|
Emil Haussmann
Emil Haussmann (11 October 1910 – 31 July 1947) was a German SS functionary during the Nazi era. He was part of Einsatzkommando 12 of Einsatzgruppe D, which perpetrated the Holocaust in occupied Ukraine. Haussmann was charged with crimes against humanity in 1947 in the Einsatzgruppen Trial. Two days after his indictment, Haussmann committed suicide. Life Emil Haussmann was the son of an accountant in Ravensburg. He joined the Nazi Party in January 1930—three years before the ''Machtergreifung''—at the age of 19. Haussmann was a grade school teacher. In 1937, he became a full-time employee of the ''Sicherheitsdienst'' (SD), and took over the Southwest, based in the Judenreferat in Stuttgart. Klaus-Michael Mallmann, Jochen Böhler und Jürgen Matthäus: ''Einsatzgruppen in Polen''. WBG, Stuttgart 2008, p. 39-40. During the invasion of Poland, Haussmann was part of Einsatzgruppe VI. There he was the "right hand man" for Albert Rapp, the leader of the Eins. Commandin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Era
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a totalitarian dictatorship. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", referred to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945, after 12 years, when the Allies defeated Germany and entered the capital, Berlin, ending World War II in Europe. After Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany in 1933, the Nazi Party began to eliminate political opposition and consolidate power. A 1934 German referendum confirmed Hitler as sole ''Führer'' (leader). Power was centralised in Hitler's person, and his word became the highest law. The government was not a coordinated, cooperat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
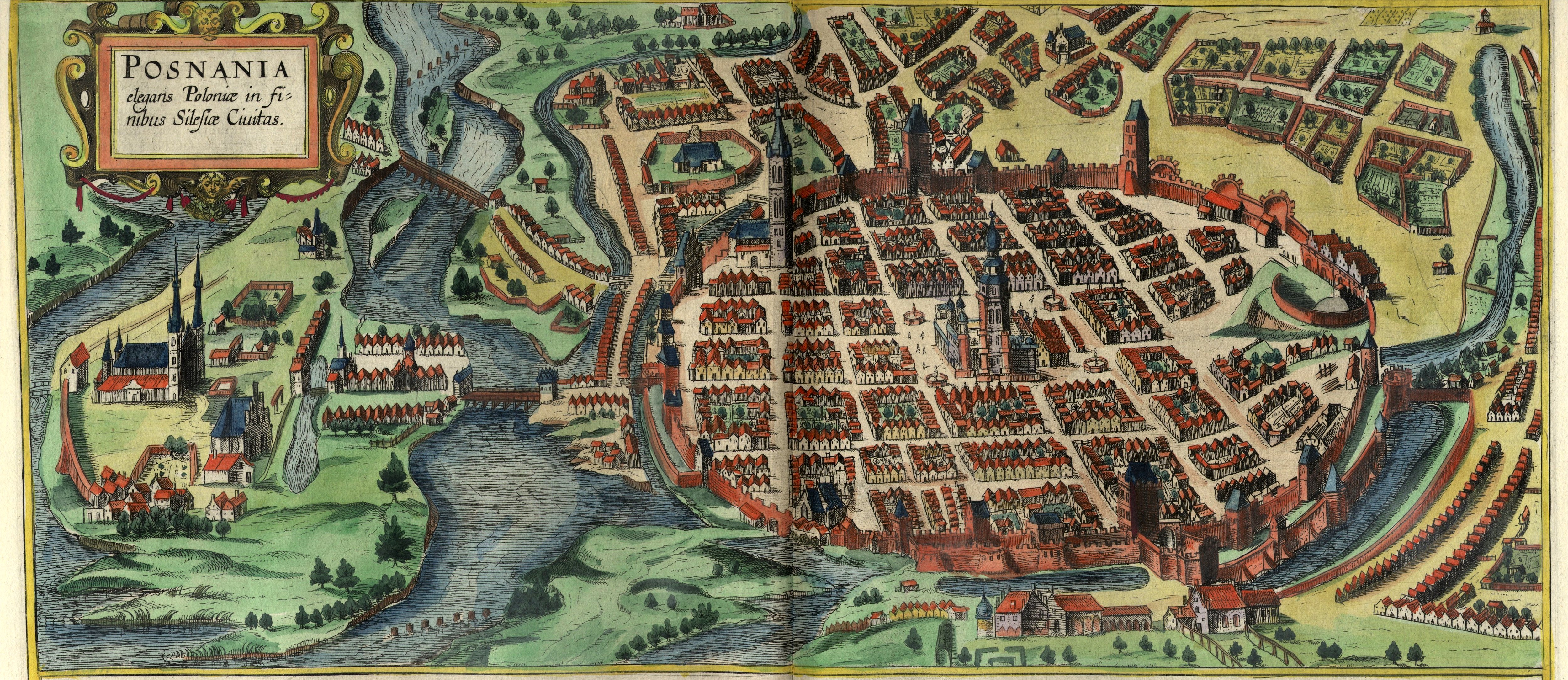
Poznań
Poznań ( ) is a city on the Warta, River Warta in west Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business center and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's Fair, Poznań, Saint John's Fair (''Jarmark Świętojański''), traditional St. Martin's croissant, Saint Martin's croissants and a local dialect. Among its most important heritage sites are the Renaissance in Poland, Renaissance Old Town, Poznań Town Hall, Town Hall and Poznań Cathedral. Poznań is the fifth-largest List of cities and towns in Poland#Cities, city in Poland. As of 2023, the city's population is 540,146, while the Poznań metropolitan area (''Metropolia Poznań'') comprising Poznań County and several other communities is inhabited by over 1.029 million people. It is one of four historical capitals of medieval Poland and the ancient capital of the Greater Poland region, currently the administrative capital of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erich Naumann
Erich Naumann (29 April 1905 – 7 June 1951) was an SS-''Brigadeführer'' and member of the SD. Naumann had a key role in the Holocaust in Eastern Europe as the commander of '' Einsatzgruppe VI'' and the commander of '' Einsatzgruppe B''. A convicted war criminal, Naumann was sentenced to death and hanged on 7 June 1951. Early life and career Born 29 April 1905, in Meissen, Saxony, Erich Naumann left school at the age of sixteen and was employed in a commercial firm in his home town of Meissen. He joined the Nazi Party in November 1929 (nr. 170257). In 1933, Naumann joined the SA in a full-time capacity and then became an official and officer of police. He joined the ''Sicherheitsdienst'' (SD) in 1935. Naumann was the commander of '' Einsatzgruppe VI'' during its short-lived existence. During the invasion of Poland, the unit murdered over 6,000 people as part of Operation Tannenberg. Afterwards, Naumann was Chief of '' Einsatzgruppe B'' from November 1941 until February or M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Poland
The invasion of Poland, also known as the September Campaign, Polish Campaign, and Polish Defensive War of 1939 (1 September – 6 October 1939), was a joint attack on the Second Polish Republic, Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany, the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic, and the Soviet Union, which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week after the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact between Germany and the Soviet Union, and one day after the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union had approved the pact. The Soviet invasion of Poland, Soviets invaded Poland on 17 September. The campaign ended on 6 October with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland under the terms of the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty. The aim of the invasion was to disestablish Poland as a sovereign country, with its citizens destined for The Holocaust, extermination. German and Field Army Bernolák, Slovak forces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jürgen Matthäus
Jürgen Matthäus (born 1959) is a German historian and head of the research department of the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. He is an author and editor of multiple works on the history of World War II and the Holocaust. Matthäus was a contributor to Christopher Browning's 2004 work ''The Origins of the Final Solution''. Education and career Matthäus studied history and philosophy at the University of Bochum (Germany) where he earned his PhD in 1992. His first book on nation building in Australia before the First World War came out in 1993. Afterwards, he was senior historian at the Australian Department of Justice in Sydney. Since 1994, he has worked at the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum in Washington, D.C., where he currently serves as director of the research department at the Jack, Joseph and Morton Mandel Center for Advanced Holocaust Studies. He has held several guest professorships in the USA, Australia and Germany. He is a member of the internat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jochen Böhler
Jochen Böhler (born 1969 in Rheinfelden) is a German historian, specializing in the history of Eastern Europe in the 19th and 20th century, especially the World Wars, the Holocaust, nationality and borderland studies. He is the recipient of several international awards. and known to a larger audience due to frequent appearances in TV productions and articles in national newspapers such as, for example, Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung or DIE ZEIT. His main thesis on the beginning of WWII and the end of WWI in Eastern Europe has been discussed vividly in German, English, and Polish academic circles. Childhood Böhler grew up in Switzerland, the Ruhr, Ghana, the Black Forest, and Trier at the trijunction of France, Luxembourg, and Germany. Professional career Böhler obtained a Magister's degree at University of Cologne in 1999, where he specialized in modern and medieval history, as well as ethnology and political economy. His Magisterial thesis, ''Wehrmacht war crimes in Polan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klaus-Michael Mallmann
Klaus-Michael Mallmann (born 3 November 1948, in Kaiserslautern) is a German historian at the University of Stuttgart. Scientific career Mallmann studied history, Sociology, Politics and German studies at the Saarland University. In 1979 he was awarded the Kurt Magnus Prize after working as a television journalist for Saarländischer Rundfunk from 1976 to 1987. He obtained his doctorate in 1980, with a study of the "beginnings of the mine workers' movement on the Saar (1848 - 1904)". He was an academic assistant at the Saarland university from 1988 to 1992, in a research project titled "Resistance and refusal in Saarland 1935 - 1945". Afterwards he worked at the Free University of Berlin on the research project "The Gestapo 1933 - 1945" under Professor Dr. Peter Steinbach. He qualified as a university lecturer in 1995 at the University of Essen with the study "Milieu and Avant-garde. On the social history of German communism 1918 - 1933". He taught in Essen as lecturer for mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; ; Swabian German, Swabian: ; Alemannic German, Alemannic: ; Italian language, Italian: ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, largest city of the States of Germany, German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the Neckar river in a fertile valley known as the ''Stuttgarter Kessel'' (Stuttgart Cauldron) and lies an hour from the Swabian Jura and the Black Forest. Stuttgart has a population of 632,865 as of 2022, making it the list of cities in Germany by population, sixth largest city in Germany, while over 2.8 million people live in the city's administrative region and nearly 5.5 million people in Stuttgart Metropolitan Region, its metropolitan area, making it the metropolitan regions in Germany, fourth largest metropolitan area in Germany. The city and metropolitan area are consistently ranked among the List of EU metropolitan regions by GDP#2021 ranking of top four German metropolitan regions, top 5 Europea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reich Security Head Office Referat IV B4
Reich Security Main Office Referat IV B4, known as RSHA IV B4 (German: ''Eichmannreferat'' IV D4 until March 1941, or ''Judenreferat''), was a sub-department of Germany's Reich Security Main Office (''Reichssicherheitshauptamt'' or RSHA) and the Gestapo during the Holocaust. Led by SS-''Obersturmbannführer'' Adolf Eichmann, RSHA IV B4 was responsible for "Jewish affairs and evacuation" in German-occupied Europe, and specifically for the deportation of Jews from outside Poland to concentration or extermination camps. Within Poland, the liquidation of the ghettos and transport of Jews was handled by the SS and local police departments. The sub-department was a natural successor to the Central Office for Jewish Emigration which had initially been established by Eichmann in Vienna in August 1938. On 24 January 1939, the ''Reich Central Office for Jewish Emigration'' (''Reichszentrale für jüdische Auswanderung'') was established in Berlin by Hermann Göring with Reinhard Heydrich as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicherheitsdienst
' (, "Security Service"), full title ' ("Security Service of the ''Reichsführer-SS''"), or SD, was the intelligence agency of the Schutzstaffel, SS and the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany. Established in 1931, the SD was the first Nazi intelligence organization and the Gestapo (formed in 1933) was considered its sister organization through the integration of SS members and operational procedures. The SD was administered as an independent SS office between 1933 and 1939. That year, the SD was transferred over to the Reich Security Main Office (''Reichssicherheitshauptamt''; RSHA), as one of its seven departments. Its first director, Reinhard Heydrich, intended for the SD to bring every single individual within the Third Reich's reach under "continuous supervision". Following Germany's defeat in World War II, the tribunal at the Nuremberg trials officially declared that the SD was a criminal organisation, along with the rest of Heydrich's RSHA (including the Gestapo) both individually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volksschule
The German term ''Volksschule'' () generally refers to compulsory education, denoting an educational institution every person (i.e. the people, ''Volk'') is required to attend. In Germany and Switzerland it is equivalent to a combined primary (''Grundschule'' and ''Primarschule'', respectively) and lower secondary education (''Hauptschule'' or ''Sekundarschule''), usually comprising mandatory attendance of nine years. In Austria, ''Volksschule'' only refers to primary school lasting four years. In Denmark and Norway, they were referred to as ''folkeskole'' and in Sweden as ''folkskola''; the Finnish term ''kansakoulu'' is a direct translation. These Nordic schools covered the first years of primary education, from the ages of 7 to 11 or 12. History In medieval times, church schools were established in the Holy Roman Empire to educate the future members of the clergy, as stipulated by the 1215 Fourth Council of the Lateran, later adopted by the sunday schools of the Protes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |