring an actual change to the debt securities—Share capital, equity or debt—issued by the company. Corporate actions are typically agreed upon by a company's board of directors and authorized by the shareholders. For some events, shareholders or bondholders are permitted to vote on the event. Examples of corporate actions include stock splits, dividends, mergers and acquisitions, rights issues, and Corporate spin-off, spin-offs. Some corporate actions such as a dividend (for equity securities) or Bond_(finance)#Coupon, coupon payment (for debt securities) may have a direct financial impact on the shareholders or bondholders; another example is a call (early redemption) of a debt security. Other corporate actions such as stock split may have an indirect financial impact, as the increased liquidity of shares may cause the price of the stock to decrease. Some corporate actions, such as name chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Result
The financial result is the difference between earnings before interest and taxes and earnings before taxes. It is determined by the earning or the loss which results from financial affairs. Interpretation For most industrial companies the financial result is negative, as the interest charged on borrowing generally exceeds income from investments (dividends). If a company records a positive financial Result over several periods, then one has to ask how much capital is invested at which interest rate, and if this capital would not bear a greater yield if it were invested in the company's growth. In case of constant, positive financial results a company also has to deal with increasing demands for special distributions to its shareholders. Calculation formula In mathematical terms financial result is defined as follows: \textstyle Advantages The advantages of the use of financial result as a key performance indicator * The financial result provides information about fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Option
In finance, the style or family of an option is the class into which the option falls, usually defined by the dates on which the option may be exercised. The vast majority of options are either European or American (style) options. These options—as well as others where the payoff is calculated similarly—are referred to as " vanilla options". Options where the payoff is calculated differently are categorized as " exotic options". Exotic options can pose challenging problems in valuation and hedging. American and European options The key difference between American and European options relates to when the options can be exercised: * A European option may be exercised only at the expiration date of the option, i.e. at a single pre-defined point in time. * An American option on the other hand may be exercised at any time before the expiration date. For both, the payoff—when it occurs—is given by * \max\, for a call option * \max\, for a put option where K is the strik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Option (finance)
In finance, an option is a contract which conveys to its owner, the ''holder'', the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset or instrument at a specified strike price on or before a specified date, depending on the style of the option. Options are typically acquired by purchase, as a form of compensation, or as part of a complex financial transaction. Thus, they are also a form of asset (or contingent liability) and have a valuation that may depend on a complex relationship between underlying asset price, time until expiration, market volatility, the risk-free rate of interest, and the strike price of the option. Options may be traded between private parties in '' over-the-counter'' (OTC) transactions, or they may be exchange-traded in live, public markets in the form of standardized contracts. Definition and application An option is a contract that allows the holder the right to buy or sell an underlying asset or financia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black–Scholes Model
The Black–Scholes or Black–Scholes–Merton model is a mathematical model for the dynamics of a financial market containing Derivative (finance), derivative investment instruments. From the parabolic partial differential equation in the model, known as the Black–Scholes equation, one can deduce the Black–Scholes formula, which gives a theoretical estimate of the price of option style, European-style option (finance), options and shows that the option has a ''unique'' price given the risk of the security and its expected return (instead replacing the security's expected return with the risk-neutral rate). The equation and model are named after economists Fischer Black and Myron Scholes. Robert C. Merton, who first wrote an academic paper on the subject, is sometimes also credited. The main principle behind the model is to hedge (finance), hedge the option by buying and selling the underlying asset in a specific way to eliminate risk. This type of hedging is called "continuou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exercise (options)
The owner of an option contract has the right to exercise it, and thus require that the financial transaction specified by the contract is to be carried out immediately between the two parties, whereupon the option contract is terminated. When exercising a call option, the owner of the option purchases the underlying shares (or commodities, fixed interest securities, etc.) at the strike price from the option seller, while for a put option, the owner of the option sells the underlying to the option seller, again at the strike price. Styles The option style, as specified in the contract, determines when, how, and under what circumstances, the option holder may exercise it. It is at the discretion of the owner whether (and in some circumstances when) to exercise it. * European – European-style option contracts may only be exercised at the option's expiration date. Thus they can never be worth more than an American-style option with the same underlying strike price and expirati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
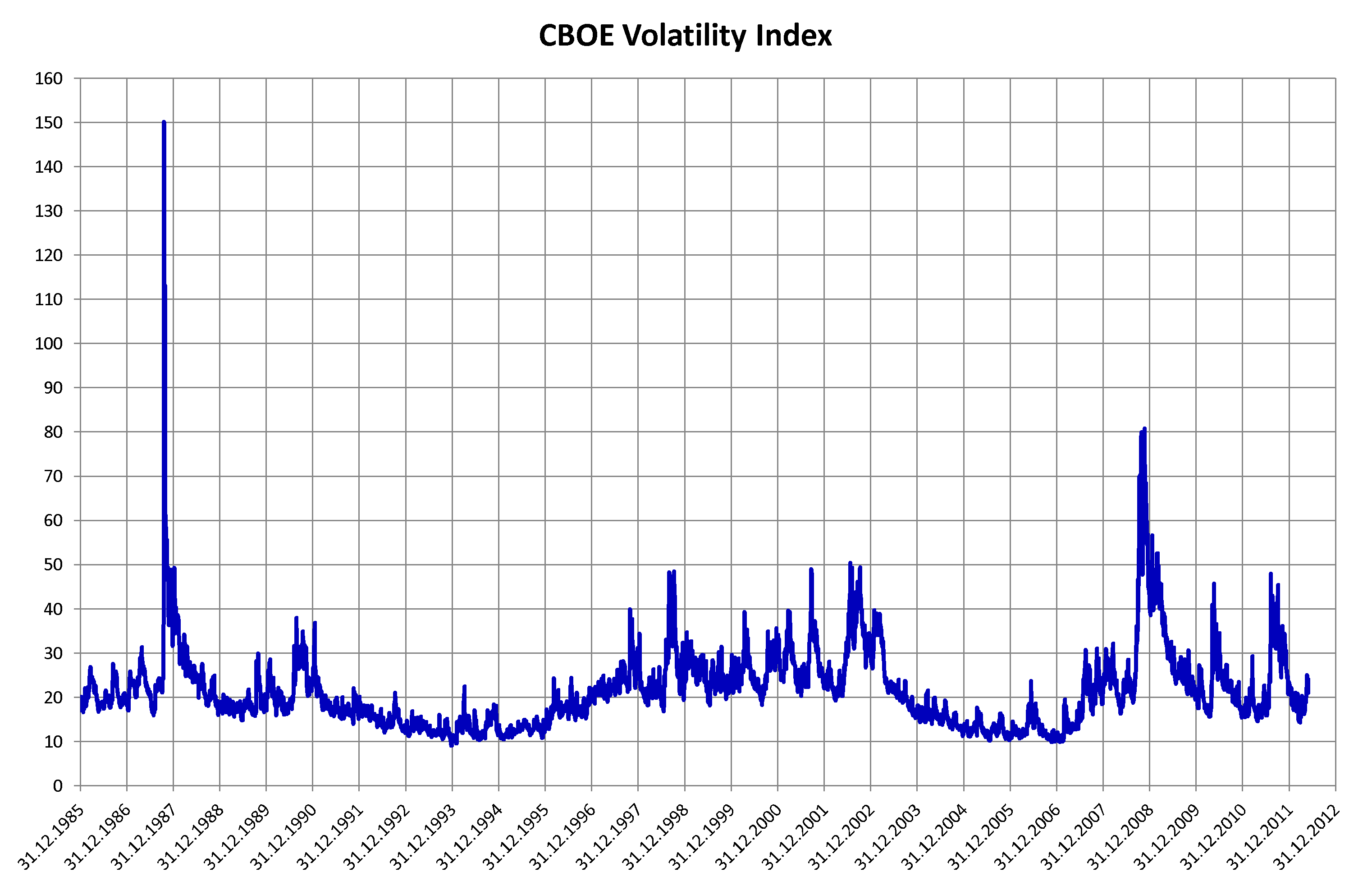
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility (usually denoted by "sigma, σ") is the Variability (statistics), degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a time series of past market prices. Implied volatility looks forward in time, being derived from the market price of a market-traded derivative (in particular, an option). Volatility terminology Volatility as described here refers to the actual volatility, more specifically: * actual current volatility of a financial instrument for a specified period (for example 30 days or 90 days), based on historical prices over the specified period with the last observation the most recent price. * actual historical volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period but with the last observation on a date in the past **near synonymous is realized volatility, the square root of the realized variance, in turn c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice Model (finance)
In quantitative finance, a lattice model is a numerical approach to the valuation of derivatives in situations requiring a discrete time model. For dividend paying equity options, a typical application would correspond to the pricing of an American-style option, where a decision to exercise is allowed at the closing of any calendar day up to the maturity. A continuous model, on the other hand, such as the standard Black–Scholes one, would only allow for the valuation of European options, where exercise is limited to the option's maturity date. For interest rate derivatives lattices are additionally useful in that they address many of the issues encountered with continuous models, such as pull to par. The method is also used for valuing certain exotic options, because of path dependence in the payoff. Traditional Monte Carlo methods for option pricing fail to account for optimal decisions to terminate the derivative by early exercise, but some methods now exist for so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contract Differences
A contract is an agreement that specifies certain legally enforceable rights and obligations pertaining to two or more parties. A contract typically involves consent to transfer of goods, services, money, or promise to transfer any of those at a future date. The activities and intentions of the parties entering into a contract may be referred to as contracting. In the event of a breach of contract, the injured party may seek judicial remedies such as damages or equitable remedies such as specific performance or rescission. A binding agreement between actors in international law is known as a treaty. Contract law, the field of the law of obligations concerned with contracts, is based on the principle that agreements must be honoured. Like other areas of private law, contract law varies between jurisdictions. In general, contract law is exercised and governed either under common law jurisdictions, civil law jurisdictions, or mixed-law jurisdictions that combine elements of bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valuation Of Options
In finance, a price (premium) is paid or received for purchasing or selling options. The calculation of this premium will require sophisticated mathematics. Premium components This price can be split into two components: intrinsic value, and time value (also called "extrinsic value"). Intrinsic value The ''intrinsic value'' is the difference between the underlying spot price and the strike price, to the extent that this is in favor of the option holder. For a call option, the option is in-the-money if the underlying spot price is higher than the strike price; then the intrinsic value is the underlying price minus the strike price. For a put option, the option is in-the-money if the ''strike'' price is higher than the underlying spot price; then the intrinsic value is the strike price minus the underlying spot price. Otherwise the intrinsic value is zero. For example, when a DJI call (bullish/long) option is 18,000 and the underlying DJI Index is priced at $18,050 then the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |