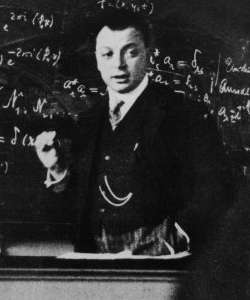|
Empiriocriticism
Ernst Waldfried Josef Wenzel Mach ( ; ; 18 February 1838 – 19 February 1916) was an Austrian physicist and philosopher, who contributed to the understanding of the physics of shock waves. The ratio of the speed of a flow or object to that of sound is named the Mach number in his honour. As a philosopher of science, he was a major influence on logical positivism and American pragmatism. Through his criticism of Isaac Newton's theories of space and time, he foreshadowed Albert Einstein's theory of relativity. Biography Early life Mach was born in Chrlice (), Moravia, Austrian Empire (now part of Brno in the Czech Republic). His father Jan Nepomuk Mach, who had graduated from Charles-Ferdinand University in Prague, acted as tutor to the noble Brethon family in Zlín in eastern Moravia. His grandfather, Wenzl Lanhaus, an administrator of the Chirlitz estate, was also master builder of the streets there. His activities in that field later influenced Ernst Mach's theoretical wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empirio-criticism
Ernst Waldfried Josef Wenzel Mach ( ; ; 18 February 1838 – 19 February 1916) was an Austrian Empire, Austrian physicist and philosopher, who contributed to the understanding of the physics of shock waves. The ratio of the speed of a flow or object to speed of sound, that of sound is named the Mach number in his honour. As a Philosophy of science, philosopher of science, he was a major influence on logical positivism and American pragmatism. Through his criticism of Isaac Newton's theories of space and time, he foreshadowed Albert Einstein's theory of relativity. Biography Early life Mach was born in Chrlice (), Moravia, Austrian Empire (now part of Brno in the Czech Republic). His father Jan Nepomuk Mach, who had graduated from Charles-Ferdinand University in Prague, acted as tutor to the noble Brethon family in Zlín in eastern Moravia. His grandfather, Wenzl Lanhaus, an administrator of the Chirlitz estate, was also master builder of the streets there. His activities in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brno
Brno ( , ; ) is a Statutory city (Czech Republic), city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava (river), Svitava and Svratka (river), Svratka rivers, Brno has about 403,000 inhabitants, making it the second-largest city in the Czech Republic after the capital, Prague, and one of the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 100 largest cities of the European Union. The Brno metropolitan area has approximately 730,000 inhabitants. Brno is the former capital city of Moravia and the political and cultural hub of the South Moravian Region. It is the centre of the Judiciary of the Czech Republic, Czech judiciary, with the seats of the Constitutional Court of the Czech Republic, Constitutional Court, the Supreme Court of the Czech Republic, Supreme Court, the Supreme Administrative Court of the Czech Republic, Supreme Administrative Court, and the Supreme Public Prosecutor's Office, and a number of state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mach Reflection
Mach reflection is a supersonic fluid dynamics effect, named for Ernst Mach, and is a shock wave reflection pattern involving three shocks. Introduction Mach reflection can exist in steady, pseudo-steady and unsteady flows. When a shock wave, which is moving with a constant velocity, propagates over a solid wedge, the flow generated by the shock impinges on the wedge thus generating a second reflected shock, which ensures that the velocity of the flow is parallel to the wedge surface. Viewed in the frame of the reflection point, this flow is locally steady, and the flow is referred to as pseudosteady. When the angle between the wedge and the primary shock is sufficiently large, a single reflected shock is not able to turn the flow to a direction parallel to the wall and a transition to Mach reflection occurs. In a steady flow situation, if a wedge is placed into a steady supersonic flow in such a way that its oblique attached shock impinges on a flat wall parallel to the free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate causes of Phenomenon, phenomena, and usually frame their understanding in mathematical terms. They work across a wide range of Physics#Research fields, research fields, spanning all length scales: from atom, sub-atomic and particle physics, through biological physics, to physical cosmology, cosmological length scales encompassing the universe as a whole. The field generally includes two types of physicists: Experimental physics, experimental physicists who specialize in the observation of natural phenomena and the development and analysis of experiments, and Theoretical physics, theoretical physicists who specialize in mathematical modeling of physical systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. Physicists can apply their k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, which spans 32 volumes and 32,640 pages, was the last printed edition. Since 2016, it has been published exclusively as an online encyclopedia, online encyclopaedia. Printed for 244 years, the ''Britannica'' was the longest-running in-print encyclopaedia in the English language. It was first published between 1768 and 1771 in Edinburgh, Scotland, in three volumes. The encyclopaedia grew in size; the second edition was 10 volumes, and by its fourth edition (1801–1810), it had expanded to 20 volumes. Its rising stature as a scholarly work helped recruit eminent contributors, and the 9th (1875–1889) and Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition, 11th editions (1911) are landmark encyclopaedias for scholarship and literary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfgang Pauli
Wolfgang Ernst Pauli ( ; ; 25 April 1900 – 15 December 1958) was an Austrian theoretical physicist and a pioneer of quantum mechanics. In 1945, after having been nominated by Albert Einstein, Pauli received the Nobel Prize in Physics "for the discovery of the Exclusion Principle, also called the Pauli exclusion principle, Pauli Principle". The discovery involved Spin (physics), spin theory, which is the basis of a theory of the Matter#Structure, structure of matter. To preserve the conservation of energy in beta decay, he posited the existence of a small neutral particle, dubbed the neutrino by Enrico Fermi. The neutrino was detected in 1956. Early life Pauli was born in Vienna to a chemist, (''né'' Wolf Pascheles, 1869–1955), and his wife, Bertha Camilla Schütz; his sister was Hertha Pauli, a writer and actress. Pauli's middle name was given in honor of his Godparent, godfather, physicist Ernst Mach. Pauli's paternal grandparents were from prominent Jewish families of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Mach
Ludwig Mach (8 November 1868 Prague – September 1951) was an Austrian physician and chemist. Building on the work of Ludwig Zehnder in 1891, Mach added refinements to an instrument which became known as the Mach–Zehnder interferometer. He went on to employ photography for collecting visual data streamlines in the field of aerodynamics. Ludwig is the son of the physicist Ernst Mach Ernst Waldfried Josef Wenzel Mach ( ; ; 18 February 1838 – 19 February 1916) was an Austrian physicist and philosopher, who contributed to the understanding of the physics of shock waves. The ratio of the speed of a flow or object to that of .... In 1894 he registered the patent for Magnalium, an aluminum alloy with 2 to 30% magnesium, which was to be the precursor of the entire 5000 series of aluminum alloys. Its commercialization brought him significant profits. See also * Velocimetry References {{DEFAULTSORT:Mach, Ludwig 1868 births 1951 deaths Austrian physicists Austrian chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereokinetic Stimulus
Stereokinetic stimulus, stereokinetic depth, stereokinetic illusion is an illusion of depth induced by moving two-dimensional stimuli. A stereokinetic stimuli generates 3D perception based on 2D rotational motion. A stereokinetic effect is created when flat displays are rotated in the frontal plane and are perceived as having three-dimensional structure. History Ernst Mach first reported a depth effect produced by motion in the frontoparallel plane in 1886. Marcel Duchamp Henri-Robert-Marcel Duchamp (, ; ; 28 July 1887 – 2 October 1968) was a French painter, sculptor, chess player, and writer whose work is associated with Cubism, Dada, Futurism and conceptual art. He is commonly regarded, along with Pablo Pica ... first experimented with stereokinetic depth in 1935. References Visual perception {{sci-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock Wave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a medium, but is characterized by an abrupt, nearly discontinuous, change in pressure, temperature, and density of the medium. For the purpose of comparison, in supersonic speed, supersonic flows, additional increased expansion may be achieved through an expansion fan, also known as a Prandtl–Meyer expansion fan. The accompanying expansion wave may approach and eventually collide and recombine with the shock wave, creating a process of destructive interference. The sonic boom associated with the passage of a supersonic aircraft is a type of sound wave produced by Wave interference, constructive interference. Unlike solitons (another kind of nonlinear wave), the energy and speed of a shock wave alone dissipates relatively quickly with distan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relationalism
Relationalism is any theoretical position that gives importance to the relational nature of things. For relationalism, things exist and function only as relational entities. Relationalism (philosophical theory) Relationalism, in the broadest sense, applies to any system of thought that gives importance to the relational nature of reality. In its narrower and more philosophically restricted sense, as propounded by the Indian philosopher Joseph Kaipayil and others, relationalism refers to the theory of reality that interprets the existence, nature, and meaning of things in terms of their relationality or relatedness. In the relationalist view, things are neither self-standing entities nor vague events but relational particulars. Particulars are inherently relational, as they are ontologically open to other particulars in their constitution and action. Relational particulars, in the relationalist view, are the ultimate constituents of reality. Relationalism (theory of space and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oblique Effect
Oblique effect is the name given to the relative deficiency in perceptual performance for oblique contours as compared to the performance for horizontal or vertical contours. Background The earliest known observation of this effect came about in 1861 when Ernst Mach completed an experiment in which he set a line to make it appear parallel to an adjoining one, and found observers' errors to be least for horizontal and vertical orientations and largest for an inclination of 45 degrees. The effect can be demonstrated for many visual tasks and was named ''oblique effect'' in the widely cited article by Stuart Appelle. The phenomenon The effect is exhibited predominantly in tasks involving discrimination of the angle of tilt of patterns or contours. People are very good at detecting whether a picture is hung vertical, but are two- to fourfold worse for a 45-degree oblique contour, even when a comparison is available. However there is no oblique deficit in some other tasks, such as j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bucket Argument
Isaac Newton's rotating bucket argument (also known as Newton's bucket) is a thought experiment that was designed to demonstrate that true rotational motion cannot be defined as the relative rotation of the body with respect to the immediately surrounding bodies. It is one of five arguments from the "properties, causes, and effects" of "true motion and rest" that support his contention that, in general, true motion and rest cannot be defined as special instances of motion or rest relative to other bodies, but instead can be defined only by reference to absolute space. Alternatively, these experiments provide an operational definition of what is meant by " absolute rotation", and do not pretend to address the question of "rotation relative to ''what''?" General relativity dispenses with absolute space and with physics whose cause is external to the system, with the concept of geodesics of spacetime. Background These arguments, and a discussion of the distinctions between absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |