 |
Emergency Fighter Program
The Emergency Fighter Program () was the program that resulted from a decision taken on July 3, 1944 by the Luftwaffe regarding the German aircraft manufacturing companies during the last year of the Third Reich. This project was one of the products of the latter part of 1944, when the Luftwaffe High Command saw that there was a dire need for a strong defense against Allied bombing raids. Although opposed by important figures such as Luftwaffe fighter force leader Adolf Galland, the project went ahead owing to the backing of Reichsmarschall Hermann Göring. Most of the designs of the Emergency Fighter Program never proceeded past the project stage. History 1944 began with massive bombing raids by the US Army Air Force and RAF Bomber Command on a unprecedented scale. With a shift of emphasis from targeting strategic targets to the destruction of the ''Luftwaffe'', during the Big Week in late February 1944 the ''Luftwaffe'' fighter force was broken. By the summer, Allied ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Heinkel 162
Heinkel Flugzeugwerke () was a German aircraft manufacturing company founded by and named after Ernst Heinkel. It is noted for producing bomber aircraft for the Luftwaffe in World War II and for important contributions to high-speed flight, with the pioneering examples of a successful liquid-fueled rocket and a turbojet-powered aircraft in aviation history, with both Heinkel designs' first flights occurring shortly before the outbreak of World War II in Europe. History Following the successful career of Ernst Heinkel as the chief designer for the Hansa-Brandenburg aviation firm in World War I, Heinkel's own firm was established at Warnemünde in 1922, after the restrictions on German aviation imposed by the Treaty of Versailles were relaxed. By 1929, the firm's compressed air-powered catapults were in use on the German Norddeutscher Lloyd ocean-liners and to launch short-range mail planes from the liners' decks. The company's first post-World War I aircraft design success wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
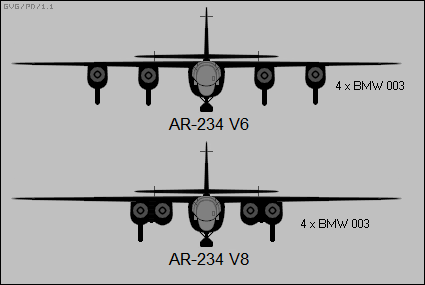 |
Arado Ar 234
The Arado Ar 234 ''Blitz'' (English: lightning) is a jet-powered bomber designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Arado. It was the world's first operational turbojet-powered bomber, seeing service during the final years of the Second World War. Development of the Ar 234 can be traced back to the latter half of 1940 and the request to tender from the Ministry of Aviation to produce a jet-powered high-speed reconnaissance aircraft. Arado was the only respondent with their ''E.370'' design. While its range was beneath that of the Ministry's specification, an initial order for two prototypes was promptly issued to the company, designated ''Ar 234''. While both of the prototypes had been mostly completed prior to the end of 1941, the Junkers Jumo 004 turbojet engines were not available prior to February 1943. Due to engine unreliability, the maiden flight of the Ar 234 V1 was delayed until 30 July 1943. In addition to the original reconnaissance-orientated ''Ar 234 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Blohm & Voss P 211
The Blohm & Voss P 211 was a design proposal submitted by Blohm & Voss to the ''Volksjäger'' jet fighter competition of the ''Luftwaffe'' Emergency Fighter Program towards the end of the Second World War. History During the latter part of 1944, when the High Command of the Luftwaffe saw that there was a dire need to put up a strong defense against the devastating allied bombing raids, on September 8 they asked aircraft manufacturers Messerschmitt, Arado, Focke-Wulf, Heinkel, Junkers and Blohm & Voss to propose designs for single-engined light fighters weighing no more than 2000 kg that would use one BMW 003 jet engine per unit. Owing to the war-related scarcity of strategic materials such as aluminum, the jets were required to be simplified in order to be built using a strict minimum, as well as to be built in adequate quantities as quickly as possible in underground factories. Despite these requirements that would impinge on the overall quality of the new planes, their pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Heinkel He 162
Heinkel Flugzeugwerke () was a German aircraft manufacturing company founded by and named after Ernst Heinkel. It is noted for producing bomber aircraft for the Luftwaffe in World War II and for important contributions to high-speed flight, with the pioneering examples of a successful liquid-fueled rocket and a turbojet-powered aircraft in aviation history, with both Heinkel designs' first flights occurring shortly before the outbreak of World War II in Europe. History Following the successful career of Ernst Heinkel as the chief designer for the Hansa-Brandenburg aviation firm in World War I, Heinkel's own firm was established at Warnemünde in 1922, after the restrictions on German aviation imposed by the Treaty of Versailles were relaxed. By 1929, the firm's compressed air-powered catapults were in use on the German Norddeutscher Lloyd ocean-liners and to launch short-range mail planes from the liners' decks. The company's first post-World War I aircraft design su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
BMW 003
The BMW 003 (full RLM designation 109-003) is an early axial turbojet engine produced by BMW AG in Germany during World War II. The 003 and the Junkers Jumo 004 were the only German turbojet engines to reach production during World War II. Work had begun on the design of the BMW 003 before its contemporary, the Jumo 004, but prolonged developmental problems meant that the BMW 003 entered production much later, and the aircraft projects that had been designed with it in mind were re-engined with the Jumo powerplant instead. The most famous case of this was the Messerschmitt Me 262, which used the 003 in two of the V-series prototypes and in the two experimental A-1b aircraft. The only production aircraft to use the BMW 003 were the Heinkel He 162 and the later C-series, four-engined versions of the Arado Ar 234. About 3,500 BMW 003 engines were built in Germany, but very few were ever installed in aircraft. The engine also formed the basis for turbojet development in Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Light Fighter
A light fighter or lightweight fighter is a fighter aircraft towards the low end of the practical range of weight, cost, and complexity over which fighters are fielded. The light or lightweight fighter retains carefully selected competitive features, in order to provide cost-effective design and performance. A well-designed lightweight fighter is able to match or better a heavier type plane-for-plane in many missions, and for lower cost. The lightweight class can therefore be strategically valuable. In attempts to scale this efficiency to still lower cost, some manufacturers have in recent years adopted the term “light fighter” to also refer to light primarily air-to-ground attack aircraft, some of which are modified trainer designs. These lower cost lightweight attack aircraft have become known as light combat aircraft (LCAs), and are sometimes considered to include some multirole light fighters. From 1926 the light fighter concept has been a regular thread in the develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Bachem Ba 349
The Bachem Ba 349 Natter () is a World War II German point-defence rocket-powered interceptor aircraft, interceptor, which was to be used in a very similar way to a manned surface-to-air missile. After a vertical take-off, which eliminated the need for airfields, most of the flight to the Allied bombers was to be controlled by an autopilot. The primary role of the relatively untrained pilot was to aim the aircraft at its target bomber and fire its armament of rockets. The pilot and the fuselage containing the rocket engine would then land using separate parachutes, while the nose section was disposable. The first and only manned vertical take-off flight, on 1 March 1945, ended in the death of the test pilot, Lothar Sieber. Development Background In 1943, ''Luftwaffe'' air superiority was being challenged by the Allies defence of the Reich, over the ''Reich'' and radical innovations were required to overcome the crisis. Surface-to-air missiles appeared to be a promising approach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Launch System
A launch vehicle is typically a rocket-powered vehicle designed to carry a payload (a crewed spacecraft or satellites) from Earth's surface or lower atmosphere to outer space. The most common form is the ballistic missile-shaped multistage rocket, but the term is more general and also encompasses vehicles like the Space Shuttle. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pad, supported by a launch control center and systems such as vehicle assembly and fueling. Launch vehicles are engineered with advanced aerodynamics and technologies, which contribute to high operating costs. An orbital launch vehicle must lift its payload at least to the boundary of space, approximately and accelerate it to a horizontal velocity of at least . Suborbital vehicles launch their payloads to lower velocity or are launched at elevation angles greater than horizontal. Practical orbital launch vehicles use chemical propellants such as solid fuel, liquid hydrogen, kerosene, liquid ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Arado E
Arado may refer to: * Arado Flugzeugwerke, a German aircraft company * Arwad Arwad (; ), the classical antiquity, classical Aradus, is a town in Syria on an eponymous List of islands of Syria, island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is the administrative center of the Arwad nahiyah, Subdistrict (''nahiyah''), of which it is ..., an ancient city in Syria {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Blohm & Voss BV 40
The Blohm & Voss BV 40 was a prototype armoured German glider initially designed in mid-1943 by Blohm & Voss to attack Allied bomber formations during World War II. The BV 40 would be towed to high altitude by single-engined fighters and then ram the bombers while in a dive, but this concept was rejected before its first flight in May 1944 in favour of using its guns. The Luftwaffe had lost interest in the BV 40's original mission the month prior; development continued as its mission changed to attacking ships with specialized bombs. Blohm & Voss discovered that the prototypes were significantly overweight, and some of the armour and one gun had to be removed to conduct flight testing. The BV 40 was cancelled in August with only 6 gliders completed out of the 21 ordered. All of the aircraft were destroyed in an air raid in October. Design and description Conceived in mid-1943 by Richard Vogt, chief designer and technical director of Blohm & Voss, the BV 40 was to be towed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
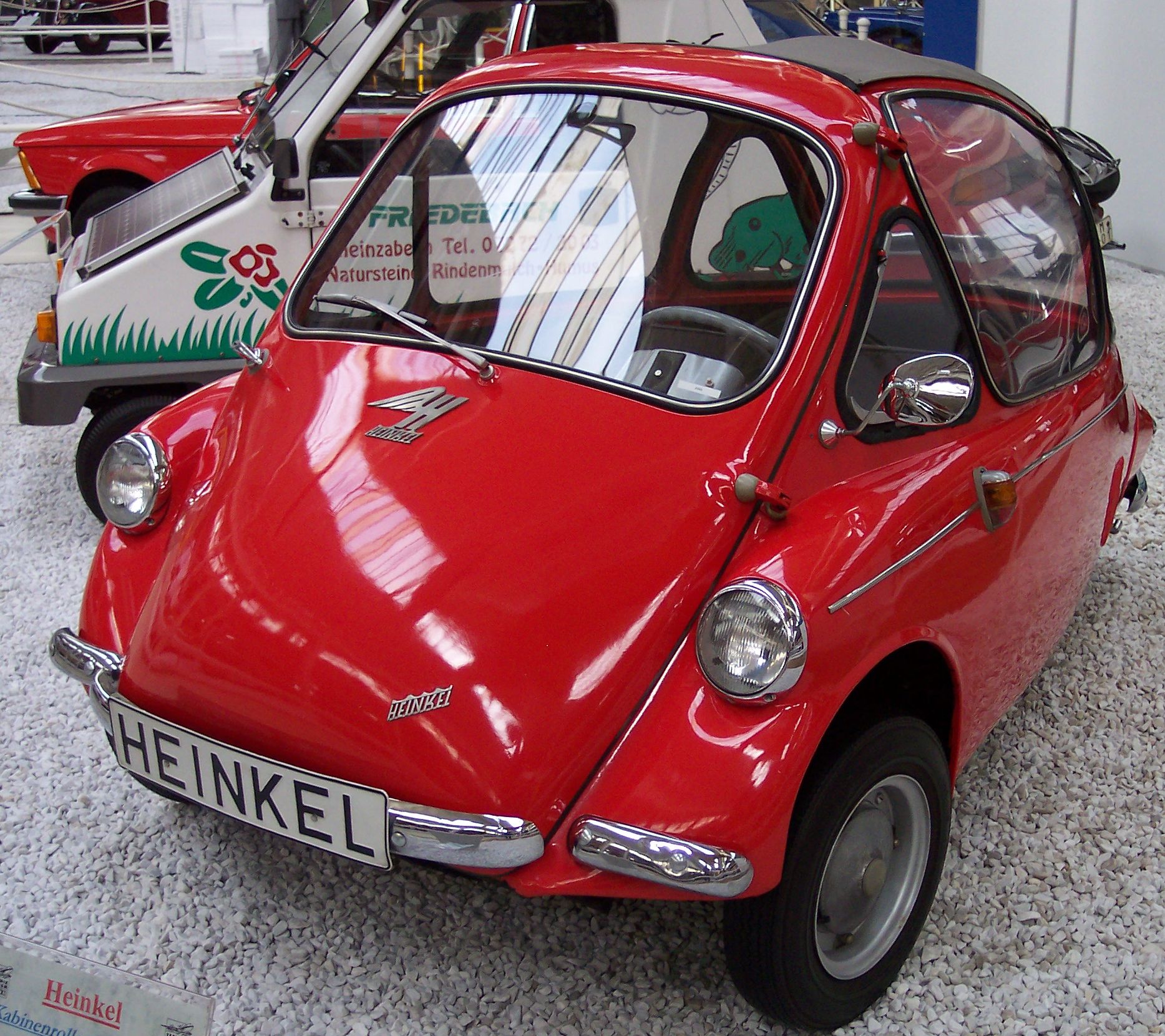 |
Heinkel P
Heinkel Flugzeugwerke () was a German aircraft manufacturing company founded by and named after Ernst Heinkel. It is noted for producing bomber aircraft for the Luftwaffe in World War II and for important contributions to high-speed flight, with the pioneering examples of a successful liquid-fueled rocket and a turbojet-powered aircraft in aviation history, with both Heinkel designs' first flights occurring shortly before the outbreak of World War II in Europe. History Following the successful career of Ernst Heinkel as the chief designer for the Hansa-Brandenburg aviation firm in World War I, Heinkel's own firm was established at Warnemünde in 1922, after the restrictions on German aviation imposed by the Treaty of Versailles were relaxed. By 1929, the firm's compressed air-powered catapults were in use on the German Norddeutscher Lloyd ocean-liners and to launch short-range mail planes from the liners' decks. The company's first post-World War I aircraft design success w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |