|
Emiliodonta
''Emiliodonta'' is an extinct genus of bivalve in the extinct family Praenuculidae. The genus is one of three genera in the subfamily Concavodontinae. ''Emiliodonta'' is known solely from late Ordovician, Caradocian epoch, fossils found in South America. The genus contains a single accepted species, ''Emiliodonta cuerdai''. Description ''Emiliodonta cuerdai'' is a bivalve first described in 1999 by Teresa M. Sánchez from fossils from sediments of the late Middle Ordovician, Caradocian-aged Don Braulio Formation. The formation outcrops on the flank of Sierra de Villicum in the Argentina precordillera.The Paleobiology database "Sierra de Villicum" entry accessed 17 January 2012 Generally the shells of ''Emiliodonta cuerdai'' are rounded and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concavodontinae
Concavodontinae is an extinct subfamily of prehistoric bivalves in the family Praenuculidae. Concavodontinae species lived from the middle Ordovician, Caradoc epoch through the late Ordovician Ashgill epoch.The Paleobiology Database Concavodontinae entry accessed 19 January 2012The Paleobiology Database ''Concavodonta'' entry accessed 19 January 2012 Concavodontinae fossils are found in Europe and South America, and species are thought to have been stationary attached to substrate in sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praenuculidae
Praenuculidae is an extinct family (biology), family of prehistoric bivalves in the superfamily (taxonomy), superfamily Nuculoidea. Praenuculidae species lived from the early Ordovician, Arenig, Arenig stage through the Early Devonian Emsian, Emsian stage.The Paleobiology Database Praenuculidae entry accessed 11 January 2012 Praenuculidae fossils are found worldwide, present on every continent except Antarctica. Species in this family are thought to have been Sessility (zoology), sessile, attached to the substrate in shallow infaunal marine water environments, where they formed shells of an aragonite composition. The family Praenuculidae was named by A. Lee McAlester in 1969. Description Praenuculidae first eme ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caradoc (age)
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Geological Congress. Life continued to flourish during the Ordovician as it did in the earlier Cambrian Perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
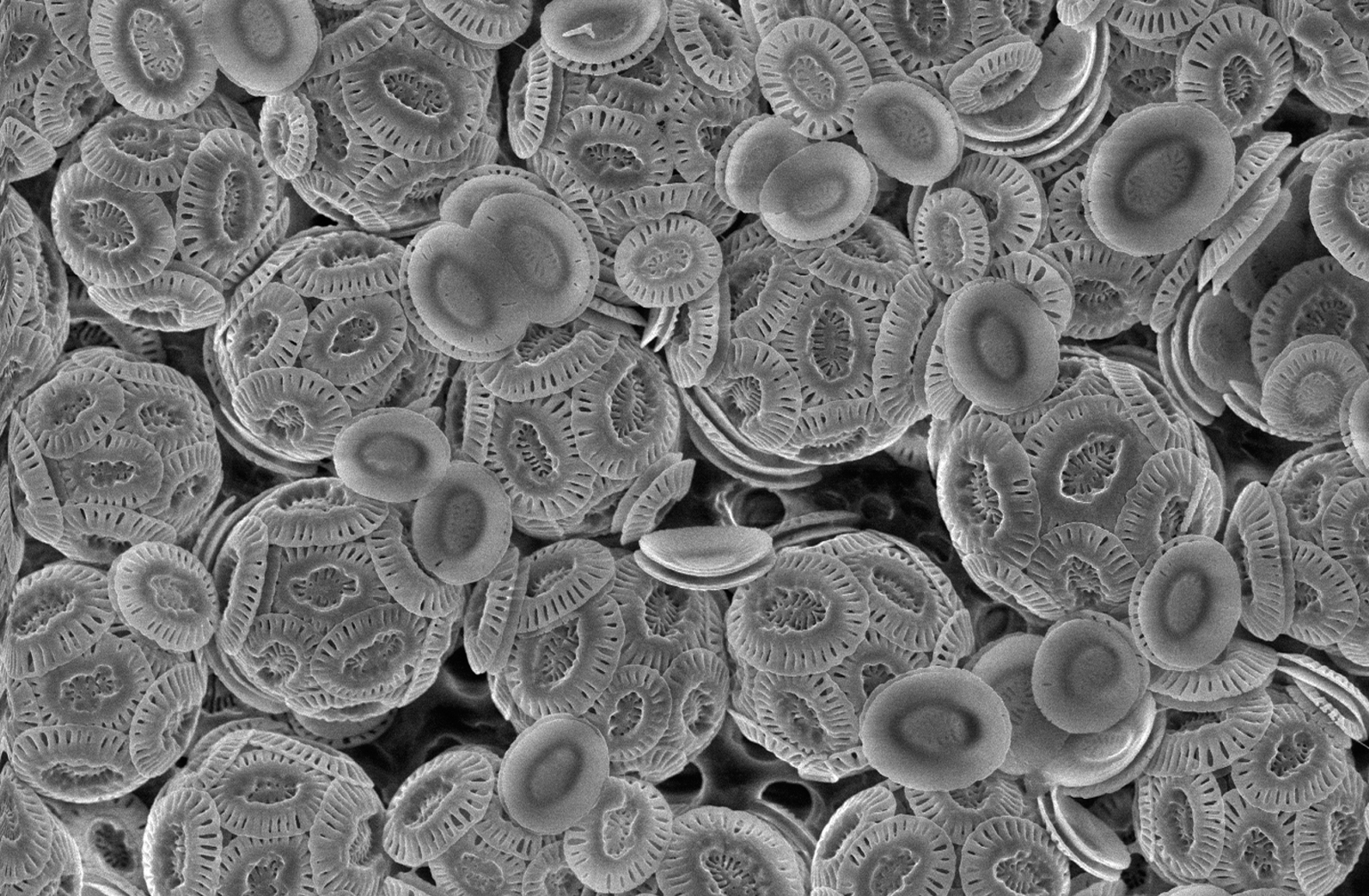
Emiliania (coccolithophore)
''Emiliania'' is a global coccolithophorid genus. The genus name of ''Emiliania'' is in honour of Cesare Emiliani (1922–1995), who was an Italian-American scientist, geologist, micropaleontologist, and founder of paleoceanography, developing the timescale of marine isotope stages. The genus was circumscribed In geometry, the circumscribed circle or circumcircle of a polygon is a circle that passes through all the vertices of the polygon. The center of this circle is called the circumcenter and its radius is called the circumradius. Not every po ... by Hanspeter Mohler and William Winn Hay in Trans. Gulf Coast Ass. Geol. Soc. Vol.17 on page 447 in 1967. It includes the species '' Emiliania huxleyi''. References Haptophyte genera {{Haptophyte-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician Bivalves
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Geological Congress. Life continued to flourish during the Ordovician as it did in the earlier Cambrian Peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Bivalve Genera
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universidad De La Plata
The La Plata National University ( es, Universidad Nacional de La Plata, UNLP) is one of the most important Argentina, Argentine national universities and the biggest one situated in the city of La Plata, capital of Buenos Aires Province. It has over 90,000 regular students, 10,000 teaching staff, 17 departments and 106 available degrees. UNLP comprises the Rafael Hernández National College, the Victor Mercante Lyceum, the Bachelor of Fine Arts program, the School of Agronomy, the La Plata University Radio, the La Plata University Press and numerous academic centers for research and outreach including La Plata Museum, La Plata Museum of Natural Sciences, the University Public Library, the Samay Huasi, Samay Huasi Retreat for Artists and Writers, the Institute of Physical Education, the La Plata Observatory, Astronomical Observatory and the Santa Catalina Rural Association. The institution began operations on April 18, 1897, as the ''Universidad Provincial de La Plata'' with D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdom Protista, according to Robert Whittaker's Five kingdom classification, or clade Hacrobia, according to a newer biological classification system. Within the Hacrobia, the coccolithophores are in the phylum or division Haptophyta, class Prymnesiophyceae (or Coccolithophyceae). Coccolithophores are almost exclusively marine, are photosynthetic, and exist in large numbers throughout the sunlight zone of the ocean. Coccolithophores are the most productive calcifying organisms on the planet, covering themselves with a calcium carbonate shell called a '' coccosphere''. However, the reasons they calcify remains elusive. One key function may be that the coccosphere offers protection against microzooplankton predation, which is one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homonym (biology)
In biology, a homonym is a name for a taxon that is identical in spelling to another such name, that belongs to a different taxon. The rule in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature is that the first such name to be published is the senior homonym and is to be used (it is "valid"); any others are junior homonyms and must be replaced with new names. It is, however, possible that if a senior homonym is archaic, and not in "prevailing usage," it may be declared a ''nomen oblitum'' and rendered unavailable, while the junior homonym is preserved as a ''nomen protectum''. :For example: :*Cuvier proposed the genus ''Echidna'' in 1797 for the spiny anteater. :*However, Forster had already published the name ''Echidna'' in 1777 for a genus of moray eels. :*Forster's use thus has priority, with Cuvier's being a junior homonym. :* Illiger published the replacement name ''Tachyglossus'' in 1811. Similarly, the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (IC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the eighth-largest country in the world. It shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a federal state subdivided into twenty-three provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty over the Falkland Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, and a part of Antarctica. The earliest recorded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precordillera
Precordillera is a Spanish geographical term for hills and mountains lying before a greater range, foothills. The term is derived from ''cordillera'' (mountain range)—literally "pre-mountain range"—and applied usually to the Andes. Some places usually called precordillera are: *Andean mountains east of the main ranges of Andes in Argentina. It is separated from the much higher Frontal Cordillera to the west by Uspallata Valley in Argentina. Precordillera mountains reach around 3,000 m a.s.l. in Sierras de Villavicencio. *Used all over Chile from north to south as a morphological unit lying just between the Andes and the Intermediate Depression. See also * Geological history of the precordillera terrane The Precordillera terrane of western Argentina is a large mountain range located southeast of the main Andes mountain range. The evolution of the Precordillera is noted for its unique formation history compared to the region nearby. The Cambrian- ... * References {{Geo-term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds ( taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)